In-vivo evidence of systemic endothelial vascular dysfunction in COVID-19
- PMID: 34706286
- PMCID: PMC8542397
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2021.10.140
In-vivo evidence of systemic endothelial vascular dysfunction in COVID-19
Abstract
Background: Endothelial dysfunction is one of the underlying mechanisms to vascular and cardiac complications in patients with COVID-19. We sought to investigate the systemic vascular endothelial function and its temporal changes in COVID-19 patients from a non-invasive approach with reactive hyperemia peripheral arterial tonometry (PAT).
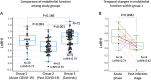
Methods: This is a prospective, observational, case-control and blinded study. The population was comprised by 3 groups: patients investigated during acute COVID-19 (group 1), patients investigated during past COVID-19 (group 2), and controls 1:1 matched to COVID-19 patients by demographics and cardiovascular risk factors (group 3). The natural logarithmic scaled reactive hyperemia index (LnRHI), a measure of endothelium-mediated dilation of peripheral arteries, was obtained in all the participants and compared between study groups.
Results: 144 participants were enrolled (72 COVID-19 patients and 72 matched controls). Median time from COVID-19 symptoms to PAT assessment was 9.5 and 101.5 days in groups 1 and 2, respectively. LnRHI was significantly lower in group 2 compared to both group 1 and controls (0.53 ± 0.23 group 2 vs. 0.72 ± 0.26 group 1, p = 0.0043; and 0.79 ± 0.23 in group 3, p < 0.0001). In addition, within group 1, it was observed a markedly decrease in LnRHI from acute COVID-19 to post infection stage (0.73 ± 0.23 vs. 0.42 ± 0.26, p = 0.0042).
Conclusions: This study suggests a deleterious effect of SARS-CoV-2 infection on systemic vascular endothelial function. These findings open new venues to investigate the clinical implication and prognostic role of vascular endothelial dysfunction in COVID-19 patients and post-COVID syndrome using non-invasive techniques.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; Systemic vascular endothelial function.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors state that they do not have any conflict of interest related with the submitted study.
Figures
Comment in
-
Endothelial dysfunction in COVID-19: A potential predictor of long-COVID?Int J Cardiol. 2022 Feb 15;349:155-156. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2021.11.051. Epub 2021 Nov 24. Int J Cardiol. 2022. PMID: 34838682 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Endothelial dysfunction and COVID-19: What's the true impact on surrogate outcomes?Int J Cardiol. 2022 Feb 1;348:175. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2021.11.070. Epub 2021 Nov 29. Int J Cardiol. 2022. PMID: 34856293 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Peripheral-arterial tonometry for assessing endothelial function in relation to dietary habits.J Investig Med. 2013 Jun;61(5):867-71. doi: 10.2310/JIM.0b013e318292fc7d. J Investig Med. 2013. PMID: 23612150
-
Improvement of Vascular Endothelial Function Reflects Nonrecurrence After Catheter Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation.J Am Heart Assoc. 2021 Sep 7;10(17):e021551. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.121.021551. Epub 2021 Aug 21. J Am Heart Assoc. 2021. PMID: 34423655 Free PMC article.
-
Reliability of peripheral arterial tonometry in patients with heart failure, diabetic nephropathy and arterial hypertension.Vasc Med. 2017 Aug;22(4):292-300. doi: 10.1177/1358863X17706752. Epub 2017 May 30. Vasc Med. 2017. PMID: 28555533
-
Testing endothelial function and its clinical relevance.J Atheroscler Thromb. 2013;20(1):1-8. doi: 10.5551/jat.14340. Epub 2012 Sep 10. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2013. PMID: 22972428 Review.
-
Endothelial dysfunction in COVID-19: a position paper of the ESC Working Group for Atherosclerosis and Vascular Biology, and the ESC Council of Basic Cardiovascular Science.Cardiovasc Res. 2020 Dec 1;116(14):2177-2184. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvaa230. Cardiovasc Res. 2020. PMID: 32750108 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The CSHQ-DE Questionnaire Uncovers Relevant Sleep Disorders in Children and Adolescents with Long COVID.Children (Basel). 2022 Sep 19;9(9):1419. doi: 10.3390/children9091419. Children (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36138727 Free PMC article.
-
The role of the endothelium in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection and pathogenesis.Curr Opin Physiol. 2023 Aug;34:100670. doi: 10.1016/j.cophys.2023.100670. Epub 2023 Apr 1. Curr Opin Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37159613 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dysregulated autoantibodies targeting vaso- and immunoregulatory receptors in Post COVID Syndrome correlate with symptom severity.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 27;13:981532. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.981532. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36238301 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19. Biology, pathophysiology, and immunology: a pathologist view.Pathologica. 2023 Oct;115(5):248-256. doi: 10.32074/1591-951X-954. Pathologica. 2023. PMID: 38054899 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Insights into Endothelial Dysfunction in Cardiometabolic Diseases: Potential Mechanisms and Clinical Implications.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 4;25(5):2973. doi: 10.3390/ijms25052973. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38474219 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rubinshtein R., Kuvin J.T., Soffler M., et al. Assessment of endothelial function by non-invasive peripheral arterial tonometry predicts late cardiovascular adverse events. Eur. Heart J. 2010;31:1142–1148. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

