The biology, function, and applications of exosomes in cancer
- PMID: 34589397
- PMCID: PMC8463268
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.01.001
The biology, function, and applications of exosomes in cancer
Abstract
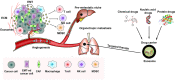
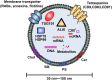
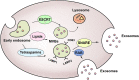
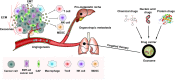
Exosomes are cell-derived nanovesicles with diameters from 30 to 150 nm, released upon fusion of multivesicular bodies with the cell surface. They can transport nucleic acids, proteins, and lipids for intercellular communication and activate signaling pathways in target cells. In cancers, exosomes may participate in growth and metastasis of tumors by regulating the immune response, blocking the epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and promoting angiogenesis. They are also involved in the development of resistance to chemotherapeutic drugs. Exosomes in liquid biopsies can be used as non-invasive biomarkers for early detection and diagnosis of cancers. Because of their amphipathic structure, exosomes are natural drug delivery vehicles for cancer therapy.
Keywords: ABCA3, ATP-binding cassette transporter A3; APCs, antigen-presenting cells; Biomarkers; CAFs, cancer-associated fibroblasts; CCRCC, clear-cell renal cell carcinoma; CD-UPRT, cytosine deaminase-uracil phosphoribosyltransferase; CDH3, cadherin 3; CRC, colorectal cancer; DC, dendritic cells; DEXs, DC-derived exosomes; DLBCL, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; DNM3, dynamin 3; Del-1, developmental endothelial locus-1; Drug delivery; Drug resistance; ECM, extracellular matrix; EMT, epithelial–mesenchymal transition; ESCRT, endosomal sorting complex required for transport; Exosomes; GPC1, glypican-1; HA, hyaluronic acid; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; HIF1, hypoxia-inducible factor 1; HTR, hormone therapy-resistant; HUVECs, human umbilical vein endothelial cells; ILVs, intraluminal vesicles; MDSCs, myeloid-derived suppressor cells; MIF, migration inhibitory factor; MSC, mesenchymal stem cells; MVB, multivesicular body; NKEXOs, natural killer cell-derived exosomes; NNs, nanoparticles; NSCLC, non-small cell lung cancer; PA, phosphatidic acid; PCC, pheochromocytoma; PD-L1, programmed cell death receptor ligand 1; PDAC, pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; PGL, paraganglioma; PI, phosphatidylinositol; PS, phosphatidylserine; PTRF, polymerase I and transcript release factor; RCC, renal cell carcinoma; SM, sphingomyelin; SNARE, soluble NSF-attachment protein receptor; TEX, tumor-derived exosomes; TSG101, tumor susceptibility gene 101; Tumor immunity; Tumor metastasis; circRNAs, circular RNAs; dsDNA, double stranded DNA; hTERT, human telomerase reverse transcriptase; lamp2b, lysosome-associated membrane glycoprotein 2b; lncRNAs, long non-coding RNAs; miRNA, microRNA; mtDNA, mitochondrial DNA; ncRNA, non-coding RNAs.
© 2021 Chinese Pharmaceutical Association and Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of exosomes in cancer biology by shedding light on their lipid contents.Pathol Res Pract. 2023 Oct;250:154813. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2023.154813. Epub 2023 Sep 12. Pathol Res Pract. 2023. PMID: 37769395 Review.
-
The role of extracellular vesicles in mediating progression, metastasis and potential treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 10;8(2):3683-3695. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12465. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 27713136 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Review on circular RNAs and new insights into their roles in cancer.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021 Jan 22;19:910-928. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2021.01.018. eCollection 2021. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021. PMID: 33598105 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma-derived exosomal miRNA-21 contributes to tumor progression by converting hepatocyte stellate cells to cancer-associated fibroblasts.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Dec 27;37(1):324. doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-0965-2. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30591064 Free PMC article.
-
The application of nanoparticles in cancer immunotherapy: Targeting tumor microenvironment.Bioact Mater. 2020 Dec 26;6(7):1973-1987. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2020.12.010. eCollection 2021 Jul. Bioact Mater. 2020. PMID: 33426371 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
[Exosomal FZD10 derived from non-small cell lung cancer cells promotes angiogenesis of human umbilical venous endothelial cells in vitro].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2022 Sep 20;42(9):1351-1358. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2022.09.11. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2022. PMID: 36210708 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Circulating plasma exosomal long non-coding RNAs LINC00265, LINC00467, UCA1, and SNHG1 as biomarkers for diagnosis and treatment monitoring of acute myeloid leukemia.Front Oncol. 2022 Oct 7;12:1033143. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1033143. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36276083 Free PMC article.
-
Small Extracellular Vesicles and Oral Mucosa: The Power Couple in Regenerative Therapies?Cells. 2024 Sep 10;13(18):1514. doi: 10.3390/cells13181514. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39329698 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomal LncRNAs in Gastrointestinal Cancer: Biological Functions and Emerging Clinical Applications.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Feb 2;15(3):959. doi: 10.3390/cancers15030959. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36765913 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progress of regulatory RNA in small extracellular vesicles in colorectal cancer.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Jul 12;11:1225965. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1225965. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37519298 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Trams E.G., Lauter C.J., Salem N., Jr., Heine U. Exfoliation of membrane ecto-enzymes in the form of micro-vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981;645:63–70. - PubMed
-
- Johnstone R.M., Adam M., Hammond J.R., Orr L., Turbide C. Vesicle formation during reticulocyte maturation. Association of plasma membrane activities with released vesicles (exosomes) J Biol Chem. 1987;262:9412–9420. - PubMed
-
- Liu Y., Wang Y., Lv Q., Li X. Exosomes: from garbage bins to translational medicine. Int J Pharm. 2020;583:119333. - PubMed
-
- Thery C., Zitvogel L., Amigorena S. Exosomes: composition, biogenesis and function. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2:569–579. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

