The Role of EBV-Encoded LMP1 in the NPC Tumor Microenvironment: From Function to Therapy
- PMID: 33718235
- PMCID: PMC7947715
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.640207
The Role of EBV-Encoded LMP1 in the NPC Tumor Microenvironment: From Function to Therapy
Abstract
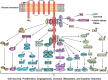
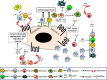
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is closely associated with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection. It is also characterized by heavy infiltration with non-malignant leucocytes. The EBV-encoded latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) is believed to play an important role in NPC pathogenesis by virtue of its ability to activate multiple cell signaling pathways which collectively promote cell proliferation and survival, angiogenesis, invasiveness, and aerobic glycolysis. LMP1 also affects cell-cell interactions, antigen presentation, and cytokine and chemokine production. Here, we discuss how LMP1 modulates local immune responses that contribute to the establishment of the NPC tumor microenvironment. We also discuss strategies for targeting the LMP1 protein as a novel therapy for EBV-driven malignancies.
Keywords: Epstein-Barr virus; latent membrane protein 1; nasopharyngeal carcinoma; therapy; tumor microenvironment.
Copyright © 2021 Lo, Dawson, Lung, Wong and Young.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Activation of the FGFR1 signalling pathway by the Epstein-Barr virus-encoded LMP1 promotes aerobic glycolysis and transformation of human nasopharyngeal epithelial cells.J Pathol. 2015 Oct;237(2):238-48. doi: 10.1002/path.4575. Epub 2015 Aug 3. J Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26096068
-
Activation of sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 (SREBP1)-mediated lipogenesis by the Epstein-Barr virus-encoded latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) promotes cell proliferation and progression of nasopharyngeal carcinoma.J Pathol. 2018 Oct;246(2):180-190. doi: 10.1002/path.5130. Epub 2018 Aug 22. J Pathol. 2018. PMID: 29968360 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Epstein-Barr virus oncoprotein LMP1-mediated glycolysis sensitizes nasopharyngeal carcinoma to radiation therapy.Oncogene. 2014 Sep 11;33(37):4568-78. doi: 10.1038/onc.2014.32. Epub 2014 Mar 24. Oncogene. 2014. PMID: 24662831 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenic role of Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein-1 in the development of nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Cancer Lett. 2013 Aug 28;337(1):1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2013.05.018. Epub 2013 May 17. Cancer Lett. 2013. PMID: 23689138 Review.
-
EBV Infection and Glucose Metabolism in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;1018:75-90. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-5765-6_6. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 29052133 Review.
Cited by
-
Revolutionizing the treatment for nasopharyngeal cancer: the impact, challenges and strategies of stem cell and genetically engineered cell therapies.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 10;15:1484535. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1484535. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39450176 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) Epithelial Associated Malignancies: Exploring Pathologies and Current Treatments.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 19;23(22):14389. doi: 10.3390/ijms232214389. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430864 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathogenesis and therapeutic implications of EBV-associated epithelial cancers.Front Oncol. 2023 Oct 2;13:1202117. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1202117. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37901329 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early Stage and Locally Advanced Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Treatment from Present to Future: Where Are We and Where Are We Going?Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2023 Jul;24(7):845-866. doi: 10.1007/s11864-023-01083-2. Epub 2023 May 5. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37145382 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epstein-Barr virus: the molecular virology and the associated diseases.Fujita Med J. 2023 May;9(2):65-72. doi: 10.20407/fmj.2022-018. Epub 2022 Oct 28. Fujita Med J. 2023. PMID: 37234394 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

