Why Cells and Viruses Cannot Survive without an ESCRT
- PMID: 33668191
- PMCID: PMC7995964
- DOI: 10.3390/cells10030483
Why Cells and Viruses Cannot Survive without an ESCRT
Abstract
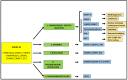
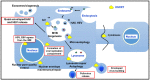
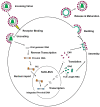
Intracellular organelles enwrapped in membranes along with a complex network of vesicles trafficking in, out and inside the cellular environment are one of the main features of eukaryotic cells. Given their central role in cell life, compartmentalization and mechanisms allowing their maintenance despite continuous crosstalk among different organelles have been deeply investigated over the past years. Here, we review the multiple functions exerted by the endosomal sorting complex required for transport (ESCRT) machinery in driving membrane remodeling and fission, as well as in repairing physiological and pathological membrane damages. In this way, ESCRT machinery enables different fundamental cellular processes, such as cell cytokinesis, biogenesis of organelles and vesicles, maintenance of nuclear-cytoplasmic compartmentalization, endolysosomal activity. Furthermore, we discuss some examples of how viruses, as obligate intracellular parasites, have evolved to hijack the ESCRT machinery or part of it to execute/optimize their replication cycle/infection. A special emphasis is given to the herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) interaction with the ESCRT proteins, considering the peculiarities of this interplay and the need for HSV-1 to cross both the nuclear-cytoplasmic and the cytoplasmic-extracellular environment compartmentalization to egress from infected cells.
Keywords: ESCRT; HSV-1; cellular membranes; extracellular vesicles; viruses.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Cellular ESCRT complex and its roles in enveloped viruses budding].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2012 Sep;28(9):1031-7. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2012. PMID: 23289305 Review. Chinese.
-
Herpes simplex virus type 1 production requires a functional ESCRT-III complex but is independent of TSG101 and ALIX expression.J Virol. 2009 Nov;83(21):11254-64. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00574-09. Epub 2009 Aug 19. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19692479 Free PMC article.
-
[Virus hijacking ESCRT system to promote self-replication: a review].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2023 Oct 25;39(10):3948-3965. doi: 10.13345/j.cjb.230323. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2023. PMID: 37877384 Review. Chinese.
-
ESCRT & Co.Biol Cell. 2010 Mar 12;102(5):293-318. doi: 10.1042/BC20090161. Biol Cell. 2010. PMID: 20222872 Review.
-
The multifaceted interactions between pathogens and host ESCRT machinery.PLoS Pathog. 2023 May 4;19(5):e1011344. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011344. eCollection 2023 May. PLoS Pathog. 2023. PMID: 37141275 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
EhVps23: A Component of ESCRT-I That Participates in Vesicular Trafficking and Phagocytosis of Entamoeba histolytica.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Oct 29;11:770759. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.770759. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34778112 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Tsg101 Binding Partners Regulate Viral L Domain Trafficking.Viruses. 2021 Jun 15;13(6):1147. doi: 10.3390/v13061147. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34203832 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Temporal insights into molecular and cellular responses during rAAV production in HEK293T cells.Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2024 Jun 8;32(3):101278. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2024.101278. eCollection 2024 Sep 12. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2024. PMID: 39022743 Free PMC article.
-
Research progress on the mechanism of exosome-mediated virus infection.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Jun 26;14:1418168. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1418168. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38988816 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamic, but Not Necessarily Disordered, Human-Virus Interactions Mediated through SLiMs in Viral Proteins.Viruses. 2021 Nov 26;13(12):2369. doi: 10.3390/v13122369. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34960638 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

