Risk Factors for Major Amputation in Diabetic Foot Ulcer Patients
- PMID: 33976562
- PMCID: PMC8106455
- DOI: 10.2147/DMSO.S307815
Risk Factors for Major Amputation in Diabetic Foot Ulcer Patients
Abstract
Background: The purpose of our study was to identify the new and the more specific risk factors for major amputation in patients with diabetic foot ulcer (DFU).
Methods: We used data from the Electronic Medical Record (EMR) database of our hospital from February 2014 to July 2020. Patients with DFU and amputation were included in the study. The logistic regression model was adjusted for demographic characteristics and related comorbidities between major and minor amputation groups.
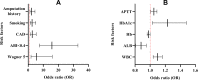
Results: Among 3654 patients with DFU, 363 (9.9%) were amputated. Patients with major versus minor amputation, in multivariable logistic regression models, major amputation independent factors included previous amputation history (odds ratio [OR] 2.31 [95% CI 1.17-4.53], p = 0.02), smoking (2.58 [1.31-5.07], p = 0.01), coronary artery disease (CAD) (2.67 [1.35-5.29], p = 0.03), ankle brachial index (ABI) <0.4 (15.77 [7.51-33.13], p < 0.01), Wagner 5 (5.50 [1.89-16.01], p < 0.01), activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT) (1.23 [1.03-1.48], p = 0.01), glycosylated hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) (1.23 [1.03-1.48], p = 0.03), hemoglobin (Hb) (0.98 [0.96-1.00], p = 0.01), plasma albumin (ALB) (0.88 [0.81-0.95], p < 0.01) and white blood cell (WBC) (1.10 [1.04-1.16], p < 0.01).
Conclusion: Major amputation was associated with previous amputation history, smoking, CAD, Wagner 5, ABI <0.4, HbA1c, Hb, ALB, WBC, and APTT might be a new independent factor. In view of these factors, early prevention and guidance promptly orientated by multidisciplinary is of great significance to reduce the disability rate and economic burden.
Keywords: diabetic foot ulcers; major amputation; minor amputation; retrospective analysis; risk factors.
© 2021 Lu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical characteristics and risk factors of lower extremity amputation in the diabetic inpatients with foot ulcers.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Mar 31;14:1144806. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1144806. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37065766 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiology of type 2 diabetic foot problems and predictive factors for amputation in China.Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2015 Mar;14(1):19-27. doi: 10.1177/1534734614564867. Epub 2015 Jan 8. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2015. PMID: 25573978
-
[Incidence and risk factors of amputation among inpatients with diabetic foot].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2012 Jun 26;92(24):1686-9. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 22944159 Chinese.
-
Prognostic Factors for Lower Extremity Amputation in Diabetic Foot Ulcer Patients.J Acute Med. 2019 Jun 1;9(2):59-63. doi: 10.6705/j.jacme.201906_9(2).0003. J Acute Med. 2019. PMID: 32995232 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical characteristics and risk factors of lower extremity amputation in patients with diabetic foot.Pak J Med Sci. 2022 Nov-Dec;38(8):2253-2258. doi: 10.12669/pjms.38.8.5635. Pak J Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 36415262 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Risk Prediction of Diabetic Foot Amputation Using Machine Learning and Explainable Artificial Intelligence.J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2024 Jan 30:19322968241228606. doi: 10.1177/19322968241228606. Online ahead of print. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2024. PMID: 38288696 Free PMC article.
-
Cognitive dysfunction in diabetes-related foot complications: A cohort study.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2024 Jan 22;23(1):1017-1038. doi: 10.1007/s40200-023-01381-4. eCollection 2024 Jun. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2024. PMID: 38932904 Free PMC article.
-
Multimodal Identification of Molecular Factors Linked to Severe Diabetic Foot Ulcers Using Artificial Intelligence.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 4;25(19):10686. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910686. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39409014 Free PMC article.
-
New Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches in Diabetic Microvascular Complications.Biomedicines. 2024 Aug 15;12(8):1858. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12081858. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39200322 Free PMC article.
-
Association between tissue loss type and amputation risk among Medicare patients with concomitant diabetes and peripheral arterial disease.J Vasc Surg. 2024 Nov;80(5):1543-1552.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2024.06.019. Epub 2024 Jun 14. J Vasc Surg. 2024. PMID: 38880181
References
-
- IDF Diabetes Atlas. Ninth edition 2019. International Diabetes Federation; 2019. Available from: http://www.diabetesatlas.org. Accessed April19, 2021.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous