Efficacy and safety of crizotinib plus bevacizumab in ALK/ROS-1/c-MET positive non-small cell lung cancer: an open-label, single-arm, prospective observational study
- PMID: 33841676
- PMCID: PMC8014364
Efficacy and safety of crizotinib plus bevacizumab in ALK/ROS-1/c-MET positive non-small cell lung cancer: an open-label, single-arm, prospective observational study
Abstract
Background: Crizotinib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) effective in ALK/ROS-1/c-MET positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. Bevacizumab is an antiangiogenic monoclonal antibody, and improves clinical benefit of NSCLC in combination with EGFR-TKIs or chemotherapy. However, the efficacy and safety of crizotinib plus bevacizumab in treating naive ALK/ROS-1/c-MET positive NSCLC patients have not been studied.
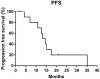
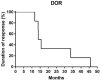
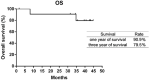
Methods: In this open-label, single-arm, prospective observational study, locally advanced or metastatic ALK rearrangement/ROS-1 fusion/c-MET amplification NSCLC patients were treated with crizotinib (250 mg orally twice daily) and bevacizumab (7.5 mg/kg intravenous every three weeks) until disease progression or intolerant toxicity or death. Primary end point was progressive free survival (PFS), secondary end points were duration of response (DOR), overall response rate (ORR), disease control rate (DCR) and safety. Patients receiving ≥1 cycle of treatment were evaluated.
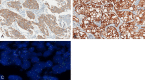
Findings: Fourteen patients were eligible for analyzing between June 2016 and October 2017. There were 12 patients with ALK rearrangement, 1 patient with ROS-1 fusion, and 1 patient with c-MET amplification. The median follow-up time was 42.8 months. The median PFS and DOR of the patients with ALK rearrangement were 13.9 and 14.8 months respectively. Of the 12 patients, 7 gained partial response, 5 gained stable disease. The ORR and DCR were 58.3% and 100%. The PFS were 12.9 months and 1.9 months for patient with ROS-1 fusion or c-MET amplification. The most two common treatment-related adverse events were fatigue (28.6%) and rash (21.4%). 3 patients discontinued therapy because of liver damage or hemoptysis.
Interpretation: This study demonstrated that crizotinib plus bevacizumab showed benefit in treating naive ALK rearrangement NSCLC patients, and the toxicity was relatively tolerant. Our results suggested that crizotinib plus bevacizumab might be a promising treatment strategy in ALK/ROS-1/c-MET positive NSCLC patients.
Keywords: ALK; Crizotinib; ROS-1; bevacizumab; brain metastasis; c-MET.
AJTR Copyright © 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Iruplinalkib (WX-0593) Versus Crizotinib in ALK TKI-Naive Locally Advanced or Metastatic ALK-Positive NSCLC: Interim Analysis of a Randomized, Open-Label, Phase 3 Study (INSPIRE).J Thorac Oncol. 2024 Jun;19(6):912-927. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2024.01.013. Epub 2024 Jan 25. J Thorac Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38280448 Clinical Trial.
-
The tyrosine kinase inhibitor crizotinib does not have clinically meaningful activity in heavily pre-treated patients with advanced alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma with FOXO rearrangement: European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer phase 2 trial 90101 'CREATE'.Eur J Cancer. 2018 May;94:156-167. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2018.02.011. Epub 2018 Mar 20. Eur J Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29567632 Clinical Trial.
