Merging Established Mechanisms with New Insights: Condensates, Hubs, and the Regulation of RNA Polymerase II Transcription
- PMID: 34474085
- PMCID: PMC8748285
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2021.167216
Merging Established Mechanisms with New Insights: Condensates, Hubs, and the Regulation of RNA Polymerase II Transcription
Abstract
The regulation of RNA polymerase II (pol II) transcription requires a complex and context-specific array of proteins and protein complexes, as well as nucleic acids and metabolites. Every major physiological process requires coordinated transcription of specific sets of genes at the appropriate time, and a breakdown in this regulation is a hallmark of human disease. A proliferation of recent studies has revealed that many general transcription components, including sequence-specific, DNA-binding transcription factors, Mediator, and pol II itself, are capable of liquid-liquid phase separation, to form condensates that partition these factors away from the bulk aqueous phase. These findings hold great promise for next-level understanding of pol II transcription; however, many mechanistic aspects align with more conventional models, and whether phase separation per se regulates pol II activity in cells remains controversial. In this review, we describe the conventional and condensate-dependent models, and why their similarities and differences are important. We also compare and contrast these models in the context of genome organization and pol II transcription (initiation, elongation, and termination), and highlight the central role of RNA in these processes. Finally, we discuss mutations that disrupt normal partitioning of transcription factors, and how this may contribute to disease.
Keywords: RNA polymerase II; condensates; liquid-liquid phase separation; mediator; transcription.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interest statement D.J.T. is a member of the scientific advisory board at Dewpoint Therapeutics.
Figures
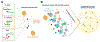
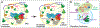
Similar articles
-
Pol II phosphorylation regulates a switch between transcriptional and splicing condensates.Nature. 2019 Aug;572(7770):543-548. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1464-0. Epub 2019 Aug 7. Nature. 2019. PMID: 31391587 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation and specific DNA improved the incorporation ability of p53 into functional condensates.Int J Biol Macromol. 2023 Mar 1;230:123221. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.123221. Epub 2023 Jan 10. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023. PMID: 36634798
-
Mediator and RNA polymerase II clusters associate in transcription-dependent condensates.Science. 2018 Jul 27;361(6400):412-415. doi: 10.1126/science.aar4199. Epub 2018 Jun 21. Science. 2018. PMID: 29930094 Free PMC article.
-
The Mediator complex as a master regulator of transcription by RNA polymerase II.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2022 Nov;23(11):732-749. doi: 10.1038/s41580-022-00498-3. Epub 2022 Jun 20. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 35725906 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nuclear Protein Condensates and Their Properties in Regulation of Gene Expression.J Mol Biol. 2022 Jan 15;434(1):167151. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2021.167151. Epub 2021 Jul 14. J Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 34271007 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Coevolution of the Ess1-CTD axis in polar fungi suggests a role for phase separation in cold tolerance.Sci Adv. 2022 Sep 9;8(36):eabq3235. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abq3235. Epub 2022 Sep 7. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 36070379 Free PMC article.
-
Multiprotein GLI Transcriptional Complexes as Therapeutic Targets in Cancer.Life (Basel). 2022 Nov 24;12(12):1967. doi: 10.3390/life12121967. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36556332 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemical inhibitors of transcription-associated kinases.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2022 Oct;70:102186. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2022.102186. Epub 2022 Aug 1. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2022. PMID: 35926294 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional bodies manage tight resources.Nat Cell Biol. 2024 Apr;26(4):512-513. doi: 10.1038/s41556-024-01395-x. Nat Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38589532 No abstract available.
-
DNA-Stimulated Liquid-Liquid phase separation by eukaryotic topoisomerase ii modulates catalytic function.Elife. 2022 Nov 7;11:e81786. doi: 10.7554/eLife.81786. Elife. 2022. PMID: 36342377 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bergeron-Sandoval LP, Safaee N, Michnick SW. Mechanisms and Consequences of Macromolecular Phase Separation. Cell. 2016;165:1067–79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

