Tackling Drug Resistance in EGFR Exon 20 Insertion Mutant Lung Cancer
- PMID: 33727854
- PMCID: PMC7955704
- DOI: 10.2147/PGPM.S242045
Tackling Drug Resistance in EGFR Exon 20 Insertion Mutant Lung Cancer
Abstract
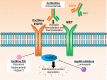
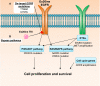
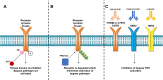
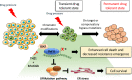
Insertion mutations in exon 20 (Ex20ins) of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) gene are the largest class of EGFR mutations in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) for which there are currently no approved targeted therapies. NSCLC patients with these mutations do not respond to clinically approved EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) and have poor outcomes. A number of early phase clinical trials are currently underway to evaluate the efficacy of a new generation of TKIs that are capable of binding to and blocking Ex20ins. Although these agents have shown some clinical activity, patient responses have been restricted by dose-limiting toxicity or rapid acquisition of resistance after a short response. Here we review the current understanding of the mechanisms of resistance to these compounds, which include on-target EGFR secondary mutations, compensatory bypass pathway activation and acquisition of an EMT phenotype. Taking lessons from conventional EGFR inhibitor therapy in NSCLC, we also consider other potential sources of resistance including the presence of drug-tolerant persister cells. We will discuss therapeutic strategies which have the potential to overcome different forms of drug resistance. We conclude by evaluating recent technological developments in drug discovery such as PROTACs as a means to better tackle TKI resistance in NSCLC harbouring Ex20ins mutations.
Keywords: EGFR; PROTACs; drug resistance; exon 20 insertions; lung cancer; poziotinib.
© 2021 Pacini et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
EGFR exon20 insertion mutations in non-small cell lung cancer: Clinical implications and recent advances in targeted therapies.Cancer Treat Rev. 2023 Nov;120:102605. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2023.102605. Epub 2023 Aug 6. Cancer Treat Rev. 2023. PMID: 37703723 Review.
-
EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: current status and perspectives.Biomark Res. 2022 Apr 13;10(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s40364-022-00372-6. Biomark Res. 2022. PMID: 35418149 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging therapies for non-small cell lung cancer harboring EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations: narrative review.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Dec;10(23):1283. doi: 10.21037/atm-2022-56. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36618815 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Case report: sequential use of almonertinib based on the EGFR exon 20 insertion mutation achieves long-term control for advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients.Transl Cancer Res. 2022 Jun;11(6):1836-1843. doi: 10.21037/tcr-21-2728. Transl Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35836508 Free PMC article.
-
Immune microenvironment features and efficacy of PD-1/PD-L1 blockade in non-small cell lung cancer patients with EGFR or HER2 exon 20 insertions.Thorac Cancer. 2021 Jan;12(2):218-226. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13748. Epub 2020 Nov 18. Thorac Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33210451 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Discovery of mobocertinib, a new irreversible tyrosine kinase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer harboring EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations.Med Chem Res. 2022;31(10):1647-1662. doi: 10.1007/s00044-022-02952-5. Epub 2022 Sep 1. Med Chem Res. 2022. PMID: 36065226 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting EGFR Exon 20 Insertion Mutations in Non-small-Cell Lung Cancer: Changes in Treatment Strategies are Coming.Cancer Control. 2024 Jan-Dec;31:10732748241292782. doi: 10.1177/10732748241292782. Cancer Control. 2024. PMID: 39417568 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[EGFR Exon 20 Insertion Mutation: Research Status and New Treatment Strategies].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2024 Aug 20;27(8):579-592. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2024.106.19. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39318251 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
From targeted therapy to a novel way: Immunogenic cell death in lung cancer.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Dec 23;9:1102550. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.1102550. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36619616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multinational proficiency tests for EGFR exon 20 insertions reveal that the assay design matters.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 6;14(1):13069. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-63821-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38844820 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

