Guselkumab induces robust reduction in acute phase proteins and type 17 effector cytokines in active psoriatic arthritis: results from phase 3 trials
- PMID: 34011674
- PMCID: PMC8137258
- DOI: 10.1136/rmdopen-2021-001679
Guselkumab induces robust reduction in acute phase proteins and type 17 effector cytokines in active psoriatic arthritis: results from phase 3 trials
Abstract
Objective: To investigate serum protein expression in participants with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) and changes after guselkumab treatment.
Methods: Participants with PsA were treated with guselkumab or placebo in the DISCOVER-1 and DISCOVER-2 studies. Serum levels of acute phase reactants C reactive protein (CRP) and serum amyloid A (SAA) and inflammatory cytokines/chemokines were measured at weeks 0, 4 and 24 in 300 study participants and 34 healthy controls (HCs). The PSUMMIT studies measured serum interleukin (IL)-17A, IL-17F and CRP after ustekinumab treatment and levels with ustekinumab versus guselkumab treatment were compared.
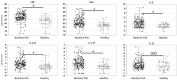
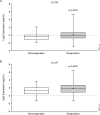
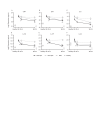
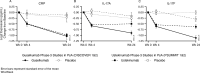
Results: Baseline serum levels of CRP, SAA, IL-6, IL-17A and IL-17F were elevated in participants with active PsA vs HCs (p<0.05, geometric mean (GM) ≥40% higher). Baseline T-helper cell 17 (Th17) effector cytokines were significantly associated with baseline psoriasis but not joint disease activity. Compared with placebo, guselkumab treatment resulted in decreases in serum CRP, SAA, IL-6, IL-17A, IL-17F and IL-22 as early as week 4 and continued to decrease through week 24 (p<0.05, GM decrease from baseline ≥33%). At week 24, IL-17A and IL-17F levels were not significantly different from HCs, suggesting normalisation of peripheral IL-23/Th17 axis effector cytokines postguselkumab treatment. Reductions in IL-17A/IL-17F levels were greater in guselkumab-treated versus ustekinumab-treated participants, whereas effects on CRP levels were similar.
Conclusion: Guselkumab treatment reduced serum protein levels of acute phase and Th17 effector cytokines and achieved comparable levels to those in HCs. In participants with PsA, reductions of IL-17A and IL-17F were of greater magnitude after treatment with guselkumab than with ustekinumab.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT03162796 NCT03158285.
Keywords: Arthritis; Biological Therapy; Cytokines; Psoriatic.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2021. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: KS, QS, MJL, KM, KL, VL, CF and PC are employees of Janssen Research & Development, a wholly owned subsidiary of Johnson & Johnson and own company stock. SS, FRCP, PhD has received research grants, consulting fees and/or honoraria (all <US$10 000 per annum) from AbbVie, Amgen (previously Celgene), Biogen, Janssen, and Novartis. Iain B. McInnes, FRCP, PhD has received research grants, consulting fees, and/or honoraria (all US$<10 000 per annum) from AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli Lilly and Company, Gilead, GSK, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi and UCB.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of guselkumab on serum biomarkers in patients with active psoriatic arthritis and inadequate response to tumor necrosis factor inhibitors: results from the COSMOS phase 3b study.Arthritis Res Ther. 2023 Aug 16;25(1):150. doi: 10.1186/s13075-023-03125-4. Arthritis Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 37587493 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Responsiveness of Serum C-Reactive Protein, Interleukin-17A, and Interleukin-17F Levels to Ustekinumab in Psoriatic Arthritis: Lessons From Two Phase III, Multicenter, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trials.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019 Oct;71(10):1660-1669. doi: 10.1002/art.40921. Epub 2019 Sep 3. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019. PMID: 31070869 Clinical Trial.
-
Correlation of changes in inflammatory and collagen biomarkers with durable guselkumab efficacy through 2 years in participants with active psoriatic arthritis: results from a phase III randomized controlled trial.Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2024 Oct 27;16:1759720X241283536. doi: 10.1177/1759720X241283536. eCollection 2024. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2024. PMID: 39493888 Free PMC article.
-
Guselkumab: the First Selective IL-23 Inhibitor for Active Psoriatic Arthritis in Adults.Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2021 Jan;17(1):5-13. doi: 10.1080/1744666X.2020.1857733. Epub 2020 Dec 7. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33251833 Review.
-
Pathogenic Role of IL-17 and Therapeutic Targeting of IL-17F in Psoriatic Arthritis and Spondyloarthropathies.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 18;24(12):10305. doi: 10.3390/ijms241210305. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37373452 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The potential role of serum amyloid A as biomarker of rheumatic diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Exp Med. 2024 Jun 29;24(1):141. doi: 10.1007/s10238-024-01413-0. Clin Exp Med. 2024. PMID: 38951267 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Orchestrated Cytokines Mediated by Biologics in Psoriasis and Its Mechanisms of Action.Biomedicines. 2022 Feb 20;10(2):498. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10020498. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35203707 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparing Efficacy of Guselkumab versus Ustekinumab in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis: An Adjusted Comparison Using Individual Patient Data from the DISCOVER and PSUMMIT Trials.Rheumatol Ther. 2024 Apr;11(2):457-474. doi: 10.1007/s40744-024-00644-7. Epub 2024 Feb 28. Rheumatol Ther. 2024. PMID: 38416392 Free PMC article.
-
Guselkumab Modulates Differentially Expressed Genes in Blood of Patients With Psoriatic Arthritis: Results from Two Phase 3, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trials.ACR Open Rheumatol. 2023 Sep;5(9):490-498. doi: 10.1002/acr2.11589. Epub 2023 Aug 8. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2023. PMID: 37553909 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of T Helper 22 Cells in Dermatological Disorders.Front Immunol. 2022 Jul 14;13:911546. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.911546. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35911703 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Siebert S, Sweet K, Dasgupta B, et al. . Responsiveness of serum C-reactive protein, interleukin-17A, and Interleukin-17F levels to ustekinumab in psoriatic arthritis: lessons from two phase III, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials. Arthritis Rheumatol 2019;71:1660–9. 10.1002/art.40921 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mease PJ, Smolen JS, Behrens F, et al. . A head-to-head comparison of the efficacy and safety of ixekizumab and adalimumab in biological-naïve patients with active psoriatic arthritis: 24-week results of a randomised, open-label, blinded-assessor trial. Ann Rheum Dis 2020;79:123–31. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-215386 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
