Butorphanol Promotes Macrophage Phenotypic Transition to Inhibit Inflammatory Lung Injury via κ Receptors
- PMID: 34305926
- PMCID: PMC8294090
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.692286
Butorphanol Promotes Macrophage Phenotypic Transition to Inhibit Inflammatory Lung Injury via κ Receptors
Abstract
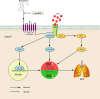
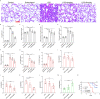
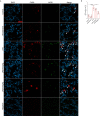
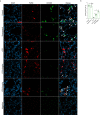
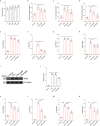
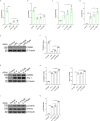
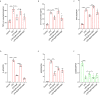
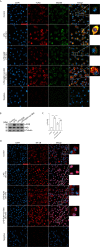
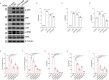
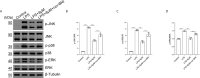
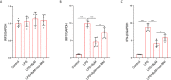
Acute lung injury (ALI)/acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is characterized by diffuse inflammation of the lung parenchyma and refractory hypoxemia. Butorphanol is commonly used clinically for perioperative pain relief, but whether butorphanol can regulate LPS-induced alveolar macrophage polarization is unclear. In this study, we observed that butorphanol markedly attenuated sepsis-induced lung tissue injury and mortality in mice. Moreover, butorphanol also decreased the expression of M1 phenotype markers (TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β and iNOS) and enhanced the expression of M2 marker (CD206) in alveolar macrophages in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) of LPS-stimulated mice. Butorphanol administration reduced LPS-induced numbers of proinflammatory (M1) macrophages and increased numbers of anti-inflammatory (M2) macrophages in the lungs of mice. Furthermore, we found that butorphanol-mediated suppression of the LPS-induced increases in M1 phenotype marker expression (TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β and iNOS) in bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs), and this effect was reversed by κ-opioid receptor (KOR) antagonists. Moreover, butorphanol inhibited the interaction of TLR4 with MyD88 and further suppressed NF-κB and MAPKs activation. In addition, butorphanol prevented the Toll/IL-1 receptor domain-containing adaptor inducing IFN-β (TRIF)-mediated IFN signaling pathway. These effects were ameliorated by KOR antagonists. Thus, butorphanol may promote macrophage polarization from a proinflammatory to an anti-inflammatory phenotype secondary to the inhibition of NF-κB, MAPKs, and the TRIF-mediated IFN signaling pathway through κ receptors.
Keywords: acute lung injury; butorphanol; inflammation; macrophage; κ receptor.
Copyright © 2021 Luan, Pan, Bu, Wu, Wang and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Wogonin prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury and inflammation in mice via peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma-mediated attenuation of the nuclear factor-kappaB pathway.Immunology. 2014 Oct;143(2):241-57. doi: 10.1111/imm.12305. Immunology. 2014. PMID: 24766487 Free PMC article.
-
Syringic acid attenuates acute lung injury by modulating macrophage polarization in LPS-induced mice.Phytomedicine. 2024 Jul;129:155591. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155591. Epub 2024 Apr 15. Phytomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38692075
-
Anti-inflammatory action of Athyrium multidentatum extract suppresses the LPS-induced TLR4 signaling pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2018 May 10;217:220-227. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2018.02.031. Epub 2018 Feb 21. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29476961
-
Regulatory impact of statins on macrophage polarization: mechanistic and therapeutic implications.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 5;76(7):763-775. doi: 10.1093/jpp/rgae024. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38470222 Review.
-
The role of immunometabolism in macrophage polarization and its impact on acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome.Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 20;14:1117548. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1117548. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37020557 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Different Doses of Butorphanol on Postoperative Shivering in Elderly Patients: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2023 Mar 20;17:839-849. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S396309. eCollection 2023. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2023. PMID: 36969707 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Protective effects of butorphanol in oleic acid-endotoxin "two-hit" induced rat lung injury by suppression of inflammation and apoptosis.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 20;14(1):14231. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-53483-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38902260 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of Opioids with TLR4-Mechanisms and Ramifications.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Oct 21;13(21):5274. doi: 10.3390/cancers13215274. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34771442 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mouse Model of Latent Cryptococcal Infection and Reactivation.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2667:87-98. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3199-7_6. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37145277
-
Pain Management in Animals with Oncological Disease: Opioids as Influencers of Immune and Tumor Cellular Balance.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Aug 29;16(17):3015. doi: 10.3390/cancers16173015. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39272873 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dellinger RP, Levy MM, Rhodes A, Annane D, Gerlach H, Opal SM, et al. . Surviving Sepsis Campaign Guidelines Committee Including the Pediatric, Surviving Sepsis Campaign: International Guidelines for Management of Severe Sepsis and Septic Shock: 2012. Crit Care Med (2013) 41(2):580–637. 10.1007/s00134-012-2769-8 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