-
Crizotinib with or without an EGFR-TKI in treating EGFR-mutant NSCLC patients with acquired MET amplification after failure of EGFR-TKI therapy: a multicenter retrospective study.J Transl Med. 2019 Feb 21;17(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s12967-019-1803-9. J Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 30791921 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted therapy for advanced anaplastic lymphoma kinase (<I>ALK</I>)-rearranged non-small cell lung cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jan 7;1(1):CD013453. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013453.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 34994987 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment Optimization for Brain Metastasis from Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Rearrangement Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer.Oncol Res Treat. 2019;42(11):599-606. doi: 10.1159/000502755. Epub 2019 Sep 17. Oncol Res Treat. 2019. PMID: 31527380 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Landscape of ALK-Rearranged Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Comprehensive Review of Clinicopathologic, Genomic Characteristics, and Therapeutic Perspectives.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Sep 29;14(19):4765. doi: 10.3390/cancers14194765. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36230686 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein posttranslational modifications in health and diseases: Functions, regulatory mechanisms, and therapeutic implications.MedComm (2020). 2023 May 2;4(3):e261. doi: 10.1002/mco2.261. eCollection 2023 Jun. MedComm (2020). 2023. PMID: 37143582 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cutting-Edge Therapies for Lung Cancer.Cells. 2024 Mar 1;13(5):436. doi: 10.3390/cells13050436. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38474400 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genomic Profiling Identifies Putative Pathogenic Alterations in NSCLC Brain Metastases.JTO Clin Res Rep. 2022 Nov 11;3(12):100435. doi: 10.1016/j.jtocrr.2022.100435. eCollection 2022 Dec. JTO Clin Res Rep. 2022. PMID: 36561283 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Angiogenic Therapy in ALK Rearranged Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC).Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 9;23(16):8863. doi: 10.3390/ijms23168863. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36012123 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ettinger DS, Akerley W, Bepler G, Blum MG, Chang A, Cheney RT, Chirieac LR, D’Amico TA, Demmy TL, Ganti AK, Govindan R, Grannis FW Jr, Jahan T, Jahanzeb M, Johnson DH, Kessinger A, Komaki R, Kong FM, Kris MG, Krug LM, Le QT, Lennes IT, Martins R, O’Malley J, Osarogiagbon RU, Otterson GA, Patel JD, Pisters KM, Reckamp K, Riely GJ, Rohren E, Simon GR, Swanson SJ, Wood DE, Yang SC Members NN-SCLCP. Non-small cell lung cancer. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2010;8:740–801. - PubMed
-
- Sequist LV, Heist RS, Shaw AT, Fidias P, Rosovsky R, Temel JS, Lennes IT, Digumarthy S, Waltman BA, Bast E, Tammireddy S, Morrissey L, Muzikansky A, Goldberg SB, Gainor J, Channick CL, Wain JC, Gaissert H, Donahue DM, Muniappan A, Wright C, Willers H, Mathisen DJ, Choi NC, Baselga J, Lynch TJ, Ellisen LW, Mino-Kenudson M, Lanuti M, Borger DR, Iafrate AJ, Engelman JA, Dias-Santagata D. Implementing multiplexed genotyping of non-small-cell lung cancers into routine clinical practice. Ann Oncol. 2011;22:2616–2624. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Choi YL, Takeuchi K, Soda M, Inamura K, Togashi Y, Hatano S, Enomoto M, Hamada T, Haruta H, Watanabe H, Kurashina K, Hatanaka H, Ueno T, Takada S, Yamashita Y, Sugiyama Y, Ishikawa Y, Mano H. Identification of novel isoforms of the EML4-ALK transforming gene in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2008;68:4971–4976. - PubMed
-
- Rikova K, Guo A, Zeng Q, Possemato A, Yu J, Haack H, Nardone J, Lee K, Reeves C, Li Y, Hu Y, Tan Z, Stokes M, Sullivan L, Mitchell J, Wetzel R, Macneill J, Ren JM, Yuan J, Bakalarski CE, Villen J, Kornhauser JM, Smith B, Li D, Zhou X, Gygi SP, Gu TL, Polakiewicz RD, Rush J, Comb MJ. Global survey of phosphotyrosine signaling identifies oncogenic kinases in lung cancer. Cell. 2007;131:1190–1203. - PubMed
-
- Takeuchi K, Soda M, Togashi Y, Suzuki R, Sakata S, Hatano S, Asaka R, Hamanaka W, Ninomiya H, Uehara H, Lim Choi Y, Satoh Y, Okumura S, Nakagawa K, Mano H, Ishikawa Y. RET, ROS1 and ALK fusions in lung cancer. Nat Med. 2012;18:378–381. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
