Human Herpesvirus 6A Tegument Protein U14 Induces NF-κB Signaling by Interacting with p65
- PMID: 34549982
- PMCID: PMC8577390
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01269-21
Human Herpesvirus 6A Tegument Protein U14 Induces NF-κB Signaling by Interacting with p65
Abstract
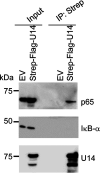
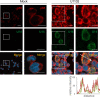
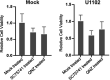
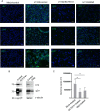
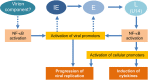
Viral infection induces host cells to mount a variety of immune responses, which may either limit viral propagation or create conditions conducive to virus replication in some instances. In this regard, activation of the NF-κB transcription factor is known to modulate virus replication. Human herpesvirus 6A (HHV-6A), which belongs to the Betaherpesvirinae subfamily, is frequently found in patients with neuroinflammatory diseases, although its role in disease pathogenesis has not been elucidated. In this study, we found that the HHV-6A-encoded U14 protein activates NF-κB signaling following interaction with the NF-κB complex protein, p65. Through induction of nuclear translocation of p65, U14 increases the expression of interleukin-6 (IL-6), IL-8, and monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 transcripts. We also demonstrated that activation of NF-κB signaling is important for HHV-6A replication, since inhibition of this pathway reduced virus protein accumulation and viral genome copy number. Taken together, our results suggest that HHV-6A infection activates the NF-κB pathway and promotes viral gene expression via late gene products, including U14. IMPORTANCE Human herpesvirus 6A (HHV-6A) is frequently found in patients with neuro-inflammation, although its role in the pathogenesis of this disease has not been elucidated. Most viral infections activate the NF-κB pathway, which causes the transactivation of various genes, including those encoding proinflammatory cytokines. Our results indicate that HHV-6A U14 activates the NF-κB pathway, leading to upregulation of proinflammatory cytokines. We also found that activation of the NF-κB transcription factor is important for efficient viral replication. This study provides new insight into HHV-6A U14 function in host cell signaling and identifies potential cellular targets involved in HHV-6A pathogenesis and replication.
Keywords: HHV-6; NF-κB; gene expression; herpes; tegument.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Human herpesvirus 6A nuclear matrix protein U37 interacts with heat shock transcription factor 1 and activates the heat shock response.J Virol. 2023 Sep 28;97(9):e0071823. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00718-23. Epub 2023 Sep 6. J Virol. 2023. PMID: 37671864 Free PMC article.
-
ATF1 Restricts Human Herpesvirus 6A Replication via Beta Interferon Induction.J Virol. 2022 Oct 12;96(19):e0126422. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01264-22. Epub 2022 Sep 26. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 36154610 Free PMC article.
-
Human herpesvirus 6A U27 plays an essential role for the virus propagation.Microbiol Immunol. 2020 Oct;64(10):703-711. doi: 10.1111/1348-0421.12840. Microbiol Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32827324
-
Molecular biology of human herpesviruses 6A and 6B.Infect Agents Dis. 1993 Dec;2(6):343-60. Infect Agents Dis. 1993. PMID: 8012736 Review.
-
The U94 Gene of Human Herpesvirus 6: A Narrative Review of Its Role and Potential Functions.Cells. 2020 Dec 4;9(12):2608. doi: 10.3390/cells9122608. Cells. 2020. PMID: 33291793 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of FXR agonist GW4064 in the treatment of hilar cholangiocarcinoma in rats.Sci Rep. 2022 Nov 7;12(1):18873. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-23539-5. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36344586 Free PMC article.
-
Human herpesvirus 6A nuclear matrix protein U37 interacts with heat shock transcription factor 1 and activates the heat shock response.J Virol. 2023 Sep 28;97(9):e0071823. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00718-23. Epub 2023 Sep 6. J Virol. 2023. PMID: 37671864 Free PMC article.
-
The Cytomegalovirus M35 Protein Directly Binds to the Interferon-β Enhancer and Modulates Transcription of Ifnb1 and Other IRF3-Driven Genes.J Virol. 2023 Jun 29;97(6):e0040023. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00400-23. Epub 2023 Jun 8. J Virol. 2023. PMID: 37289084 Free PMC article.
-
The MGF300-2R protein of African swine fever virus is associated with viral pathogenicity by promoting the autophagic degradation of IKKα and IKKβ through the recruitment of TOLLIP.PLoS Pathog. 2023 Aug 11;19(8):e1011580. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011580. eCollection 2023 Aug. PLoS Pathog. 2023. PMID: 37566637 Free PMC article.
-
ATF1 Restricts Human Herpesvirus 6A Replication via Beta Interferon Induction.J Virol. 2022 Oct 12;96(19):e0126422. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01264-22. Epub 2022 Sep 26. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 36154610 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aubin JT, Collandre H, Candotti D, Ingrand D, Rouzioux C, Burgard M, Richard S, Huraux JM, Agut H. 1991. Several groups among human herpesvirus-6 strains can be distinguished by southern blotting and polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol 29:367–372. 10.1128/jcm.29.2.367-372.1991. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ablashi D, Agut H, Alvarez-Lafuente R, Clark DA, Dewhurst S, DiLuca D, Flamand L, Frenkel N, Gallo R, Gompels UA, Hollsberg P, Jacobson S, Luppi M, Lusso P, Malnati M, Medveczky P, Mori Y, Pellett PE, Pritchett JC, Yamanishi K, Yoshikawa T. 2014. Classification of HHV-6A and HHV-6B as distinct viruses. Arch Virol 159:863–870. 10.1007/s00705-013-1902-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yamanishi K, Mori Y, Pellet PE. 2013. Human herpesviruses 6 and 7, p 2058–2079. In Knipe DM, Howley PM, Cohen JI, Griffin DE, Lamb RA, Martin MA, Racaniello VR, Roizman B (ed), Fields virology, 6th ed. Lippincott-Williams &Wilkins, Philadelphia, PA.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 20wm0325005h/Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED)
- Grants for Scientific Research/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- MSD Life Science Foundation, Public Interest Incorporated Foundation (SD Life Science Foundation)
- 19H05286/Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT)
- Leading Initiative for Excellent Young Researchers Grant/Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

