Human Adipose Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes: A Key Player in Wound Healing
- PMID: 33547566
- PMCID: PMC8325736
- DOI: 10.1007/s13770-020-00316-x
Human Adipose Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes: A Key Player in Wound Healing
Abstract
Background: Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (AMSCs) are an attractive resource for wound healing because their regenerative capacity improves injury repair. Recently, stem cell-derived exosomes have been shown to play a positive role in stem cell-based therapies. However, the effects of exosomes derived from AMSCs (AEXOs) on wound healing are unclear. In this study, we aimed to examine the role of AEXOs in attenuating inflammation and explore their effects in normal wound healing.
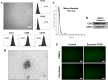
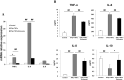
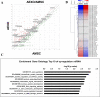
Methods: We isolated exosomes from AMSCs and established a cellular model of inflammation by treatment with the inflammatory cytokines, interferon gamma and tumor necrosis factor alpha, to determine whether AEXOs can inhibit inflammation. We examined the wound healing effects of AEXOs in in vitro wound healing models and performed a miRNA array to understand the role of AEXOs in inflammation and wound healing.
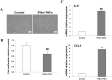
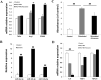
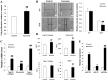
Results: A significant difference was observed in wound closure and the expression of anti-inflammatory and wound-healing-related factors between control and AEXO-treated cells.
Conclusion: Our results showed that besides alleviating the inflammation response, AEXOs also promote wound healing. Thus, AEXOs represent a novel, stem-cell-based, therapeutic strategy for wound healing.
Keywords: Adipose-derived stem cells; Exosomes; Inflammation; Wound healing.
© 2021. The Korean Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MiR-223-3p overexpressed adipose mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promote wound healing via targeting MAPK10.Acta Histochem. 2023 Dec;125(8):152102. doi: 10.1016/j.acthis.2023.152102. Epub 2023 Oct 12. Acta Histochem. 2023. PMID: 37837832
-
Exosomes derived from mmu_circ_0000250-modified adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote wound healing in diabetic mice by inducing miR-128-3p/SIRT1-mediated autophagy.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2020 May 1;318(5):C848-C856. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00041.2020. Epub 2020 Mar 11. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32159361
-
Selenium-Stimulated Exosomes Enhance Wound Healing by Modulating Inflammation and Angiogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 29;23(19):11543. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911543. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36232844 Free PMC article.
-
Prospective application of exosomes derived from adipose-derived stem cells in skin wound healing: A review.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2020 Mar;19(3):574-581. doi: 10.1111/jocd.13215. Epub 2019 Nov 21. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2020. PMID: 31755172 Review.
-
Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells: A promising cell-free therapeutic tool for cutaneous wound healing.Biochimie. 2023 Jun;209:73-84. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2023.01.013. Epub 2023 Jan 18. Biochimie. 2023. PMID: 36681232 Review.
Cited by
-
Adipose stem cells-released extracellular vesicles as a next-generation cargo delivery vehicles: a survey of minimal information implementation, mass production and functional modification.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022 May 3;13(1):182. doi: 10.1186/s13287-022-02849-5. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 35505389 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomes and ultrasound: The future of theranostic applications.Mater Today Bio. 2023 Jan 20;19:100556. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2023.100556. eCollection 2023 Apr. Mater Today Bio. 2023. PMID: 36756211 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosome-mediated Advancements in Plastic Surgery: Navigating Therapeutic Potential in Skin Rejuvenation and Wound Healing.Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2024 Aug 1;12(8):e6021. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000006021. eCollection 2024 Aug. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2024. PMID: 39534068 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering of Cell Derived-Nanovesicle as an Alternative to Exosome Therapy.Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2024 Jan;21(1):1-19. doi: 10.1007/s13770-023-00610-4. Epub 2023 Dec 8. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2024. PMID: 38066355 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stem cell-derived exosomes: emerging therapeutic opportunities for wound healing.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023 Apr 26;14(1):107. doi: 10.1186/s13287-023-03345-0. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 37101197 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
