Multi-omics data integration and network-based analysis drives a multiplex drug repurposing approach to a shortlist of candidate drugs against COVID-19
- PMID: 34009288
- PMCID: PMC8135326
- DOI: 10.1093/bib/bbab114
Multi-omics data integration and network-based analysis drives a multiplex drug repurposing approach to a shortlist of candidate drugs against COVID-19
Abstract
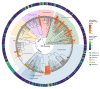
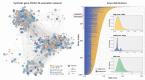
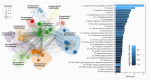
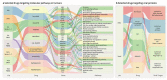
The severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) pandemic is undeniably the most severe global health emergency since the 1918 Influenza outbreak. Depending on its evolutionary trajectory, the virus is expected to establish itself as an endemic infectious respiratory disease exhibiting seasonal flare-ups. Therefore, despite the unprecedented rally to reach a vaccine that can offer widespread immunization, it is equally important to reach effective prevention and treatment regimens for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Contributing to this effort, we have curated and analyzed multi-source and multi-omics publicly available data from patients, cell lines and databases in order to fuel a multiplex computational drug repurposing approach. We devised a network-based integration of multi-omic data to prioritize the most important genes related to COVID-19 and subsequently re-rank the identified candidate drugs. Our approach resulted in a highly informed integrated drug shortlist by combining structural diversity filtering along with experts' curation and drug-target mapping on the depicted molecular pathways. In addition to the recently proposed drugs that are already generating promising results such as dexamethasone and remdesivir, our list includes inhibitors of Src tyrosine kinase (bosutinib, dasatinib, cytarabine and saracatinib), which appear to be involved in multiple COVID-19 pathophysiological mechanisms. In addition, we highlight specific immunomodulators and anti-inflammatory drugs like dactolisib and methotrexate and inhibitors of histone deacetylase like hydroquinone and vorinostat with potential beneficial effects in their mechanisms of action. Overall, this multiplex drug repurposing approach, developed and utilized herein specifically for SARS-CoV-2, can offer a rapid mapping and drug prioritization against any pathogen-related disease.
Keywords: COVID-19; multi-omics integrative analysis; multiplex drug repurposing.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Structure-based drug repurposing against COVID-19 and emerging infectious diseases: methods, resources and discoveries.Brief Bioinform. 2021 Nov 5;22(6):bbab113. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbab113. Brief Bioinform. 2021. PMID: 33993214 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of potential pan-coronavirus therapies using a computational drug repurposing platform.Methods. 2022 Jul;203:214-225. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2021.11.002. Epub 2021 Nov 9. Methods. 2022. PMID: 34767922 Free PMC article.
-
Repurposing novel therapeutic candidate drugs for coronavirus disease-19 based on protein-protein interaction network analysis.BMC Biotechnol. 2021 Mar 12;21(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s12896-021-00680-z. BMC Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33711981 Free PMC article.
-
Drug repurposing approach to combating coronavirus: Potential drugs and drug targets.Med Res Rev. 2021 May;41(3):1375-1426. doi: 10.1002/med.21763. Epub 2020 Dec 5. Med Res Rev. 2021. PMID: 33277927 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Repositioning of Drugs to Counter COVID-19 Pandemic - An Insight.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2021;22(2):192-199. doi: 10.2174/1389201021999200820155927. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 32867651 Review.
Cited by
-
Inflammatory activation and immune cell infiltration are main biological characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 infected myocardium.Bioengineered. 2022 Feb;13(2):2486-2497. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2014621. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35037831 Free PMC article.
-
Saracatinib prompts hemin-induced K562 erythroid differentiation but suppresses erythropoiesis of hematopoietic stem cells.Hum Cell. 2024 May;37(3):648-665. doi: 10.1007/s13577-024-01034-5. Epub 2024 Feb 22. Hum Cell. 2024. PMID: 38388899 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating transcriptomics and network analysis-based multiplexed drug repurposing to screen drug candidates for M2 macrophage-associated castration-resistant prostate cancer bone metastases.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 26;13:989972. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.989972. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36389722 Free PMC article.
-
Vir2Drug: a drug repurposing framework based on protein similarities between pathogens.Brief Bioinform. 2023 Jan 19;24(1):bbac536. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbac536. Brief Bioinform. 2023. PMID: 36513376 Free PMC article.
-
Multiomics integration-based molecular characterizations of COVID-19.Brief Bioinform. 2022 Jan 17;23(1):bbab485. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbab485. Brief Bioinform. 2022. PMID: 34864875 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pushpakom S, Iorio F, Eyers PA, et al. . Drug repurposing: Progress, challenges and recommendations. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2018;18:41–58. - PubMed
-
- Zhou S, Wang Y, Zhu T, et al. . CT Features of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Pneumonia in 62 Patients in Wuhan, China. Am J Roentgenol 2020;214:1287–94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

