MicroRNA and Other Non-Coding RNAs in Epstein-Barr Virus-Associated Cancers
- PMID: 34359809
- PMCID: PMC8345394
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13153909
MicroRNA and Other Non-Coding RNAs in Epstein-Barr Virus-Associated Cancers
Abstract
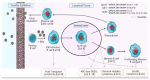
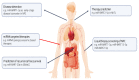
EBV is a direct causative agent in around 1.5% of all cancers. The oncogenic properties of EBV are related to its ability to activate processes needed for cellular proliferation, survival, migration, and immune evasion. The EBV latency program is required for the immortalization of infected B cells and involves the expression of non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs), including viral microRNAs. These ncRNAs have different functions that contribute to virus persistence in the asymptomatic host and to the development of EBV-associated cancers. In this review, we discuss the function and potential clinical utility of EBV microRNAs and other ncRNAs in EBV-associated malignancies. This review is not intended to be comprehensive, but rather to provide examples of the importance of ncRNAs.
Keywords: Burkitt lymphoma; EBV; carcinogenesis; classical Hodgkin’s lymphoma; diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; gastric carcinoma; immune evasion; miRNA; microRNAome; nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The BHLF1 Locus of Epstein-Barr Virus Contributes to Viral Latency and B-Cell Immortalization.J Virol. 2020 Aug 17;94(17):e01215-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01215-20. Print 2020 Aug 17. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 32581094 Free PMC article.
-
The oncogenic role of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microRNAs in Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric carcinoma.J Cell Mol Med. 2018 Jan;22(1):38-45. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13354. Epub 2017 Oct 9. J Cell Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 28990284 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Function and Therapeutic Potential of Epstein-Barr Virus-Encoded MicroRNAs in Cancer.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2019 Sep 6;17:657-668. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2019.07.002. Epub 2019 Jul 15. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2019. PMID: 31400608 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs of Epstein-Barr Virus Attenuate T-Cell-Mediated Immune Control In Vivo.mBio. 2019 Jan 15;10(1):e01941-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01941-18. mBio. 2019. PMID: 30647153 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microRNAs as regulators in host immune responses.Int J Biol Sci. 2018 Apr 5;14(5):565-576. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.24562. eCollection 2018. Int J Biol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29805308 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The potential of circulating microRNAs as novel diagnostic biomarkers of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Infect Dis. 2024 Sep 19;24(1):1011. doi: 10.1186/s12879-024-09915-8. BMC Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39300343 Free PMC article.
-
Initial clinical presentation of multiple sclerosis with concurrent COVID-19 infection: Case report and literature review.Curr J Neurol. 2022 Oct 7;21(4):251-255. doi: 10.18502/cjn.v21i4.11723. Curr J Neurol. 2022. PMID: 38011371 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Differential miRNA Profiling Reveals miR-4433a-5p as a Key Regulator of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Progression via PIK3R2- mediated Phenotypic Modulation.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2024;27(16):2323-2334. doi: 10.2174/0113862073243966231030093213. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2024. PMID: 38178680 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of mature tertiary lymphoid structures on prognosis and therapeutic response of Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric cancer patients.Front Immunol. 2022 Dec 14;13:973085. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.973085. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36591236 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into Epstein‑Barr virus‑associated tumors: Exosomes (Review).Oncol Rep. 2022 Jan;47(1):13. doi: 10.3892/or.2021.8224. Epub 2021 Nov 15. Oncol Rep. 2022. PMID: 34779497 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

