3D virtual reality vs. 2D desktop registration user interface comparison
- PMID: 34705835
- PMCID: PMC8550408
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0258103
3D virtual reality vs. 2D desktop registration user interface comparison
Abstract
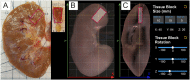
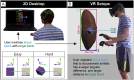
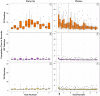
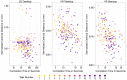
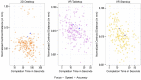
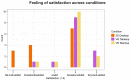
Working with organs and extracted tissue blocks is an essential task in many medical surgery and anatomy environments. In order to prepare specimens from human donors for further analysis, wet-bench workers must properly dissect human tissue and collect metadata for downstream analysis, including information about the spatial origin of tissue. The Registration User Interface (RUI) was developed to allow stakeholders in the Human Biomolecular Atlas Program (HuBMAP) to register tissue blocks-i.e., to record the size, position, and orientation of human tissue data with regard to reference organs. The RUI has been used by tissue mapping centers across the HuBMAP consortium to register a total of 45 kidney, spleen, and colon tissue blocks, with planned support for 17 organs in the near future. In this paper, we compare three setups for registering one 3D tissue block object to another 3D reference organ (target) object. The first setup is a 2D Desktop implementation featuring a traditional screen, mouse, and keyboard interface. The remaining setups are both virtual reality (VR) versions of the RUI: VR Tabletop, where users sit at a physical desk which is replicated in virtual space; VR Standup, where users stand upright while performing their tasks. All three setups were implemented using the Unity game engine. We then ran a user study for these three setups involving 42 human subjects completing 14 increasingly difficult and then 30 identical tasks in sequence and reporting position accuracy, rotation accuracy, completion time, and satisfaction. All study materials were made available in support of future study replication, alongside videos documenting our setups. We found that while VR Tabletop and VR Standup users are about three times as fast and about a third more accurate in terms of rotation than 2D Desktop users (for the sequence of 30 identical tasks), there are no significant differences between the three setups for position accuracy when normalized by the height of the virtual kidney across setups. When extrapolating from the 2D Desktop setup with a 113-mm-tall kidney, the absolute performance values for the 2D Desktop version (22.6 seconds per task, 5.88 degrees rotation, and 1.32 mm position accuracy after 8.3 tasks in the series of 30 identical tasks) confirm that the 2D Desktop interface is well-suited for allowing users in HuBMAP to register tissue blocks at a speed and accuracy that meets the needs of experts performing tissue dissection. In addition, the 2D Desktop setup is cheaper, easier to learn, and more practical for wet-bench environments than the VR setups.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The HRA Organ Gallery affords immersive superpowers for building and exploring the Human Reference Atlas with virtual reality.Front Bioinform. 2023 Apr 27;3:1162723. doi: 10.3389/fbinf.2023.1162723. eCollection 2023. Front Bioinform. 2023. PMID: 37181487 Free PMC article.
-
The HRA Organ Gallery Affords Immersive Superpowers for Building and Exploring the Human Reference Atlas with Virtual Reality.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Feb 15:2023.02.13.528002. doi: 10.1101/2023.02.13.528002. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Front Bioinform. 2023 Apr 27;3:1162723. doi: 10.3389/fbinf.2023.1162723. PMID: 36824790 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Comparing virtual reality, desktop-based 3D, and 2D versions of a category learning experiment.PLoS One. 2022 Oct 6;17(10):e0275119. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0275119. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36201546 Free PMC article.
-
[Virtual reality in medicine].Radiologe. 1995 Sep;35(9):563-8. Radiologe. 1995. PMID: 8588036 Review. German.
-
The Potential of Immersive Virtual Reality for Cognitive Training in Elderly.Gerontology. 2020;66(6):614-623. doi: 10.1159/000509830. Epub 2020 Sep 9. Gerontology. 2020. PMID: 32906122 Review.
Cited by
-
Segmentation of human functional tissue units in support of a Human Reference Atlas.Commun Biol. 2023 Jul 19;6(1):717. doi: 10.1038/s42003-023-04848-5. Commun Biol. 2023. PMID: 37468557 Free PMC article.
-
The HRA Organ Gallery affords immersive superpowers for building and exploring the Human Reference Atlas with virtual reality.Front Bioinform. 2023 Apr 27;3:1162723. doi: 10.3389/fbinf.2023.1162723. eCollection 2023. Front Bioinform. 2023. PMID: 37181487 Free PMC article.
-
Specimen, biological structure, and spatial ontologies in support of a Human Reference Atlas.Sci Data. 2023 Mar 27;10(1):171. doi: 10.1038/s41597-023-01993-8. Sci Data. 2023. PMID: 36973309 Free PMC article.
-
The HRA Organ Gallery Affords Immersive Superpowers for Building and Exploring the Human Reference Atlas with Virtual Reality.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Feb 15:2023.02.13.528002. doi: 10.1101/2023.02.13.528002. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Front Bioinform. 2023 Apr 27;3:1162723. doi: 10.3389/fbinf.2023.1162723. PMID: 36824790 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Tissue registration and exploration user interfaces in support of a human reference atlas.Commun Biol. 2022 Dec 13;5(1):1369. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-03644-x. Commun Biol. 2022. PMID: 36513738 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

