Bioinformatics reveal macrophages marker genes signature in breast cancer to predict prognosis
- PMID: 34187256
- PMCID: PMC8253219
- DOI: 10.1080/07853890.2021.1914343
Bioinformatics reveal macrophages marker genes signature in breast cancer to predict prognosis
Abstract
Background: Breast cancer is a pivotal cause of global women cancer death. Immunotherapy has become a promising means to cure breast cancer. As constitutes of immune microenvironment of breast cancer, macrophages exert complicated functions in the tumour development and treatment. This study aims to develop a prognostic macrophage marker genes signature (MMGS).Methods: Single cell RNA sequence data analysis was performed to identify macrophage marker genes in breast cancer. TCGA database was used to construct MMGS model as a training cohort, and GSE96058 dataset was used to validate the MMGS as a validation cohort.Results: Genes included in the MMGS model were: SERPINA1, CD74, STX11, ADAM9, CD24, NFKBIA, PGK1. MMGS risk score stratified by overall survival of patients divided them into high- and low-risk groups. And MMGS risk score remained independent prognostic factor in multivariate analysis after adjusting for classical clinical factors in both training and validation cohorts. Besides, hormone receptors negative and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) positive patients had higher risk score. MMGS showed better distinguishing capability between high-risk and low-risk groups in hormone receptor positive and HER2 negative subgroup.Conclusion: MMGS provides a new understanding of immune cell marker genes in breast cancer prognosis and may offer reference for immunotherapy decision for breast cancer patients.
Keywords: Breast cancer; bioinformatics; macrophages marker genes; prognostic signature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
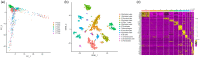
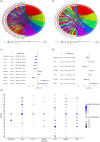
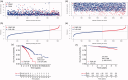
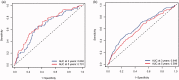

Similar articles
-
Bioinformatics Analysis Reveals Prognostic Significance of the Macrophage Marker Gene Signature in Gastric Adenocarcinoma.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2024 May 6;29(5):172. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2905172. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2024. PMID: 38812299
-
Validating a Macrophage Marker Gene Signature (MMGS) in Lung Adenocarcinoma Prognosis and Response to Immunotherapy.J Immunother. 2023 Jul-Aug 01;46(6):205-215. doi: 10.1097/CJI.0000000000000477. Epub 2023 May 24. J Immunother. 2023. PMID: 37220007
-
Comprehensive scRNA-seq analysis to identify new markers of M2 macrophages for predicting the prognosis of prostate cancer.Ann Med. 2024 Dec;56(1):2398195. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2024.2398195. Epub 2024 Sep 2. Ann Med. 2024. PMID: 39221762 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and validation of a novel signature based on macrophage marker genes for predicting prognosis and drug response in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma by integrated analysis of single cell and bulk RNA sequencing.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 Mar 20;16(6):5676-5702. doi: 10.18632/aging.205671. Epub 2024 Mar 20. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 38517387 Free PMC article.
-
A novel hypoxia- and lactate metabolism-related signature to predict prognosis and immunotherapy responses for breast cancer by integrating machine learning and bioinformatic analyses.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 7;13:998140. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.998140. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36275774 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Exosomal circ-0100519 promotes breast cancer progression via inducing M2 macrophage polarisation by USP7/NRF2 axis.Clin Transl Med. 2024 Aug;14(8):e1763. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.1763. Clin Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39107958 Free PMC article.
-
Natural killer cell-related prognostic risk model predicts prognosis and treatment outcomes in triple-negative breast cancer.Front Immunol. 2023 Jul 13;14:1200282. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1200282. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37520534 Free PMC article.
-
Anoikis-related gene signatures in colorectal cancer: implications for cell differentiation, immune infiltration, and prognostic prediction.Sci Rep. 2024 May 21;14(1):11525. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-62370-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38773226 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of AP002498.1 and LINC01871 as prognostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets for distant metastasis of colorectal adenocarcinoma.Cancer Med. 2024 Jan;13(1):e6823. doi: 10.1002/cam4.6823. Epub 2023 Dec 11. Cancer Med. 2024. PMID: 38083905 Free PMC article.
-
MED1 induces M2 polarization of tumor-associated macrophages to aggravate breast cancer.Genes Genomics. 2023 Dec;45(12):1517-1525. doi: 10.1007/s13258-023-01435-0. Epub 2023 Aug 18. Genes Genomics. 2023. PMID: 37594664
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, et al. . Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Schmid P, Adams S, Rugo HS, et al. . Atezolizumab and nab-paclitaxel in advanced triple-negative breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:2108–2121. - PubMed
-
- Billan S, Kaidar-Person O, Gil Z.. Treatment after progression in the era of immunotherapy. Lancet Oncol. 2020;21:e463–e476. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
