Autophagy Modulators in Cancer: Focus on Cancer Treatment
- PMID: 34440583
- PMCID: PMC8401266
- DOI: 10.3390/life11080839
Autophagy Modulators in Cancer: Focus on Cancer Treatment
Abstract
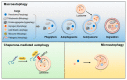
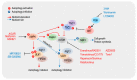
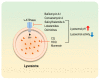
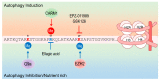
Uncontrolled autophagy has been associated with the development and progression of various cancers that are resistant to cancer therapy. Therefore, many efforts to modulate uncontrolled autophagy as a cancer treatment have been attempted, from basic science to clinical trials. However, it remains difficult to equally apply autophagy modulators to cancer therapy because autophagy is a double-edged sword in cancer: it can be tumor-suppressive or tumor-protective. Therefore, the precise mechanisms of autophagy modulators and their varied responsiveness to each cancer type should be addressed in detail. This study will describe the precise mechanisms of developing various autophagy modulators, their current therapeutic applications and future perspectives.
Keywords: autophagy; autophagy enhancer; autophagy inhibitor; cancer treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Is targeting autophagy mechanism in cancer a good approach? The possible double-edge sword effect.Cell Biosci. 2021 Mar 20;11(1):56. doi: 10.1186/s13578-021-00570-z. Cell Biosci. 2021. PMID: 33743781 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Multifaceted Role of Flavonoids in Cancer Therapy: Leveraging Autophagy with a Double-Edged Sword.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Jul 19;10(7):1138. doi: 10.3390/antiox10071138. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34356371 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crosstalk between autophagy and epithelial-mesenchymal transition and its application in cancer therapy.Mol Cancer. 2019 May 24;18(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1030-2. Mol Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31126310 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dual role of autophagy/mitophagy in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2019 Jun;56:116-125. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2019.04.002. Epub 2019 Apr 17. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2019. PMID: 31004748 Review.
-
Driving Cytotoxic Natural Killer Cells into Melanoma: If CCL5 Plays the Music, Autophagy Calls the Shots.Crit Rev Oncog. 2018;23(5-6):321-332. doi: 10.1615/CritRevOncog.2018027526. Crit Rev Oncog. 2018. PMID: 30311563 Review.
Cited by
-
DSTYK inhibition increases the sensitivity of lung cancer cells to T cell-mediated cytotoxicity.J Exp Med. 2022 Dec 5;219(12):e20220726. doi: 10.1084/jem.20220726. Epub 2022 Sep 28. J Exp Med. 2022. PMID: 36169652 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Natural and Synthetic Compounds in Modulating NRF2/KEAP1 Signaling Pathway in Prostate Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jun 2;15(11):3037. doi: 10.3390/cancers15113037. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37296999 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Amino acid deprivation in cancer cells with compensatory autophagy induction increases sensitivity to autophagy inhibitors.Mol Cell Oncol. 2024 Jul 14;11(1):2377404. doi: 10.1080/23723556.2024.2377404. eCollection 2024. Mol Cell Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39021618 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy-Related Gene WD Repeat Domain 45B Promotes Tumor Proliferation and Migration of Hepatocellular Carcinoma through the Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathway.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Feb 27;13(5):906. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13050906. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36900050 Free PMC article.
-
Health horizons: Future trends and technologies from the European Medicines Agency's horizon scanning collaborations.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Dec 8;9:1064003. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.1064003. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36569125 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Klionsky D.J., Abdelmohsen K., Abe A., Abedin M.J., Abeliovich H., Acevedo Arozena A., Adachi H., Adams C.M., Adams P.D., Adeli K., et al. Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy (3rd edition) Autophagy. 2016;12:1–222. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2015.1100356. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

