Locoregional Combined With Systemic Therapies for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: An Inevitable Trend of Rapid Development
- PMID: 33928118
- PMCID: PMC8076864
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.635243
Locoregional Combined With Systemic Therapies for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: An Inevitable Trend of Rapid Development
Abstract
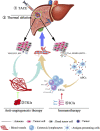
Despite the application of antiviral drugs and improved surveillance tools, the number of patients diagnosed with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) at an advanced stage and with a dismal prognosis is still on the rise. Systemic treatment with multiple multitargeted tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), such as sorafenib, has been a widely utilized approach for a decade. In addition, the use of a combination of TKIs with other types of compounds, including immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) and antiangiogenic inhibitors, has shown efficacy in treating advanced HCC. However, the presence of intolerable adverse events, low disease response and control rates, and relative short overall survival of such combinatory therapies makes novel or optimized therapies for advance HCC urgently needed. Locoregional therapy (transarterial chemoembolization, and thermal ablation) can destroy primary tumors and decrease tumor burden and is widely used for HCC management. This type of treatment modality can result in local hypoxia and increased vascular permeability, inducing immunogenic effects by releasing tumor antigens from dying cancer cells and producing damage-associated molecular patterns that facilitate antiangiogenic therapy and antitumor immunity. The combination of systemic and locoregional therapies may further produce synergistic effects without overlapping toxicity that can improve prognoses for advanced HCC. In preliminary studies, several combinations of therapeutic modes exhibited promising levels of safety, feasibility, and antitumor effects in a clinical setting and have, thus, garnered much attention. This review aims to provide a comprehensive, up-to-date overview of the underlying mechanisms of combined systemic and locoregional therapies in the treatment of advanced HCC, commenting on both their current status and future direction.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma; immune checkpoint inhibitors; thermal ablation; transarterial chemoembolization; tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
Copyright © 2021 Li, Wang, Ye and Liang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Emerging Opportunities for Combining Locoregional Therapy with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Curr Oncol Rep. 2020 Jun 29;22(8):76. doi: 10.1007/s11912-020-00943-6. Curr Oncol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32596779 Review.
-
New insights into mechanisms and interventions of locoregional therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma.Chin J Cancer Res. 2024 Apr 30;36(2):167-194. doi: 10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2024.02.06. Chin J Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38751435 Free PMC article.
-
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Monotherapies and Combined Therapies.Front Oncol. 2022 Jun 16;12:898964. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.898964. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35785169 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A multidisciplinary approach with immunotherapies for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma.J Liver Cancer. 2023 Sep;23(2):316-329. doi: 10.17998/jlc.2023.09.04. Epub 2023 Sep 22. J Liver Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37743048 Free PMC article.
-
Combination Therapy of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors with Locoregional Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Oct 20;15(20):5072. doi: 10.3390/cancers15205072. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37894439 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Combination therapies for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a beacon of light or a castle in the air.Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2022 Aug;11(4):629-631. doi: 10.21037/hbsn-2022-12. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2022. PMID: 36016739 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
A combination of locoregional treatment with systemic therapy after atezolizumab plus bevacizumab failure for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma provides survival benefit.Am J Cancer Res. 2023 Nov 15;13(11):5482-5492. eCollection 2023. Am J Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 38058809 Free PMC article.
-
Initial Incomplete Thermal Ablation Is Associated With a High Risk of Tumor Progression in Patients With Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2021 Oct 18;11:760173. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.760173. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34733792 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Predictors of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression and Dropout in Patients in Liver Transplantation Waiting List.Transplant Direct. 2022 Oct 18;8(11):e1365. doi: 10.1097/TXD.0000000000001365. eCollection 2022 Nov. Transplant Direct. 2022. PMID: 36284930 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated Analysis of Angiogenesis-Mediated Tumor Immune Microenvironment Pattern in Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) and a Novel Prognostic Model Construction to Predict Patient Outcome.Med Sci Monit. 2021 Dec 13;27:e934937. doi: 10.12659/MSM.934937. Med Sci Monit. 2021. PMID: 34897268 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

