Intravitreal Polymeric Nanocarriers with Long Ocular Retention and Targeted Delivery to the Retina and Optic Nerve Head Region
- PMID: 33810242
- PMCID: PMC8066548
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13040445
Intravitreal Polymeric Nanocarriers with Long Ocular Retention and Targeted Delivery to the Retina and Optic Nerve Head Region
Abstract
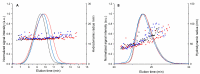
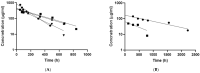
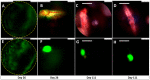
Posterior eye tissues, such as retina, are affected in many serious eye diseases, but drug delivery to these targets is challenging due to various anatomical eye barriers. Intravitreal injections are widely used, but the intervals between invasive injections should be prolonged. We synthesized and characterized (1H NMR, gel permeation chromatography) block copolymers of poly(ethylene glycol), poly(caprolactone), and trimethylene carbonate. These polymers self-assembled to polymersomes and polymeric micelles. The mean diameters of polymersomes and polymeric micelles, about 100 nm and 30-50 nm, respectively, were obtained with dynamic light scattering. Based on single particle tracking and asymmetric flow field-flow fractionation, the polymeric micelles and polymersomes were stable and diffusible in the vitreous. The materials did not show cellular toxicity in cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells in the Alamar Blue Assay. Pharmacokinetics of the intravitreal nanocarriers in the rabbits were evaluated using in vivo fluorophotometry. The half-lives of the polymersomes (100 nm) and the micelles (30 nm) were 11.4-32.7 days and 4.3-9.5 days. The intravitreal clearance values were 1.7-8.7 µL/h and 3.6-5.4 µL/h for polymersomes and polymeric micelles, respectively. Apparent volumes of distribution of the particles in the rabbit vitreous were 0.6-1.3 mL for polymeric micelles and 1.9-3.4 mL for polymersomes. Polymersomes were found in the vitreous for at least 92 days post-dosing. Furthermore, fundus imaging revealed that the polymersomes accumulated near the optic nerve and retained there even at 111 days post-injection. Polymersomes represent a promising technology for controlled and site-specific drug delivery in the posterior eye segment.
Keywords: drug delivery; intravitreal; optic nerve; polymeric micelle; polymersome; retina.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
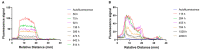
Similar articles
-
Ocular biocompatibility and tolerance study of biodegradable polymeric micelles in the rabbit eye.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2013 Dec 1;112:30-4. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2013.06.047. Epub 2013 Jul 24. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2013. PMID: 23939422
-
Docetaxel-Loaded Mixed Micelles and Polymersomes Composed of Poly (caprolactone)-Poly (ethylene glycol) (PEG-PCL) and Poly (lactic acid)-Poly (ethylene glycol) (PEG-PLA): Preparation and In-vitro Characterization.Iran J Pharm Res. 2019 Winter;18(1):142-155. Iran J Pharm Res. 2019. PMID: 31089351 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Drug and Gene Delivery Using Random Cationic Copolymers Forming Stable and pH-Sensitive Polymersomes.Macromol Biosci. 2017 Apr;17(4). doi: 10.1002/mabi.201600324. Epub 2016 Nov 23. Macromol Biosci. 2017. PMID: 27879056
-
Advanced drug and gene delivery systems based on functional biodegradable polycarbonates and copolymers.J Control Release. 2014 Sep 28;190:398-414. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2014.05.023. Epub 2014 May 21. J Control Release. 2014. PMID: 24858708 Review.
-
Multicompartment Polymeric Nanocarriers for Biomedical Applications.Macromol Rapid Commun. 2020 Sep;41(18):e2000298. doi: 10.1002/marc.202000298. Epub 2020 Jul 19. Macromol Rapid Commun. 2020. PMID: 32686228 Review.
Cited by
-
Review on the Scale-Up Methods for the Preparation of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Sep 6;14(9):1886. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14091886. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36145632 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Naringenin Nanosuspension: In Vitro and In Vivo Anti-Osteoporotic Studies.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Jul 11;14(7):1449. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14071449. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35890343 Free PMC article.
-
Fast-Fed Variability: Insights into Drug Delivery, Molecular Manifestations, and Regulatory Aspects.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Aug 27;14(9):1807. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14091807. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36145555 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overcoming Treatment Challenges in Posterior Segment Diseases with Biodegradable Nano-Based Drug Delivery Systems.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Mar 29;15(4):1094. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15041094. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37111579 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hyaluronic acid-based nanoparticles to deliver drugs to the ocular posterior segment.Drug Deliv. 2023 Dec;30(1):2204206. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2023.2204206. Drug Deliv. 2023. PMID: 37194147 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mishima S. Clinical pharmacokinetics of the eye. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1981;21:504–541. - PubMed
-
- Intravitreal Injections—Frequently Asked Questions. [(accessed on 25 March 2021)]; Available online: https://retinavitreous.com/treatments/intravitreal_injections.php.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

