A novel missense variant in ACAA1 contributes to early-onset Alzheimer's disease, impairs lysosomal function, and facilitates amyloid-β pathology and cognitive decline
- PMID: 34465723
- PMCID: PMC8408221
- DOI: 10.1038/s41392-021-00748-4
A novel missense variant in ACAA1 contributes to early-onset Alzheimer's disease, impairs lysosomal function, and facilitates amyloid-β pathology and cognitive decline
Abstract
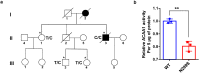
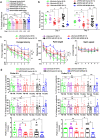
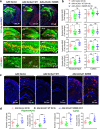
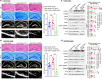
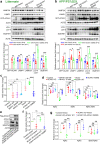
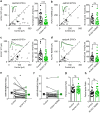
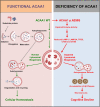
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is characterized by progressive synaptic dysfunction, neuronal death, and brain atrophy, with amyloid-β (Aβ) plaque deposits and hyperphosphorylated tau neurofibrillary tangle accumulation in the brain tissue, which all lead to loss of cognitive function. Pathogenic mutations in the well-known AD causal genes including APP, PSEN1, and PSEN2 impair a variety of pathways, including protein processing, axonal transport, and metabolic homeostasis. Here we identified a missense variant rs117916664 (c.896T>C, p.Asn299Ser [p.N299S]) of the acetyl-CoA acyltransferase 1 (ACAA1) gene in a Han Chinese AD family by whole-genome sequencing and validated its association with early-onset familial AD in an independent cohort. Further in vitro and in vivo evidence showed that ACAA1 p.N299S contributes to AD by disturbing its enzymatic activity, impairing lysosomal function, and aggravating the Aβ pathology and neuronal loss, which finally caused cognitive impairment in a murine model. Our findings reveal a fundamental role of peroxisome-mediated lysosomal dysfunction in AD pathogenesis.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Aberrant palmitoylation caused by a ZDHHC21 mutation contributes to pathophysiology of Alzheimer's disease.BMC Med. 2023 Jun 26;21(1):223. doi: 10.1186/s12916-023-02930-7. BMC Med. 2023. PMID: 37365538 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Lysosomes in a Broad Disease-Modifying Approach Evaluated across Transgenic Mouse Models of Alzheimer's Disease and Parkinson's Disease and Models of Mild Cognitive Impairment.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Sep 9;20(18):4432. doi: 10.3390/ijms20184432. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31505809 Free PMC article.
-
PLD3 is a neuronal lysosomal phospholipase D associated with β-amyloid plaques and cognitive function in Alzheimer's disease.PLoS Genet. 2021 Apr 8;17(4):e1009406. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009406. eCollection 2021 Apr. PLoS Genet. 2021. PMID: 33830999 Free PMC article.
-
APP transgenic modeling of Alzheimer's disease: mechanisms of neurodegeneration and aberrant neurogenesis.Brain Struct Funct. 2010 Mar;214(2-3):111-26. doi: 10.1007/s00429-009-0232-6. Epub 2009 Nov 29. Brain Struct Funct. 2010. PMID: 20091183 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alzheimer's disease.Subcell Biochem. 2012;65:329-52. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-5416-4_14. Subcell Biochem. 2012. PMID: 23225010 Review.
Cited by
-
Microbial infection promotes amyloid pathology in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease via modulating γ-secretase.Mol Psychiatry. 2024 May;29(5):1491-1500. doi: 10.1038/s41380-024-02428-5. Epub 2024 Jan 25. Mol Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38273109
-
DisPhaseDB: An integrative database of diseases related variations in liquid-liquid phase separation proteins.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022 May 12;20:2551-2557. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.05.004. eCollection 2022. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022. PMID: 35685370 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular docking and dynamics simulation approach of Camellia sinensis leaf extract derived compounds as potential cholinesterase inhibitors.In Silico Pharmacol. 2023 May 28;11(1):14. doi: 10.1007/s40203-023-00151-7. eCollection 2023. In Silico Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37255739 Free PMC article.
-
Association analysis between Acetyl-Coenzyme A Acyltransferase-1 gene polymorphism and growth traits in Xiangsu pigs.Front Genet. 2024 May 2;15:1346903. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1346903. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 38756449 Free PMC article.
-
Piezo2 Contributes to Traumatic Brain Injury by Activating the RhoA/ROCK1 Pathways.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Oct;61(10):7419-7430. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04058-y. Epub 2024 Feb 22. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38388773 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

