Rutaecarpine Increases Nitric Oxide Synthesis via eNOS Phosphorylation by TRPV1-Dependent CaMKII and CaMKKβ/AMPK Signaling Pathway in Human Endothelial Cells
- PMID: 34502308
- PMCID: PMC8431268
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22179407
Rutaecarpine Increases Nitric Oxide Synthesis via eNOS Phosphorylation by TRPV1-Dependent CaMKII and CaMKKβ/AMPK Signaling Pathway in Human Endothelial Cells
Abstract
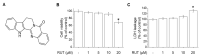
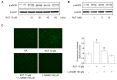
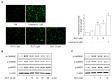
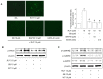
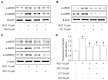
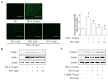
Rutaecarpine (RUT) is a bioactive alkaloid isolated from the fruit of Evodia rutaecarpa that exerts a cellular protective effect. However, its protective effects on endothelial cells and its mechanism of action are still unclear. In this study, we demonstrated the effects of RUT on nitric oxide (NO) synthesis via endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) phosphorylation in endothelial cells and the underlying molecular mechanisms. RUT treatment promoted NO generation by increasing eNOS phosphorylation. Additionally, RUT induced an increase in intracellular Ca2+ concentration and phosphorylation of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase β (CaMKKβ), AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), and Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase II (CaMKII). Inhibition of transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 (TRPV1) attenuated RUT-induced intracellular Ca2+ concentration and phosphorylation of CaMKII, CaMKKβ, AMPK, and eNOS. Treatment with KN-62 (a CaMKII inhibitor), Compound C (an AMPK inhibitor), and STO-609 (a CaMKKβ inhibitor) suppressed RUT-induced eNOS phosphorylation and NO generation. Interestingly, RUT attenuated the expression of ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 induced by TNF-α and inhibited the inflammation-related NF-κB signaling pathway. Taken together, these results suggest that RUT promotes NO synthesis and eNOS phosphorylation via the Ca2+/CaMKII and CaM/CaMKKβ/AMPK signaling pathways through TRPV1. These findings provide evidence that RUT prevents endothelial dysfunction and benefit cardiovascular health.
Keywords: AMPK; Ca2+; CaMKII; TRPV1; eNOS; rutaecarpine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Molecular mechanisms of activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase mediated by transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1.Cardiovasc Res. 2011 Aug 1;91(3):492-501. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvr104. Epub 2011 Apr 14. Cardiovasc Res. 2011. PMID: 21493704
-
Activation of AMP-activated protein kinase by vascular endothelial growth factor mediates endothelial angiogenesis independently of nitric-oxide synthase.J Biol Chem. 2010 Apr 2;285(14):10638-52. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.108688. Epub 2010 Feb 3. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20129920 Free PMC article.
-
Sesamin Induces Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase Activation via Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid Type 1.J Agric Food Chem. 2020 Mar 18;68(11):3474-3484. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b07909. Epub 2020 Mar 4. J Agric Food Chem. 2020. PMID: 32077699
-
eNOS activation and NO function: pregnancy adaptive programming of capacitative entry responses alters nitric oxide (NO) output in vascular endothelium--new insights into eNOS regulation through adaptive cell signaling.J Endocrinol. 2011 Sep;210(3):243-58. doi: 10.1530/JOE-11-0053. Epub 2011 May 9. J Endocrinol. 2011. PMID: 21555345 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resveratrol and endothelial nitric oxide.Molecules. 2014 Oct 9;19(10):16102-21. doi: 10.3390/molecules191016102. Molecules. 2014. PMID: 25302702 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanosensitive cation currents through TRPC6 and Piezo1 channels in human pulmonary arterial endothelial cells.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2022 Oct 1;323(4):C959-C973. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00313.2022. Epub 2022 Aug 15. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35968892 Free PMC article.
-
Icariside II induces rapid phosphorylation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase via multiple signaling pathways.PeerJ. 2022 Oct 25;10:e14192. doi: 10.7717/peerj.14192. eCollection 2022. PeerJ. 2022. PMID: 36312762 Free PMC article.
-
Shenfu injection: a review of pharmacological effects on cardiovascular diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Feb 14;15:1279584. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1279584. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38420190 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Unexpected Role of the Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase at the Neurovascular Unit: Beyond the Regulation of Cerebral Blood Flow.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 21;25(16):9071. doi: 10.3390/ijms25169071. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TRP (transient receptor potential) ion channel family: structures, biological functions and therapeutic interventions for diseases.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023 Jul 5;8(1):261. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01464-x. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023. PMID: 37402746 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Schneider J.C., El Kebir D., Chereau C., Lanone S., Huang X.L., De Buys Roessingh A.S., Mercier J.C., Dall’Ava-Santucci J., Dinh-Xuan A.T. Involvement of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II in endothelial NO production and endothelium-dependent relaxation. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2003;284:H2311–H2319. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00932.2001. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

