Integration of glucose and cardiolipin anabolism confers radiation resistance of HCC
- PMID: 34580888
- PMCID: PMC9299851
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.32177
Integration of glucose and cardiolipin anabolism confers radiation resistance of HCC
Abstract
Background and aims: Poor response to ionizing radiation (IR) due to resistance remains a clinical challenge. Altered metabolism represents a defining characteristic of nearly all types of cancers. However, how radioresistance is linked to metabolic reprogramming remains elusive in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
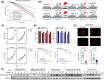
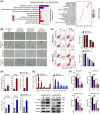
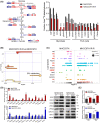
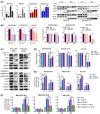
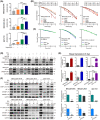
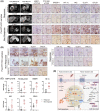
Approach and results: Baseline radiation responsiveness of different HCC cells were identified and cells with acquired radio-resistance were generated. By performing proteomics, metabolomics, metabolic flux, and other functional studies, we depicted a metabolic phenotype that mediates radiation resistance in HCC, whereby increased glucose flux leads to glucose addiction in radioresistant HCC cells and a corresponding increase in glycerophospholipids biosynthesis to enhance the levels of cardiolipin. Accumulation of cardiolipin dampens the effectiveness of IR by inhibiting cytochrome c release to initiate apoptosis. Mechanistically, mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) signaling-mediated translational control of hypoxia inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) and sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1 (SREBP1) remodels such metabolic cascade. Targeting mTORC1 or glucose to cardiolipin synthesis, in combination with IR, strongly diminishes tumor burden. Finally, activation of glucose metabolism predicts poor response to radiotherapy in cancer patients.
Conclusions: We demonstrate a link between radiation resistance and metabolic integration and suggest that metabolically dismantling the radioresistant features of tumors may provide potential combination approaches for radiotherapy in HCC.
© 2021 The Authors. Hepatology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Nothing to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
HBXIP drives metabolic reprogramming in hepatocellular carcinoma cells via METTL3-mediated m6A modification of HIF-1α.J Cell Physiol. 2021 May;236(5):3863-3880. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30128. Epub 2020 Dec 11. J Cell Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33305825
-
Sirolimus increases the anti-cancer effect of Huai Er by regulating hypoxia inducible factor-1α-mediated glycolysis in hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2022 Aug 28;28(32):4600-4619. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i32.4600. World J Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 36157928 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia-mediated sorafenib resistance can be overcome by EF24 through Von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor-dependent HIF-1α inhibition in hepatocellular carcinoma.Hepatology. 2013 May;57(5):1847-57. doi: 10.1002/hep.26224. Epub 2013 Mar 14. Hepatology. 2013. PMID: 23299930
-
Metabolic dysregulation and emerging therapeutical targets for hepatocellular carcinoma.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022 Feb;12(2):558-580. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.09.019. Epub 2021 Sep 25. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022. PMID: 35256934 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypoxia inducible factor in hepatocellular carcinoma: A therapeutic target.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Nov 14;21(42):12171-8. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i42.12171. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26576101 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Novel Somay's GLUCAR Index Efficiently Predicts Survival Outcomes in Locally Advanced Pancreas Cancer Patients Receiving Definitive Chemoradiotherapy: A Propensity-Score-Matched Cohort Analysis.J Pers Med. 2024 Jul 13;14(7):746. doi: 10.3390/jpm14070746. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 39064000 Free PMC article.
-
[Overexpression of ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme 2T induces radiotherapy resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma by enriching regulatory T cells in the tumor microenvironment].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2024 Jun 20;44(6):1149-1158. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.06.16. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2024. PMID: 38977345 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Advances in radiotherapy and immunity in hepatocellular carcinoma.J Transl Med. 2023 Aug 4;21(1):526. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04386-y. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37542324 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NUPR1 contributes to radiation resistance by maintaining ROS homeostasis via AhR/CYP signal axis in hepatocellular carcinoma.BMC Med. 2022 Oct 19;20(1):365. doi: 10.1186/s12916-022-02554-3. BMC Med. 2022. PMID: 36258210 Free PMC article.
-
SOCS2-enhanced ubiquitination of SLC7A11 promotes ferroptosis and radiosensitization in hepatocellular carcinoma.Cell Death Differ. 2023 Jan;30(1):137-151. doi: 10.1038/s41418-022-01051-7. Epub 2022 Aug 22. Cell Death Differ. 2023. PMID: 35995846 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Rajyaguru DJ, Borgert AJ, Smith AL, Thomes RM, Conway PD, Halfdanarson TR, et al. Radiofrequency ablation versus stereotactic body radiotherapy for localized hepatocellular carcinoma in nonsurgically managed patients: analysis of the national cancer database. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36:600–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

