Metabolically engineered stem cell-derived exosomes to regulate macrophage heterogeneity in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 34078596
- PMCID: PMC8172131
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abe0083
Metabolically engineered stem cell-derived exosomes to regulate macrophage heterogeneity in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Despite the remarkable advances in therapeutics for rheumatoid arthritis (RA), a large number of patients still lack effective countermeasures. Recently, the reprogramming of macrophages to an immunoregulatory phenotype has emerged as a promising therapeutic strategy for RA. Here, we report metabolically engineered exosomes that have been surface-modified for the targeted reprogramming of macrophages. Qualified exosomes were readily harvested from metabolically engineered stem cells by tangential flow filtration at a high yield while maintaining their innate immunomodulatory components. When systemically administered into mice with collagen-induced arthritis, these exosomes effectively accumulated in the inflamed joints, inducing a cascade of anti-inflammatory events via macrophage phenotype regulation. The level of therapeutic efficacy obtained with bare exosomes was achievable with the engineered exosomes of 10 times less dose. On the basis of the boosted nature to reprogram the synovial microenvironment, the engineered exosomes display considerable potential to be developed as a next-generation drug for RA.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works. Distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License 4.0 (CC BY-NC).
Figures
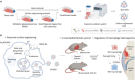
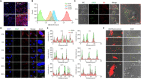
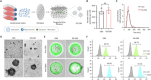

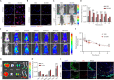
Comment in
-
Modifying exosomes to target macrophages in arthritis.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2021 Aug;17(8):443. doi: 10.1038/s41584-021-00651-w. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 34188204 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Reactive oxygen species-responsive dendritic cell-derived exosomes for rheumatoid arthritis.Acta Biomater. 2021 Jul 1;128:462-473. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2021.04.026. Epub 2021 Apr 18. Acta Biomater. 2021. PMID: 33878476
-
Therapeutic Potential of Mesenchymal Cell-Derived miRNA-150-5p-Expressing Exosomes in Rheumatoid Arthritis Mediated by the Modulation of MMP14 and VEGF.J Immunol. 2018 Oct 15;201(8):2472-2482. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1800304. Epub 2018 Sep 17. J Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30224512 Free PMC article.
-
A Targeted Exosome Therapeutic Confers Both CfDNA Scavenging and Macrophage Polarization for Ameliorating Rheumatoid Arthritis.Adv Mater. 2023 Nov;35(48):e2302503. doi: 10.1002/adma.202302503. Epub 2023 Oct 27. Adv Mater. 2023. PMID: 37681753
-
Exploring the role of exosomes in rheumatoid arthritis.Inflammopharmacology. 2023 Feb;31(1):119-128. doi: 10.1007/s10787-022-01100-0. Epub 2022 Nov 21. Inflammopharmacology. 2023. PMID: 36414831 Review.
-
Stem Cell Mimicking Nanoencapsulation for Targeting Arthritis.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 Dec 31;16:8485-8507. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S334298. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 35002240 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Engineering exosomes and their application in cardiovascular field: Bibliometric analysis from 2002 to 2022.Heliyon. 2023 Jul 29;9(8):e18809. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e18809. eCollection 2023 Aug. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37576273 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomal miR-181d-5p Derived from Rapamycin-Conditioned MDSC Alleviated Allograft Rejection by Targeting KLF6.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023 Dec;10(34):e2304922. doi: 10.1002/advs.202304922. Epub 2023 Oct 23. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023. PMID: 37870185 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes in skeletal diseases.Front Mol Biosci. 2024 Jun 6;11:1268019. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1268019. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 38903180 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adipose stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles ameliorates corticosterone-induced apoptosis in the cortical neurons via inhibition of ER stress.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022 Mar 21;13(1):110. doi: 10.1186/s13287-022-02785-4. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 35313975 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular vesicles and their cells of origin: Open issues in autoimmune diseases.Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 8;14:1090416. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1090416. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36969255 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Olumuyiwa-Akeredolu O.-o., Page M. J., Soma P., Pretorius E., Platelets: Emerging facilitators of cellular crosstalk in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 15, 237–248 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Smolen J. S., Steiner G., Therapeutic strategies for rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2, 473–488 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Fortune Business Insights (2019); www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/industry-reports/rheumatoid-arthritis-th....
-
- Smolen J. S., Aletaha D., Barton A., Burmester G. R., Emery P., Firestein G. S., Kavanaugh A., McInnes I. B., Solomon D. H., Strand V., Yamamoto K., Rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers. 4, 18001 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Udalova I. A., Mantovani A., Feldmann M., Macrophage heterogeneity in the context of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 12, 472–485 (2016). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

