Effect of High-Intensity Interval Training, Moderate Continuous Training, or Guideline-Based Physical Activity Advice on Peak Oxygen Consumption in Patients With Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction: A Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 33560320
- PMCID: PMC7873782
- DOI: 10.1001/jama.2020.26812
Effect of High-Intensity Interval Training, Moderate Continuous Training, or Guideline-Based Physical Activity Advice on Peak Oxygen Consumption in Patients With Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
Importance: Endurance exercise is effective in improving peak oxygen consumption (peak V̇o2) in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF). However, it remains unknown whether differing modes of exercise have different effects.
Objective: To determine whether high-intensity interval training, moderate continuous training, and guideline-based advice on physical activity have different effects on change in peak V̇o2 in patients with HFpEF.
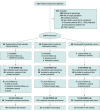
Design, setting, and participants: Randomized clinical trial at 5 sites (Berlin, Leipzig, and Munich, Germany; Antwerp, Belgium; and Trondheim, Norway) from July 2014 to September 2018. From 532 screened patients, 180 sedentary patients with chronic, stable HFpEF were enrolled. Outcomes were analyzed by core laboratories blinded to treatment groups; however, the patients and staff conducting the evaluations were not blinded.
Interventions: Patients were randomly assigned (1:1:1; n = 60 per group) to high-intensity interval training (3 × 38 minutes/week), moderate continuous training (5 × 40 minutes/week), or guideline control (1-time advice on physical activity according to guidelines) for 12 months (3 months in clinic followed by 9 months telemedically supervised home-based exercise).
Main outcomes and measures: Primary end point was change in peak V̇o2 after 3 months, with the minimal clinically important difference set at 2.5 mL/kg/min. Secondary end points included changes in metrics of cardiorespiratory fitness, diastolic function, and natriuretic peptides after 3 and 12 months.
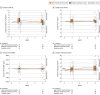
Results: Among 180 patients who were randomized (mean age, 70 years; 120 women [67%]), 166 (92%) and 154 (86%) completed evaluation at 3 and 12 months, respectively. Change in peak V̇o2 over 3 months for high-intensity interval training vs guideline control was 1.1 vs -0.6 mL/kg/min (difference, 1.5 [95% CI, 0.4 to 2.7]); for moderate continuous training vs guideline control, 1.6 vs -0.6 mL/kg/min (difference, 2.0 [95% CI, 0.9 to 3.1]); and for high-intensity interval training vs moderate continuous training, 1.1 vs 1.6 mL/kg/min (difference, -0.4 [95% CI, -1.4 to 0.6]). No comparisons were statistically significant after 12 months. There were no significant changes in diastolic function or natriuretic peptides. Acute coronary syndrome was recorded in 4 high-intensity interval training patients (7%), 3 moderate continuous training patients (5%), and 5 guideline control patients (8%).
Conclusions and relevance: Among patients with HFpEF, there was no statistically significant difference in change in peak V̇o2 at 3 months between those assigned to high-intensity interval vs moderate continuous training, and neither group met the prespecified minimal clinically important difference compared with the guideline control. These findings do not support either high-intensity interval training or moderate continuous training compared with guideline-based physical activity for patients with HFpEF.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02078947.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Searching for the Optimal Exercise Training Regimen in Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction.JAMA. 2021 Feb 9;325(6):537-539. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.26347. JAMA. 2021. PMID: 33560307 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Effect of Training on Peak Oxygen Consumption in Patients With Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction.JAMA. 2021 Aug 24;326(8):771. doi: 10.1001/jama.2021.10058. JAMA. 2021. PMID: 34427607 No abstract available.
-
Effect of Training on Peak Oxygen Consumption in Patients With Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction.JAMA. 2021 Aug 24;326(8):770-771. doi: 10.1001/jama.2021.10055. JAMA. 2021. PMID: 34427608 No abstract available.
-
Effect of Training on Peak Oxygen Consumption in Patients With Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction.JAMA. 2021 Aug 24;326(8):770. doi: 10.1001/jama.2021.10052. JAMA. 2021. PMID: 34427609 No abstract available.
-
Effect of Training on Peak Oxygen Consumption in Patients With Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction.JAMA. 2021 Aug 24;326(8):771-772. doi: 10.1001/jama.2021.10049. JAMA. 2021. PMID: 34427610 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
High-intensity interval training is effective and superior to moderate continuous training in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: A randomized clinical trial.Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2020 Nov;27(16):1733-1743. doi: 10.1177/2047487319901206. Epub 2020 Jan 21. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 31964186 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of Praliciguat on Peak Rate of Oxygen Consumption in Patients With Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction: The CAPACITY HFpEF Randomized Clinical Trial.JAMA. 2020 Oct 20;324(15):1522-1531. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.16641. JAMA. 2020. PMID: 33079154 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of endurance exercise training on endothelial function and arterial stiffness in older patients with heart failure and preserved ejection fraction: a randomized, controlled, single-blind trial.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013 Aug 13;62(7):584-92. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.04.033. Epub 2013 May 9. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23665370 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of exercise training in patients with chronotropic incompetence and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: Training-HR study protocol.Curr Probl Cardiol. 2024 Dec;49(12):102839. doi: 10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2024.102839. Epub 2024 Sep 4. Curr Probl Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 39242065
-
Exercise training in patients with heart failure and preserved ejection fraction: meta-analysis of randomized control trials.Circ Heart Fail. 2015 Jan;8(1):33-40. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.114.001615. Epub 2014 Nov 16. Circ Heart Fail. 2015. PMID: 25399909 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical Perspectives on Cardiac Rehabilitation After Heart Failure in Elderly Patients with Frailty: A Narrative Review.Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2022 Oct 27;18:1009-1028. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S350748. eCollection 2022. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2022. PMID: 36324527 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiac Biomarkers and Exercise Training in People With Diabetes: When a Negative Is a Positive.JACC Adv. 2023 Jan 27;2(1):100193. doi: 10.1016/j.jacadv.2022.100193. eCollection 2023 Jan. JACC Adv. 2023. PMID: 38939029 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of exercise-based cardiac rehabilitation delivery modes on exercise capacity and health-related quality of life in heart failure: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Open Heart. 2022 Jun;9(1):e001949. doi: 10.1136/openhrt-2021-001949. Open Heart. 2022. PMID: 35680170 Free PMC article.
-
High-Intensity Interval Training for Heart Failure Patients With Preserved Ejection Fraction (HIT-HF)-Rational and Design of a Prospective, Randomized, Controlled Trial.Front Physiol. 2021 Sep 24;12:734111. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.734111. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34630155 Free PMC article.
-
Personalized remotely guided preventive exercise therapy for a healthy heart (PRIORITY): protocol for an assessor-blinded, multicenter randomized controlled trial.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Jun 29;10:1194693. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1194693. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 37456813 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

