REGEN-COV Antibody Combination and Outcomes in Outpatients with Covid-19
- PMID: 34587383
- PMCID: PMC8522800
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2108163
REGEN-COV Antibody Combination and Outcomes in Outpatients with Covid-19
Abstract
Background: In the phase 1-2 portion of an adaptive trial, REGEN-COV, a combination of the monoclonal antibodies casirivimab and imdevimab, reduced the viral load and number of medical visits in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19). REGEN-COV has activity in vitro against current severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) variants of concern.
Methods: In the phase 3 portion of an adaptive trial, we randomly assigned outpatients with Covid-19 and risk factors for severe disease to receive various doses of intravenous REGEN-COV or placebo. Patients were followed through day 29. A prespecified hierarchical analysis was used to assess the end points of hospitalization or death and the time to resolution of symptoms. Safety was also evaluated.
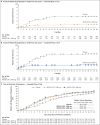
Results: Covid-19-related hospitalization or death from any cause occurred in 18 of 1355 patients in the REGEN-COV 2400-mg group (1.3%) and in 62 of 1341 patients in the placebo group who underwent randomization concurrently (4.6%) (relative risk reduction [1 minus the relative risk], 71.3%; P<0.001); these outcomes occurred in 7 of 736 patients in the REGEN-COV 1200-mg group (1.0%) and in 24 of 748 patients in the placebo group who underwent randomization concurrently (3.2%) (relative risk reduction, 70.4%; P = 0.002). The median time to resolution of symptoms was 4 days shorter with each REGEN-COV dose than with placebo (10 days vs. 14 days; P<0.001 for both comparisons). REGEN-COV was efficacious across various subgroups, including patients who were SARS-CoV-2 serum antibody-positive at baseline. Both REGEN-COV doses reduced viral load faster than placebo; the least-squares mean difference in viral load from baseline through day 7 was -0.71 log10 copies per milliliter (95% confidence interval [CI], -0.90 to -0.53) in the 1200-mg group and -0.86 log10 copies per milliliter (95% CI, -1.00 to -0.72) in the 2400-mg group. Serious adverse events occurred more frequently in the placebo group (4.0%) than in the 1200-mg group (1.1%) and the 2400-mg group (1.3%); infusion-related reactions of grade 2 or higher occurred in less than 0.3% of the patients in all groups.
Conclusions: REGEN-COV reduced the risk of Covid-19-related hospitalization or death from any cause, and it resolved symptoms and reduced the SARS-CoV-2 viral load more rapidly than placebo. (Funded by Regeneron Pharmaceuticals and others; ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT04425629.).
Copyright © 2021 Massachusetts Medical Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of timing of casirivimab and imdevimab administration relative to mRNA-1273 COVID-19 vaccination on vaccine-induced SARS-CoV-2 neutralising antibody responses: a prospective, open-label, phase 2, randomised controlled trial.Lancet Infect Dis. 2025 Jan;25(1):52-67. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(24)00421-3. Epub 2024 Sep 2. Lancet Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 39236733 Clinical Trial.
-
A Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibody for Hospitalized Patients with Covid-19.N Engl J Med. 2021 Mar 11;384(10):905-914. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2033130. Epub 2020 Dec 22. N Engl J Med. 2021. PMID: 33356051 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Antiviral efficacy of molnupiravir versus ritonavir-boosted nirmatrelvir in patients with early symptomatic COVID-19 (PLATCOV): an open-label, phase 2, randomised, controlled, adaptive trial.Lancet Infect Dis. 2024 Jan;24(1):36-45. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00493-0. Epub 2023 Sep 28. Lancet Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 37778363 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Nirmatrelvir combined with ritonavir for preventing and treating COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Nov 30;11(11):CD015395. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015395.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 38032024 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antibody tests for identification of current and past infection with SARS-CoV-2.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Nov 17;11(11):CD013652. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013652.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36394900 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Rethinking treatment paradigms for the deployment of SARS-CoV-2 antiviral drugs on the shifting landscape of new variants.Front Microbiol. 2022 Oct 12;13:998287. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.998287. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36312942 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Drug effectiveness for COVID-19 inpatients inferred from Japanese medical claim data using propensity score matching.F1000Res. 2024 Jan 22;12:398. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.131102.1. eCollection 2023. F1000Res. 2024. PMID: 39105097 Free PMC article.
-
Care for adults with COVID-19: living guidelines from the National COVID-19 Clinical Evidence Taskforce.Med J Aust. 2022 Oct 3;217(7):368-378. doi: 10.5694/mja2.51718. Med J Aust. 2022. PMID: 36150213 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccine-boosted convalescent plasma therapy for patients with immunosuppression and COVID-19.Blood Adv. 2022 Dec 13;6(23):5951-5955. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2022008932. Blood Adv. 2022. PMID: 36156121 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Using a web platform for equitable distribution of COVID-19 monoclonal antibodies: a case study in resource allocation.Front Public Health. 2023 Nov 28;11:1226935. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1226935. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 38106886 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO coronavirus (COVID-19) dashboard. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2021. (https://covid19.who.int/table).
-
- People with certain medical conditions. Atlanta: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2021. (https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/need-extra-precautions/people-...).
-
- Onder G, Rezza G, Brusaferro S. Case-fatality rate and characteristics of patients dying in relation to COVID-19 in Italy. JAMA 2020;323:1775-1776. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
