Green Synthesis of Metallic Nanoparticles Using Some Selected Medicinal Plants from Southern Africa and Their Biological Applications
- PMID: 34579460
- PMCID: PMC8472917
- DOI: 10.3390/plants10091929
Green Synthesis of Metallic Nanoparticles Using Some Selected Medicinal Plants from Southern Africa and Their Biological Applications
Abstract
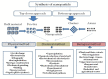
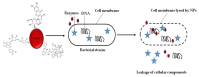
The application of metallic nanoparticles (MNPs), especially that of silver, gold, cobalt, and zinc as antimicrobial, anticancer, drug delivery, contrast, and bioimaging agents has transformed the field of medicine. Their functions, which are attributed to their physicochemical properties, have gained prominence in various technological fields. Although MNPs can be produced via rigorous physical and chemical techniques, in recent years, a biological approach utilizing natural materials has been developed. With the increasing enthusiasm for safe and efficient nanomaterials, the biological method incorporating microorganisms and plants is preferred over physical and chemical methods of nanoparticle synthesis. Of these bio-entities, plants have received great attention owing to their capability to reduce and stabilize MNPs in a single one-pot protocol. South Africa is home to ~10% of the world's plant species, making it a major contributor to the world's ecological scenery. Despite the documented contribution of South African plants, particularly in herbal medicine, very few of these plants have been explored for the synthesis of the noble MNPs. This paper provides a review of some important South African medicinal plants that have been utilized for the synthesis of MNPs. The enhanced biological properties of the biogenic MNPs attest to their relevance in medicine. In this endeavour, more of the African plant biodiversity must be explored for the synthesis of MNPs and be validated for their potential to be translated into future nanomedicine.
Keywords: antimicrobial; cytotoxicity; green nanotechnology; green synthesis; medicinal plants; metallic nanoparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Plant-mediated green synthesis of metal-based nanoparticles for dermopharmaceutical and cosmetic applications.Int J Pharm. 2021 Mar 15;597:120311. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2021.120311. Epub 2021 Feb 1. Int J Pharm. 2021. PMID: 33539998 Review.
-
Plant extract-based synthesis of metallic nanomaterials, their applications, and safety concerns.Biotechnol Bioeng. 2022 Sep;119(9):2273-2304. doi: 10.1002/bit.28148. Epub 2022 Jun 9. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2022. PMID: 35635495 Review.
-
From nature to nanotechnology: The interplay of traditional medicine, green chemistry, and biogenic metallic phytonanoparticles in modern healthcare innovation and sustainability.Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Jan;170:116083. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.116083. Epub 2023 Dec 31. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 38163395 Review.
-
Biological synthesis of metallic nanoparticles (MNPs) by plants and microbes: their cellular uptake, biocompatibility, and biomedical applications.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019 Apr;103(7):2913-2935. doi: 10.1007/s00253-019-09675-5. Epub 2019 Feb 18. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 30778643 Review.
-
Current developments in green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles using plant extracts: a review.Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018;46(sup3):S336-S343. doi: 10.1080/21691401.2018.1492931. Epub 2018 Jul 25. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 30043657
Cited by
-
Biogenic metallic nanoparticles: from green synthesis to clinical translation.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 Nov;397(11):8603-8631. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03236-y. Epub 2024 Jun 27. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38935128 Review.
-
Broad Spectrum Anti-Bacterial Activity and Non-Selective Toxicity of Gum Arabic Silver Nanoparticles.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 4;23(3):1799. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031799. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163718 Free PMC article.
-
Fabrication of anti-bacterial cotton bandage using biologically synthesized nanoparticles for medical applications.Prog Biomater. 2022 Jun;11(2):229-241. doi: 10.1007/s40204-022-00190-x. Epub 2022 May 27. Prog Biomater. 2022. PMID: 35622299 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Evaluation of Biomedical Applications of Zinc Nanoparticles Synthesized by Using Withania somnifera Plant Extracts.Plants (Basel). 2022 Jun 7;11(12):1525. doi: 10.3390/plants11121525. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35736676 Free PMC article.
-
Silver nanoparticle technology in orthopaedic infections.World J Orthop. 2023 Sep 18;14(9):662-668. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v14.i9.662. eCollection 2023 Sep 18. World J Orthop. 2023. PMID: 37744720 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dikshit P., Kumar J., Das A., Sadhu S., Sharma S., Singh S., Gupta P., Kim B. Green Synthesis of Metallic Nanoparticles: Applications and Limitations. Catalysts. 2021;11:902. doi: 10.3390/catal11080902. - DOI
-
- Abdelbasir S.M., Shalan A.E. An overview of nanomaterials for industrial wastewater treatment. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2019;36:1209–1225. doi: 10.1007/s11814-019-0306-y. - DOI
-
- Patra J.K., Baek K. Green Nanotechnology: Factors Affecting Synthesis and Characterization. J. Nanomater. 2014;2014:1417305. doi: 10.1155/2014/417305. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

