Two Ecdysteroids Isolated from Micropropagated Lychnis flos-cuculi and the Biological Activity of Plant Material
- PMID: 33572129
- PMCID: PMC7914685
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26040904
Two Ecdysteroids Isolated from Micropropagated Lychnis flos-cuculi and the Biological Activity of Plant Material
Abstract
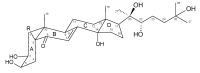
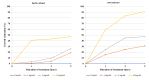
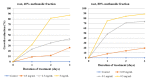
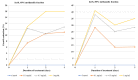
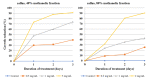
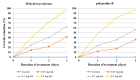
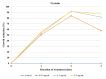
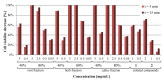
Genetically uniform plant material, derived from Lychnis flos-cuculi propagated in vitro, was used for the isolation of 20-hydroxyecdysone and polypodine B and subjected to an evaluation of the antifungal and antiamoebic activity. The activity of 80% aqueous methanolic extracts, their fractions, and isolated ecdysteroids were studied against pathogenic Acanthamoeba castellani. Additionally, a Microtox® acute toxicity assay was performed. It was found that an 80% methanolic fraction of root extract exerts the most potent amoebicidal activity at IC50 of 0.06 mg/mL at the 3rd day of treatment. Both ecdysteroids show comparable activity at IC50 of 0.07 mg/mL. The acute toxicity of 80% fractions at similar concentrations is significantly higher than that of 40% fractions. Crude extracts exhibited moderate antifungal activity, with a minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) within the range of 1.25-2.5 mg/mL. To the best of our knowledge, the present report is the first to show the biological activity of L. flos-cuculi in terms of the antifungal and antiamoebic activities and acute toxicity. It is also the first isolation of the main ecdysteroids from L. flos-cuculi micropropagated, ecdysteroid-rich plant material.
Keywords: 20-hydroxyecdysone; Acanthamoeba; Microtox; Ragged Robin; antifungal activity; plant tissue culture; polypodine B.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of Cytotoxic Activity of Cell Biomass from Eryngium planum and Lychnis flos-cuculi on Melanoma Cancer Cell.Molecules. 2024 Oct 31;29(21):5158. doi: 10.3390/molecules29215158. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39519799 Free PMC article.
-
[Structural diversity of ecdysteroids of Lychnis flos-cuculi].Acta Pharm Hung. 2001 Aug;71(2):157-67. Acta Pharm Hung. 2001. PMID: 11862663 Hungarian.
-
Preliminary phytochemical investigation of Lychnis flos-cuculi herbs.J Nat Med. 2008 Oct;62(4):473-5. doi: 10.1007/s11418-008-0261-0. Epub 2008 Jun 17. J Nat Med. 2008. PMID: 18553180
-
Phytochemical Screening, Phenolic Compounds and Antioxidant Activity of Biomass from Lychnis flos-cuculi L. In Vitro Cultures and Intact Plants.Plants (Basel). 2021 Jan 22;10(2):206. doi: 10.3390/plants10020206. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33499074 Free PMC article.
-
Phytoecdysteroids effects on mammalians, isolation and analysis.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2002 Jun;2(3):285-93. doi: 10.2174/1389557023406269. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2002. PMID: 12370070 Review.
Cited by
-
Phragmites australis (Cav.) Trin. ex Steud. Extract Induces Apoptosis-like Programmed Cell Death in Acanthamoeba castellanii Trophozoites.Plants (Basel). 2022 Dec 9;11(24):3459. doi: 10.3390/plants11243459. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36559571 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing the porosity of chitosan sponges with CBD by adding antimicrobial violacein.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 31;10(15):e35389. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35389. eCollection 2024 Aug 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39165973 Free PMC article.
-
Iris setosa Pall. ex Link Extract Reveals Amoebicidal Activity against Acanthamoeba castellanii and Acanthamoeba polyphaga with Low Toxicity to Human Corneal Cells.Microorganisms. 2024 Aug 13;12(8):1658. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12081658. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39203500 Free PMC article.
-
Chitosan-Gelatin Films Cross-Linked with Dialdehyde Cellulose Nanocrystals as Potential Materials for Wound Dressings.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 26;23(17):9700. doi: 10.3390/ijms23179700. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36077096 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Cytotoxic Activity of Cell Biomass from Eryngium planum and Lychnis flos-cuculi on Melanoma Cancer Cell.Molecules. 2024 Oct 31;29(21):5158. doi: 10.3390/molecules29215158. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39519799 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bucharow W.G., Chirva V.J., Bucharowa I.L. Triterpene glycosides from Coronaria flos-cuculi. Pharmazie. 1974;29:540. - PubMed
-
- Báthori M., Lafont R., Girault J.P., Máthé I. Structural diversity of ecdysteroids of Lychnis flos-cuculi. Acta Pharm. Hung. 2001;71:157–167. - PubMed
-
- Maliński M.P., Michalska A.D., Tomczykowa M., Tomczyk M., Thiem B. Ragged Robin (Lychnis flos-cuculi)—a plant with potential medicinal value. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2014;24:722–730. doi: 10.1016/j.bjp.2014.11.004. - DOI
-
- Costea T., Nencu I., Gîrd C.E., Popescu M.L. Ragged Robin (Lychnis flos cuculi L.) aerial parts—botanical characterization, phytochemical screening and antioxidant activity. Studia Univ. Vasile Goldis Arad Ser. Stiintele Vietii. 2017;27:231–238.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

