Wnt Inhibition Sensitizes PD-L1 Blockade Therapy by Overcoming Bone Marrow-Derived Myofibroblasts-Mediated Immune Resistance in Tumors
- PMID: 33790893
- PMCID: PMC8006364
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.619209
Wnt Inhibition Sensitizes PD-L1 Blockade Therapy by Overcoming Bone Marrow-Derived Myofibroblasts-Mediated Immune Resistance in Tumors
Abstract
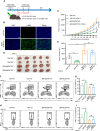
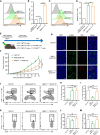
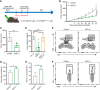
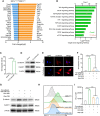
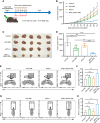
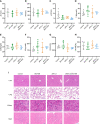
Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) has been recognized as one cause of tumor resistance to immune checkpoint blockade therapy, but the underlying mechanisms still remain elusive. In the present study, a bone marrow-derived CAF (BMF) -rich tumor model is successfully established by subcutaneously mixed inoculation of BMFs and tumor cells into mice and the BMF-mixed tumor xenografts are demonstrated to be resistant to anti-PD-L1 antibody immunotherapy compared to the mere tumor xenografts. In vitro assays via the co-culture system of BMFs and tumor cells indicate that the co-cultured BMFs are induced to overexpress PD-L1, while there is no such a phenomenon in the co-cultured cancer cells. The further knock-out of PD-L1 in BMFs rescues the sensitivity of BMF-mixed tumor xenografts to PD-L1 blockade therapy. Mechanistically, via the microarray assay, we identify that the upregulation of PD-L1 in BMFs stimulated by cancer cells is medicated by the activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in BMFs. Moreover, the administration of Wnt/β-catenin signaling inhibitors, including XAV-939 and Wnt-C59, distinctly inhibits the upregulation of PD-L1 expression in the co-cultured BMFs. The further combination administration of XAV-939 significantly potentiates the therapeutic outcome of PD-L1 blockade therapy in BMF-mixed tumors. In summary, our study demonstrates that Wnt inhibition augments PD-L1 blockade efficacy by overcoming BMF-mediated immunotherapy resistance.
Keywords: Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway; bone marrow-derived myofibroblasts; cancer-associated fibroblasts; immune checkpoint blockers; immunotherapy resistance; programmed cell death ligand 1.
Copyright © 2021 Huang, Li, Cheng, Wang, Zhang, Zhang, Tang, Li, Zhou and Tu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Reveals Stromal Evolution into LRRC15+ Myofibroblasts as a Determinant of Patient Response to Cancer Immunotherapy.Cancer Discov. 2020 Feb;10(2):232-253. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-19-0644. Epub 2019 Nov 7. Cancer Discov. 2020. PMID: 31699795
-
IR-780 Dye-based Targeting of Cancer-associated Fibroblasts Improves Cancer Immunotherapy by Increasing Intra-tumoral T Lymphocytes Infiltration.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2024;24(6):642-653. doi: 10.2174/0115680096261142231018104854. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2024. PMID: 38310462
-
IL-6 and PD-L1 blockade combination inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cancer development in mouse model.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017 Apr 29;486(2):239-244. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.02.128. Epub 2017 Mar 1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017. PMID: 28254435
-
Exosomal PD-L1: Roles in Tumor Progression and Immunotherapy.Trends Cancer. 2020 Jul;6(7):550-558. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2020.03.002. Epub 2020 Mar 29. Trends Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32610067 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Study and analysis of antitumor resistance mechanism of PD1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint blocker.Cancer Med. 2020 Nov;9(21):8086-8121. doi: 10.1002/cam4.3410. Epub 2020 Sep 2. Cancer Med. 2020. PMID: 32875727 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Application of single-cell RNA sequencing in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Chin J Cancer Res. 2023 Aug 30;35(4):331-342. doi: 10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2023.04.01. Chin J Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37691894 Free PMC article.
-
Circadian control of tumor immunosuppression affects efficacy of immune checkpoint blockade.Nat Immunol. 2024 Jul;25(7):1257-1269. doi: 10.1038/s41590-024-01859-0. Epub 2024 May 28. Nat Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38806707 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacologically Targeting the WNT/β-Catenin Signaling Cascade: Avoiding the Sword of Damocles.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2021;269:383-422. doi: 10.1007/164_2021_523. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34463849
-
The complex interplay of tumor-infiltrating cells in driving therapeutic resistance pathways.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Aug 19;22(1):405. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01776-7. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 39160622 Free PMC article. Review.
-
WNT/β-catenin regulatory roles on PD-(L)1 and immunotherapy responses.Clin Exp Med. 2024 Jan 27;24(1):15. doi: 10.1007/s10238-023-01274-z. Clin Exp Med. 2024. PMID: 38280119 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

