Nitric Oxide as a Target for Phytochemicals in Anti-Neuroinflammatory Prevention Therapy
- PMID: 33946349
- PMCID: PMC8124914
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22094771
Nitric Oxide as a Target for Phytochemicals in Anti-Neuroinflammatory Prevention Therapy
Abstract
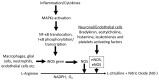
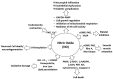
Nitric oxide (NO) is a neurotransmitter that mediates the activation and inhibition of inflammatory cascades. Even though physiological NO is required for defense against various pathogens, excessive NO can trigger inflammatory signaling and cell death through reactive nitrogen species-induced oxidative stress. Excessive NO production by activated microglial cells is specifically associated with neuroinflammatory and neurodegenerative conditions, such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, ischemia, hypoxia, multiple sclerosis, and other afflictions of the central nervous system (CNS). Therefore, controlling excessive NO production is a desirable therapeutic strategy for managing various neuroinflammatory disorders. Recently, phytochemicals have attracted considerable attention because of their potential to counteract excessive NO production in CNS disorders. Moreover, phytochemicals and nutraceuticals are typically safe and effective. In this review, we discuss the mechanisms of NO production and its involvement in various neurological disorders, and we revisit a number of recently identified phytochemicals which may act as NO inhibitors. This review may help identify novel potent anti-inflammatory agents that can downregulate NO, specifically during neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration.
Keywords: medicinal plants; neurodegeneration; neuroinflammation; nitric oxide; phytochemicals; plants derivatives; reactive nitrogen species.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phytochemicals targeting nitric oxide signaling in neurodegenerative diseases.Nitric Oxide. 2023 Jan 1;130:1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2022.11.001. Epub 2022 Nov 11. Nitric Oxide. 2023. PMID: 36375788 Review.
-
Uncovering potential anti-neuroinflammatory components of Modified Wuziyanzong Prescription through a target-directed molecular docking fingerprint strategy.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2018 Jul 15;156:328-339. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2018.05.001. Epub 2018 May 1. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2018. PMID: 29758494
-
Dual effects of antioxidants in neurodegeneration: direct neuroprotection against oxidative stress and indirect protection via suppression of glia-mediated inflammation.Curr Pharm Des. 2006;12(27):3521-33. doi: 10.2174/138161206778343109. Curr Pharm Des. 2006. PMID: 17017945 Review.
-
Phytochemicals as Substances that Affect Astrogliosis and their Implications for the Management of Neurodegenerative Diseases.Curr Med Chem. 2024;31(34):5550-5566. doi: 10.2174/0929867330666230504121523. Curr Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 37143267 Review.
-
Connection between Systemic Inflammation and Neuroinflammation Underlies Neuroprotective Mechanism of Several Phytochemicals in Neurodegenerative Diseases.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018 Oct 8;2018:1972714. doi: 10.1155/2018/1972714. eCollection 2018. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018. PMID: 30402203 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Antioxidant Activity of Urtica dioica: An Important Property Contributing to Multiple Biological Activities.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Dec 19;11(12):2494. doi: 10.3390/antiox11122494. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36552702 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discovery of dibenzylbutane lignan LCA derivatives as potent anti-inflammatory agents.RSC Med Chem. 2024 Apr 23;15(6):2114-2126. doi: 10.1039/d4md00053f. eCollection 2024 Jun 19. RSC Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38911165
-
Glycyrrhizae Radix suppresses lipopolysaccharide- and diazepam-induced nerve inflammation in the hippocampus, and contracts the duration of pentobarbital- induced loss of righting reflex in a mouse model.J Nat Med. 2023 Jun;77(3):561-571. doi: 10.1007/s11418-023-01700-2. Epub 2023 Apr 28. J Nat Med. 2023. PMID: 37115471
-
Force-Induced Nitric Oxide Promotes Osteogenic Activity during Orthodontic Tooth Movement in Mice.Stem Cells Int. 2022 Sep 6;2022:4775445. doi: 10.1155/2022/4775445. eCollection 2022. Stem Cells Int. 2022. PMID: 36110889 Free PMC article.
-
Ancient Chinese Herbal Recipe Huanglian Jie Du Decoction for Ischemic Stroke: An Overview of Current Evidence.Aging Dis. 2022 Dec 1;13(6):1733-1744. doi: 10.14336/AD.2022.0311. eCollection 2022 Dec 1. Aging Dis. 2022. PMID: 36465168 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

