Evaluation of the relative virulence of novel SARS-CoV-2 variants: a retrospective cohort study in Ontario, Canada
- PMID: 34610919
- PMCID: PMC8562985
- DOI: 10.1503/cmaj.211248
Evaluation of the relative virulence of novel SARS-CoV-2 variants: a retrospective cohort study in Ontario, Canada
Abstract
Background: Between February and June 2021, the initial wild-type strains of SARS-CoV-2 were supplanted in Ontario, Canada, by new variants of concern (VOCs), first those with the N501Y mutation (i.e., Alpha/B1.1.17, Beta/B.1.351 and Gamma/P.1 variants) and then the Delta/B.1.617 variant. The increased transmissibility of these VOCs has been documented, but knowledge about their virulence is limited. We used Ontario's COVID-19 case data to evaluate the virulence of these VOCs compared with non-VOC SARS-CoV-2 strains, as measured by risk of hospitalization, intensive care unit (ICU) admission and death.
Methods: We created a retrospective cohort of people in Ontario who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 and were screened for VOCs, with dates of test report between Feb. 7 and June 27, 2021. We constructed mixed-effect logistic regression models with hospitalization, ICU admission and death as outcome variables. We adjusted models for age, sex, time, vaccination status, comorbidities and pregnancy status. We included health units as random intercepts.
Results: Our cohort included 212 326 people. Compared with non-VOC SARS-CoV-2 strains, the adjusted elevation in risk associated with N501Y-positive variants was 52% (95% confidence interval [CI] 42%-63%) for hospitalization, 89% (95% CI 67%-117%) for ICU admission and 51% (95% CI 30%-78%) for death. Increased risk with the Delta variant was more pronounced at 108% (95% CI 78%-140%) for hospitalization, 235% (95% CI 160%-331%) for ICU admission and 133% (95% CI 54%-231%) for death.
Interpretation: The increasing virulence of SARS-CoV-2 VOCs will lead to a considerably larger, and more deadly, pandemic than would have occurred in the absence of the emergence of VOCs.
© 2021 CMA Joule Inc. or its licensors.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: David Fisman has served on advisory boards related to influenza and SARS-CoV-2 vaccines for Seqirus, Pfizer, AstraZeneca and Sanofi-Pasteur, and has served as a legal expert on issues related to COVID-19 epidemiology for the Elementary Teachers Federation of Ontario and the Registered Nurses Association of Ontario. He was previously a member of the Ontario COVID-19 Modelling Consensus Table. Ashleigh Tuite serves on the Ontario COVID-19 Modelling Consensus Table.
Figures
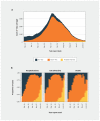
Comment in
-
Countering more virulent SARS-CoV-2 variants will require a smarter pandemic response.CMAJ. 2021 Oct 25;193(42):E1633-E1634. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.211656. Epub 2021 Oct 4. CMAJ. 2021. PMID: 34610918 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Is it time to reconsider ring vaccination for COVID-19?CMAJ. 2022 Jan 10;194(1):E19. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.80442. CMAJ. 2022. PMID: 35012951 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Age-Specific Changes in Virulence Associated With Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Variants of Concern.Clin Infect Dis. 2022 Aug 24;75(1):e69-e75. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciac174. Clin Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 35234859 Free PMC article.
-
The Clinical Severity of COVID-19 Variants of Concern: Retrospective Population-Based Analysis.JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2024 Aug 27;10:e45513. doi: 10.2196/45513. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2024. PMID: 39190434 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of shifting demographics, variants of concern and vaccination on outcomes during the first 3 COVID-19 waves in Alberta and Ontario: a retrospective cohort study.CMAJ Open. 2022 Apr 26;10(2):E400-E408. doi: 10.9778/cmajo.20210323. Print 2022 Apr-Jun. CMAJ Open. 2022. PMID: 35473827 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern.Yonsei Med J. 2021 Nov;62(11):961-968. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2021.62.11.961. Yonsei Med J. 2021. PMID: 34672129 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Health system impacts of SARS-CoV - 2 variants of concern: a rapid review.BMC Health Serv Res. 2022 Apr 23;22(1):544. doi: 10.1186/s12913-022-07847-0. BMC Health Serv Res. 2022. PMID: 35461246 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Measuring the impact of COVID-19 on cancer survival using an interrupted time series analysis.JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2024 Jan 4;8(1):pkae001. doi: 10.1093/jncics/pkae001. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38177077 Free PMC article.
-
Risk Factors of Severe COVID-19: A Review of Host, Viral and Environmental Factors.Viruses. 2023 Jan 7;15(1):175. doi: 10.3390/v15010175. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 36680215 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Changing Features of Liver Injury in COVID-19 Patients: Impact of Infection with the SARS-CoV-2 Delta (B.1.617.2) Variants.Infect Chemother. 2022 Dec;54(4):744-756. doi: 10.3947/ic.2022.0122. Infect Chemother. 2022. PMID: 36596683 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 VOC type and biological sex affect molnupiravir efficacy in severe COVID-19 dwarf hamster model.Nat Commun. 2022 Jul 29;13(1):4416. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-32045-1. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35906230 Free PMC article.
-
Emergence of SARS-CoV-2 Variants in the World: How Could This Happen?Life (Basel). 2022 Jan 28;12(2):194. doi: 10.3390/life12020194. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35207482 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tuite AR, Fisman DN, Odutayo A, et al. . Ontario COVID-19 Science Advisory Table. COVID-19 hospitalizations, ICU admissions and deaths associated with the new variants of concern. Science Table COVID-19 Advisory for Ontario; 2021. Available: https://covid19-sciencetable.ca/sciencebrief/covid-19-hospitalizations-i... (accessed 2021 July 5).
-
- Public Health Ontario. SARS-CoV-2 whole genome sequencing in Ontario, September 7, 2021. Toronto: Queen’s Printer for Ontario; 2021. Available: https://www.publichealthontario.ca/-/media/documents/ncov/epi/covid-19-s... (accessed 2021 July 5).
-
- Public Health Ontario. Estimating the prevalence and growth of SARS-CoV-2 variants in Ontario using mutation profiles. Toronto: Queen’s Printer for Ontario; 2021. Available: https://www.publichealthontario.ca/-/media/documents/ncov/epi/covid-19-p... (accessed 2021 July 5).
-
- Brown KA, Joh E, Buchan SA, et al. . Inflection in prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 infections missing the N501Y mutation as a marker of rapid Delta (B.1.617.2) lineage expansion in Ontario, Canada. medRxiv 2021. June 25. doi: 10.1101/2021.06.22.21259349. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
