Overexpressed NEDD8 as a potential therapeutic target in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 33733647
- PMCID: PMC9088192
- DOI: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2020.0484
Overexpressed NEDD8 as a potential therapeutic target in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
Objective: The hyperactivated neddylation pathway plays an important role in tumorigenesis and is emerging as a promising anticancer target. We aimed to study whether NEDD8 (neural precursor cell expressed, developmentally down-regulated 8) might serve as a therapeutic target in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC).
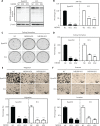
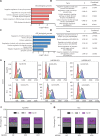
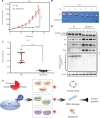
Methods: The clinical relevance of NEDD8 expression was evaluated by using The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database and tissue arrays. NEDD8-knockdown ESCC cells generated with the CRISPR/Cas9 system were used to explore the anticancer effects and mechanisms. Quantitative proteomic analysis was used to examine the variations in NEDD8 knockdown-induced biological pathways. The cell cycle and apoptosis were assessed with fluorescence activated cell sorting. A subcutaneous-transplantation mouse tumor model was established to investigate the anticancer potential of NEDD8 silencing in vivo.
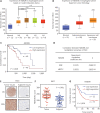
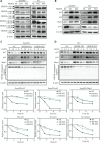
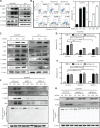
Results: NEDD8 was upregulated at both the mRNA and protein expression levels in ESCC, and NEDD8 overexpression was associated with poorer overall patient survival (mRNA level: P = 0.028, protein level: P = 0.026, log-rank test). Downregulation of NEDD8 significantly suppressed tumor growth both in vitro and in vivo. Quantitative proteomic analysis revealed that downregulation of NEDD8 induced cell cycle arrest, DNA damage, and apoptosis in ESCC cells. Mechanistic studies demonstrated that NEDD8 knockdown led to the accumulation of cullin-RING E3 ubiquitin ligases (CRLs) substrates through inactivation of CRLs, thus suppressing the malignant phenotype by inducing cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in ESCC. Rescue experiments demonstrated that the induction of apoptosis after NEDD8 silencing was attenuated by DR5 knockdown.
Conclusions: Our study elucidated the anti-ESCC effects and underlying mechanisms of NEDD8 knockdown, and validated NEDD8 as a potential target for ESCC therapy.
Keywords: NEDD8; anticancer target; apoptosis; cullin-RING E3 ubiquitin ligases; esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Copyright © 2021 Cancer Biology & Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest are disclosed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Validation of NEDD8-conjugating enzyme UBC12 as a new therapeutic target in lung cancer.EBioMedicine. 2019 Jul;45:81-91. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.06.005. Epub 2019 Jun 14. EBioMedicine. 2019. PMID: 31208947 Free PMC article.
-
Overactivated neddylation pathway as a therapeutic target in lung cancer.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2014 May 22;106(6):dju083. doi: 10.1093/jnci/dju083. Print 2014 Jun. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2014. PMID: 24853380
-
Effective targeting of the ubiquitin-like modifier NEDD8 for lung adenocarcinoma treatment.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2020 Aug;36(4):349-364. doi: 10.1007/s10565-019-09503-6. Epub 2020 Jan 6. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2020. PMID: 31907687
-
Protein neddylation: beyond cullin-RING ligases.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2015 Jan;16(1):30-44. doi: 10.1038/nrm3919. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25531226 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein neddylation and its alterations in human cancers for targeted therapy.Cell Signal. 2018 Apr;44:92-102. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2018.01.009. Epub 2018 Jan 10. Cell Signal. 2018. PMID: 29331584 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Protein neddylation and its role in health and diseases.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Apr 5;9(1):85. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01800-9. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 38575611 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NEDD9 overexpression: Prognostic and guidance value in acute myeloid leukaemia.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Oct;25(19):9331-9339. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16870. Epub 2021 Aug 25. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34432355 Free PMC article.
-
The Roles of AGTRAP, ALKBH3, DIVERSIN, NEDD8 and RRM1 in Glioblastoma Pathophysiology and Prognosis.Biomedicines. 2024 Apr 22;12(4):926. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12040926. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38672281 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive Review of Biological Roles and Interactions of Cullin-5 Protein.ACS Omega. 2022 Feb 11;7(7):5615-5624. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c06890. eCollection 2022 Feb 22. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 35224323 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of the miRNA-mRNA regulatory network associated with radiosensitivity in esophageal cancer based on integrative analysis of the TCGA and GEO data.BMC Med Genomics. 2022 Dec 1;15(1):249. doi: 10.1186/s12920-022-01392-9. BMC Med Genomics. 2022. PMID: 36456979 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre L, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: Globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Huang F, Yu S. Esophageal cancer: risk factors, genetic association, and treatment. Asian J Surg. 2018;41:210–5. - PubMed
-
- Rustgi A, El-Serag H. Esophageal carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:2499–509. - PubMed
-
- van der Veen A, Ploegh H. Ubiquitin-like proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 2012;81:323–57. - PubMed
Grants and funding
- 81602072/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81902380/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81820108022/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81625018/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2019-01-07-00-10-E00056/Innovation Program of Shanghai Municipal Education Commission
- 18XD1403800/Program of Shanghai Academic/Technology Research Leader
- 2015AA021107-019/National High Technology Research and Development Program of China
- 18411960600/Scientific Research Project of Shanghai Science and Technology Commission
- 18411950800/Shanghai Technological Innovation Action Projects
- 17YF1405000/Shanghai 'Rising Stars of Medical Talent' Youth Development Program, Outstanding Youth Medical Talents, 2018, and the Shanghai Sailing Program
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
