Fourteen-day survival among older adults with severe infection with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 treated with corticosteroid: a cohort study
- PMID: 33819571
- PMCID: PMC8016731
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmi.2021.03.021
Fourteen-day survival among older adults with severe infection with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 treated with corticosteroid: a cohort study
Abstract
Objective: To assess the effectiveness of corticosteroids among older adults with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pneumonia requiring oxygen.
Methods: We used routine care data from 36 hospitals in France and Luxembourg to assess the effectiveness of corticosteroids with at least 0.4 mg/kg/day equivalent prednisone (treatment group) versus standard of care (control group). Participants were adults aged 80 years or older with PCR-confirmed severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection or CT scan images typical of COVID-19 pneumonia, requiring oxygen ≥3 L/min, and with an inflammatory syndrome (C-reactive protein ≥40 mg/L). The primary outcome was overall survival at day 14. In our main analysis, characteristics of patients at baseline (i.e. time when patients met all inclusion criteria) were balanced by using propensity-score inverse probability of treatment weighting.
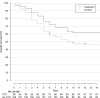
Results: Among the 267 patients included in the analysis, 98 were assigned to the treatment group. Their median age was 86 years (interquartile range 83-90 years) and 95% had a SARS-CoV-2 PCR-confirmed diagnosis. In total, 43/98 (43.9%) patients in the treatment group and 84/166 (50.6%) in the control group died before day 14 (weighted hazard ratio 0.67, 95% CI 0.46-0.99). The treatment and control groups did not differ significantly for the proportion of patients discharged to home/rehabilitation at day 14 (weighted relative risk 1.12, 95% CI 0.68-1.82). Twenty-two (16.7%) patients receiving corticosteroids developed adverse events, but only 11 (6.4%) from the control group.
Conclusions: Corticosteroids were associated with a significant increase in the overall survival at day 14 of patients aged 80 years and older hospitalized for severe COVID-19.
Keywords: Coronavirus disease 2019; Corticosteroids; Elderly; Observational study; Therapeutic evaluation.
Copyright © 2021. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Corticosteroids in patients hospitalized for COVID-19 pneumonia who require oxygen: observational comparative study using routine care data.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2021 Apr;27(4):603-610. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2020.11.035. Epub 2020 Dec 8. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2021. PMID: 33301928 Free PMC article.
-
Testing the efficacy and safety of BIO101, for the prevention of respiratory deterioration, in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia (COVA study): a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2021 Jan 11;22(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04998-5. Trials. 2021. PMID: 33430924 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of corticosteroid treatment for hospitalized patients with severe COVID-19: a multicentre study.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2021 Jan;27(1):105-111. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2020.09.014. Epub 2020 Sep 22. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2021. PMID: 32971254 Free PMC article.
-
Intramuscular versus oral corticosteroids to reduce relapses following discharge from the emergency department for acute asthma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jun 2;6(6):CD012629. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012629.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29859017 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Corticosteroid administration for viral pneumonia: COVID-19 and beyond.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2020 Sep;26(9):1171-1177. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2020.06.020. Epub 2020 Jun 27. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2020. PMID: 32603802 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of corticosteroid therapy on mortality in COVID-19 patients-A systematic review and meta-analysis.Rev Med Virol. 2022 Sep;32(5):e2386. doi: 10.1002/rmv.2386. Epub 2022 Aug 15. Rev Med Virol. 2022. PMID: 35971278 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Corticosteroid Therapy in COVID-19 Associated With In-hospital Mortality in Geriatric Patients: A Propensity Matched Cohort Study.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2022 Jul 5;77(7):1352-1360. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glac084. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 35395678 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of corticosteroid regimens for the treatment of hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a meta-analysis.Future Virol. 2022 Jul;17(7):463-489. doi: 10.2217/fvl-2021-0244. Epub 2022 Jun 3. Future Virol. 2022. PMID: 35814934 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Caring for older adults during the COVID-19 pandemic.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2022 Jun;28(6):785-791. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2022.02.040. Epub 2022 Mar 11. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2022. PMID: 35283306 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reporting of Observational Studies Explicitly Aiming to Emulate Randomized Trials: A Systematic Review.JAMA Netw Open. 2023 Sep 5;6(9):e2336023. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.36023. JAMA Netw Open. 2023. PMID: 37755828 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Angus D.C., Derde L., Al-Beidh F., Annane D., Arabi Y., Beane A. Effect of hydrocortisone on mortality and organ support in patients with severe COVID-19: the REMAP-CAP COVID-19 Corticosteroid Domain Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2020;324:1317–1329. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.17022. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tomazini B.M., Maia I.S., Cavalcanti A.B., Berwanger O., Rosa R.G., Veiga V.C. Effect of dexamethasone on days alive and ventilator-free in patients with moderate or severe acute respiratory distress syndrome and COVID-19: the CoDEX Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2020;324:1307–1316. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.17021. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tran V.-T., Mahévas M., Bani-Sadr F., Robineau O., Perpoint O., Perrodeau E. Corticosteroids in patients hospitalized for COVID-19 pneumonia who require oxygen: observational comparative study using routine care data. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2020;27:603–610. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2020.11.035. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous