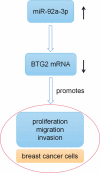
MicroRNA miR-92a-3p regulates breast cancer cell proliferation and metastasis via regulating B-cell translocation gene 2 (BTG2)
- PMID: 34082648
- PMCID: PMC8806219
- DOI: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1924543
MicroRNA miR-92a-3p regulates breast cancer cell proliferation and metastasis via regulating B-cell translocation gene 2 (BTG2)
Abstract
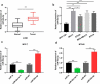
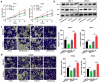
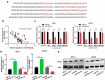
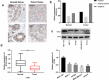
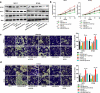
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) dysregulation contributes to tumorigenesis, and it is reported that abnormal miR-92a-3p expression participates in multiple cancers' occurrence and progression. This study focuses on miR-92a-3p's functions and regulatory mechanism in breast cancer (BC). The current study proved miR-92a-3p expression was enhanced in BC tissues and cells, and its high expression was related to increased TNM stage and larger tumor size of BC patients. Functionally, transfection of miR-92a-3p mimics facilitated BC cell proliferation and metastasis, yet transfection of miR-92a-3p inhibitors functioned oppositely. In addition, BTG2 was verified as a direct miR-92a-3p target in BC cells. This research indicated that miR-92a-3p facilitates BC cell proliferation and metastasis through repressing BTG2 expression.
Keywords: BTG2; Breast cancer; miR-92a-3p.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MiR-6875-3p promotes the proliferation, invasion and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma via BTG2/FAK/Akt pathway.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Jan 8;38(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-1020-z. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30621734 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA CARMN inhibits cervical cancer cell growth via the miR-92a-3p/BTG2/Wnt/β-catenin axis.Physiol Genomics. 2023 Jan 1;55(1):1-15. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00088.2022. Epub 2022 Oct 31. Physiol Genomics. 2023. PMID: 36314369
-
Deregulation of miR-1245b-5p and miR-92a-3p and their potential target gene, GATA3, in epithelial-mesenchymal transition pathway in breast cancer.Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2024 Feb;7(2):e1955. doi: 10.1002/cnr2.1955. Epub 2024 Jan 3. Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2024. PMID: 38173189 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNA circFLNA inhibits the development of bladder carcinoma through microRNA miR-216a-3p/BTG2 axis.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(2):11376-11389. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2008659. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34852712 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging role of anti-proliferative protein BTG1 and BTG2.BMB Rep. 2022 Aug;55(8):380-388. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2022.55.8.092. BMB Rep. 2022. PMID: 35880434 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The microRNA-381(miR-381)/Spindlin1(SPIN1) axis contributes to cell proliferation and invasion of colorectal cancer cells by regulating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(2):12036-12048. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2003663. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34753384 Free PMC article.
-
miR-92a-3p regulates cisplatin-induced cancer cell death.Cell Death Dis. 2023 Sep 13;14(9):603. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06125-z. Cell Death Dis. 2023. PMID: 37704611 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of potential microRNA diagnostic panels and uncovering regulatory mechanisms in breast cancer pathogenesis.Sci Rep. 2022 Nov 22;12(1):20135. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-24347-7. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36418345 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence of antagonistic predictive effects of miRNAs in breast cancer cohorts through data-driven networks.Sci Rep. 2022 Mar 25;12(1):5166. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-08737-5. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35338170 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Human Epicardial Adipose Tissue-Derived miR-92a-3p in Myocardial Redox State.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2023 Jul 25;82(4):317-332. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2023.05.031. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2023. PMID: 37468187 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018. Nov;68(6):394–424. - PubMed
-
- Duijf PHG, Nanayakkara D, Nones K, et al. Mechanisms of genomic instability in breast cancer. Trends Mol Med. 2019. Jul;25(7):595–611. - PubMed
-
- Xie T, Huang M, Wang Y, et al. MicroRNAs as regulators, biomarkers and therapeutic targets in the drug resistance of colorectal cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;40(1–2):62–76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
