The Small Molecule BIBR1532 Exerts Potential Anti-cancer Activities in Preclinical Models of Feline Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Through Inhibition of Telomerase Activity and Down-Regulation of TERT
- PMID: 33553285
- PMCID: PMC7855307
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2020.620776
The Small Molecule BIBR1532 Exerts Potential Anti-cancer Activities in Preclinical Models of Feline Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Through Inhibition of Telomerase Activity and Down-Regulation of TERT
Abstract
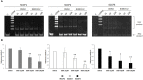
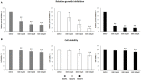
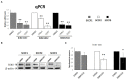
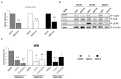
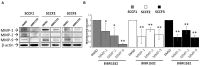
Expression of telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) and telomerase activity (TA) is a main feature of cancer, contributing to cell immortalization by causing telomeres dysfunction. BIBR1532 is a potent telomerase inhibitor that showed potential anti-tumor activities in several types of cancer, by triggering replicative senescence and apoptosis. In a previous work, we detected, for the first time, TERT expression and TA in preclinical models of feline oral squamous cell carcinoma (FOSCC); therefore, we aimed at extending our investigation by testing the effects of treatment with BIBR1532, in order to explore the role of telomerase in this tumor and foreshadow the possibility of it being considered as a future therapeutic target. In the present study, treatment of FOSCC cell lines SCCF1, SCCF2, and SCCF3 with BIBR1532 resulted in successful inhibition of TA, with subsequent cell growth stoppage and decrease in cell viability. Molecular data showed that up-regulation of cell cycle inhibitor p21, unbalancing of Bax/Bcl-2 ratio, and down-regulation of survival gene Survivin were mostly involved in the observed cellular events. Moreover, BIBR1532 diminished the expression of TERT and its transcriptional activator cMyc, resulting in the down-regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), phospho-ERK/ERK ratio, and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs)-1/-2 and-9, likely as a consequence of an impairment of TERT extra-telomeric functions. Taken together, our data suggest that BIBR1532 exerts multiple anti-cancer activities in FOSCC by inhibiting telomerase pathway and interfering with signaling routes involved in cell proliferation, cell survival, and invasion, paving the way for future translational studies aimed at evaluating its possible employment in the treatment of this severe tumor of cats.
Keywords: BIBR1532; EGFR; MMP; TERT; cancer; feline oral squamous cell carcinoma; telomerase activity.
Copyright © 2021 Altamura, degli Uberti, Galiero, De Luca, Power, Licenziato, Maiolino and Borzacchiello.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase (TERT) Expression, Telomerase Activity, and Expression of Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMP)-1/-2/-9 in Feline Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cell Lines Associated With Felis catus Papillomavirus Type-2 Infection.Front Vet Sci. 2020 Mar 27;7:148. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2020.00148. eCollection 2020. Front Vet Sci. 2020. PMID: 32292795 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody Cetuximab displays potential anti-cancer activities in feline oral squamous cell carcinoma cell lines.Front Vet Sci. 2022 Nov 17;9:1040552. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.1040552. eCollection 2022. Front Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 36467642 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of telomerase using BIBR1532 enhances doxorubicin-induced apoptosis in pre-B acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells.Hematology. 2017 Jul;22(6):330-340. doi: 10.1080/10245332.2016.1275426. Epub 2017 Jan 5. Hematology. 2017. PMID: 28054503
-
Feedback regulation of telomerase reverse transcriptase: new insight into the evolving field of telomerase in cancer.Cell Signal. 2013 Dec;25(12):2462-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.08.009. Epub 2013 Aug 29. Cell Signal. 2013. PMID: 23993966 Review.
-
Tissue formation and tissue engineering through host cell recruitment or a potential injectable cell-based biocomposite with replicative potential: Molecular mechanisms controlling cellular senescence and the involvement of controlled transient telomerase activation therapies.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2015 Dec;103(12):3993-4023. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.35515. Epub 2015 Aug 14. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2015. PMID: 26034007 Review.
Cited by
-
Τelomerase inhibitors and activators in aging and cancer: A systematic review.Mol Med Rep. 2022 May;25(5):158. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2022.12674. Epub 2022 Mar 10. Mol Med Rep. 2022. PMID: 35266017 Free PMC article.
-
Aging, Cancer, and Inflammation: The Telomerase Connection.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 5;25(15):8542. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158542. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39126110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Relevance of Telomerase and Telomere-Associated Proteins in B-Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia.Genes (Basel). 2023 Mar 10;14(3):691. doi: 10.3390/genes14030691. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36980962 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiple Actions of Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase in Cell Death Regulation.Biomedicines. 2023 Apr 4;11(4):1091. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11041091. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37189709 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From Crypts to Cancer: A Holistic Perspective on Colorectal Carcinogenesis and Therapeutic Strategies.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 30;25(17):9463. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179463. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273409 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

