Clinical outcomes in patients with Philadelphia chromosome-positive leukemia treated with ponatinib in routine clinical practice-data from a Belgian registry
- PMID: 33942128
- PMCID: PMC8195783
- DOI: 10.1007/s00277-021-04507-x
Clinical outcomes in patients with Philadelphia chromosome-positive leukemia treated with ponatinib in routine clinical practice-data from a Belgian registry
Abstract
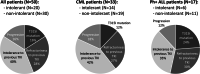
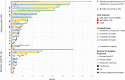
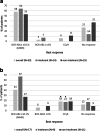
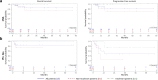
Data on clinical use of ponatinib are limited. This prospective registry aimed to evaluate outcomes of ponatinib treatment in routine practice over 3 years (2016-2019) in Belgium (NCT03678454). Patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) or Philadelphia chromosome-positive (Ph+) acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) were treated with ponatinib per current label. Fifty patients (33 CML and 17 Ph+ ALL) were enrolled. Fifty-five percent of CML and 29% of Ph+ ALL patients had received ≥3 prior tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs). Reasons for starting ponatinib were intolerance (40%), relapse or refractoriness (28%) to previous TKIs, progression (16%), or T315I mutation (16%). Median follow-up was 15 months for CML and 4.5 months for Ph+ ALL patients. Best response was a major molecular response in 58% of CML and 41% of Ph+ ALL patients. Of 20 patients who started ponatinib due to intolerance to previous TKIs, 9 (64%) CML and 4 (67%) Ph+ ALL achieved a major molecular response. Three-year estimates of overall survival were 85.3% and 85.6%, respectively, in CML and Ph+ ALL patients; estimated progression-free survival was 81.6% and 48.9%. Adverse reactions were reported in 34 patients (68%); rash (26%) and dry skin (10%) were most common. Reported cardiovascular adverse reactions included vascular stenosis (3), arterial hypertension (2), chest pain (1), palpitations (1), and vascular occlusion (1). This Belgian registry confirms results from the PACE clinical trial and supports routine ponatinib use in CML and Ph+ ALL patients who are resistant or intolerant to previous TKIs or with the T315I mutation.
Keywords: Chronic myeloid leukemia; Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia; Ponatinib; Registry; Routine clinical practice.
Conflict of interest statement
KT reports membership of advisory boards from multiple pharmaceutical companies. BB reports research funding from Incyte Biosciences Benelux BV. ADB reports ad hoc membership of advisory boards from multiple pharmaceutical companies. DD reports consultancy, honoraria, membership of Board of Directors or advisory committees, and research funding from multiple pharmaceutical companies. DS reports consultancy and travel expenses from Incyte Biosciences Benelux BV. JB and MB are employees of Incyte Biosciences. There are no relationships to disclose for TD, VH, SM, FSB, AG, GV, HV, NG, PL, KVE, MJ, AT, IV, and DM.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ponatinib: A new tyrosine kinase inhibitor for the treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia and Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Ann Pharmacother. 2013 Nov;47(11):1540-6. doi: 10.1177/1060028013501144. Epub 2013 Nov 21. Ann Pharmacother. 2013. PMID: 24265264 Review.
-
Ponatinib in the Treatment of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia and Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Acute Leukemia: Recommendations of a German Expert Consensus Panel with Focus on Cardiovascular Management.Acta Haematol. 2020;143(3):217-231. doi: 10.1159/000501927. Epub 2019 Oct 7. Acta Haematol. 2020. PMID: 31590170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ponatinib: a review of its use in adults with chronic myeloid leukaemia or Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukaemia.Drugs. 2014 May;74(7):793-806. doi: 10.1007/s40265-014-0216-6. Drugs. 2014. PMID: 24807266 Review.
-
A phase 2 trial of ponatinib in Philadelphia chromosome-positive leukemias.N Engl J Med. 2013 Nov 7;369(19):1783-96. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1306494. Epub 2013 Nov 1. N Engl J Med. 2013. PMID: 24180494 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Ponatinib in refractory Philadelphia chromosome-positive leukemias.N Engl J Med. 2012 Nov 29;367(22):2075-88. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1205127. N Engl J Med. 2012. PMID: 23190221 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Ponatinib as a Prophylactic or Pre-Emptive Strategy to Prevent Cytological Relapse after Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation in Patients with Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Transplanted in Complete Cytological Remission.Cancers (Basel). 2024 May 31;16(11):2108. doi: 10.3390/cancers16112108. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38893226 Free PMC article.
-
Ponatinib-Induced Cerebrovascular Accident (CVA).Cureus. 2022 Dec 10;14(12):e32383. doi: 10.7759/cureus.32383. eCollection 2022 Dec. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36632247 Free PMC article.
-
The proteolysis targeting chimera GMB-475 combined with dasatinib for the treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia with BCR::ABL1 mutants.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Oct 3;13:931772. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.931772. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36263131 Free PMC article.
-
Toxicity of targeted anticancer treatments on the liver in myeloproliferative neoplasms.World J Hepatol. 2023 Sep 27;15(9):1021-1032. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v15.i9.1021. World J Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 37900211 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Management of chronic myeloid leukemia in 2023 - common ground and common sense.Blood Cancer J. 2023 Apr 24;13(1):58. doi: 10.1038/s41408-023-00823-9. Blood Cancer J. 2023. PMID: 37088793 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hochhaus A, Baccarani M, Silver RT, Schiffer C, Apperley JF, Cervantes F, Clark RE, Cortes JE, Deininger MW, Guilhot F, Hjorth-Hansen H, Hughes TP, Janssen J, Kantarjian HM, Kim DW, Larson RA, Lipton JH, Mahon FX, Mayer J, Nicolini F, Niederwieser D, Pane F, Radich JP, Rea D, Richter J, Rosti G, Rousselot P, Saglio G, Saußele S, Soverini S, Steegmann JL, Turkina A, Zaritskey A, Hehlmann R. European LeukemiaNet 2020 recommendations for treating chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 2020;34(4):966–984. doi: 10.1038/s41375-020-0776-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

