miR-200b restrains EMT and aggressiveness and regulates matrix composition depending on ER status and signaling in mammary cancer
- PMID: 33543022
- PMCID: PMC7852204
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mbplus.2020.100024
miR-200b restrains EMT and aggressiveness and regulates matrix composition depending on ER status and signaling in mammary cancer
Abstract
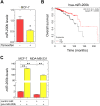
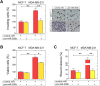
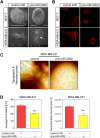
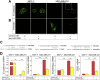
Secreted microRNAs (miRNAs) reside in a complex regulatory network with extracellular matrix (ECM) macromolecules, which affect cell-cell communication, therefore miRNA expression highlights its significance in several aspects of human diseases, including cancer. miRNA-mediated regulation of breast cancer has received considerable attention due to evidence that shows miRNAs to mediate estrogen receptor (ER) status, metastasis, chemoresistance and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT). miR-200b is a pluripotent miRNA, which is inversely regulated by ERα and ERβ in mammary cancer. It has been identified as tumor suppressor and EMT inhibitor serving as a critical biomarker, as its expression in breast tumor determines the disease-free survival, thus highlighting its roles in breast cancer invasion and metastasis. The main goal of this study was to investigate the role of miR-200b in modulating the behavior of breast cancer cells with different ER status. We demonstrate that estrogen signaling through ERs reduces miR-200b expression levels in ERα-positive breast cancer cells. Moreover, miR-200b upregulation reduces the aggressive phenotype of ERβ-positive breast cancer cells by inhibiting cell invasiveness and motility, followed by ECM reorganization as well as cytoskeletal and morphological changes concluded from deep inspection of cell topography. Future investigation towards the mechanistic perspective of miR-200b effects in the behavior of aggressive mammary cancer cells appears rewarding in order to expand our understanding of miR-200b as a novel mediator beyond breast cancer diagnosis and pharmaceutical targeting.
Keywords: Breast cancer; ECM, extracellular matrix; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; EMT, epithelial-to-mesenchymal-transition; ER, estrogen receptor; Erk, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; Estrogen receptors; Extracellular matrix; GAG, glycosaminoglycan; GF, growth factor; HER2, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2; IGF-IR, insulin-like growth factor receptor type I; IL, interleukin; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; PG, proteoglycan; PR, progesterone receptor; RISC, RNA-induced silencing complex; SERM, selective estrogen receptor modulator; TGFβ, transforming growth factor beta; miR-200b; miRNA, microRNA; miRNAs; pre-miRNA, precursor miRNA.
© 2020 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
C.R. is an employee of Serend-ip GmbH; the other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Estrogen receptor beta as epigenetic mediator of miR-10b and miR-145 in mammary cancer.Matrix Biol. 2017 Dec;64:94-111. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2017.08.002. Epub 2017 Aug 8. Matrix Biol. 2017. PMID: 28797712
-
Dual regulation by microRNA-200b-3p and microRNA-200b-5p in the inhibition of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in triple-negative breast cancer.Oncotarget. 2015 Jun 30;6(18):16638-52. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3184. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26062653 Free PMC article.
-
miR-200b regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition of chemo-resistant breast cancer cells by targeting FN1.Discov Med. 2017 Sep;24(131):75-85. Discov Med. 2017. PMID: 28972876
-
Good or not good: Role of miR-18a in cancer biology.Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 2020 Sep-Oct;25(5):808-819. doi: 10.1016/j.rpor.2020.07.006. Epub 2020 Aug 12. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 2020. PMID: 32884453 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and invadopodia markers in breast cancer: Lumican a key regulator.Semin Cancer Biol. 2020 May;62:125-133. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.08.003. Epub 2019 Aug 8. Semin Cancer Biol. 2020. PMID: 31401293 Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetic Alterations in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer-The Critical Role of Extracellular Matrix.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Feb 9;13(4):713. doi: 10.3390/cancers13040713. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33572395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dicer-mediated miR-200b expression contributes to cell migratory/invasive abilities and cancer stem cells properties of breast cancer cells.Aging (Albany NY). 2022 Aug 8;14(16):6520-6536. doi: 10.18632/aging.204205. Epub 2022 Aug 8. Aging (Albany NY). 2022. PMID: 35951366 Free PMC article.
-
Management of triple-negative breast cancer by natural compounds through different mechanistic pathways.Front Genet. 2024 Jul 26;15:1440430. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1440430. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 39130753 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Key Matrix Remodeling Enzymes: Functions and Targeting in Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Mar 22;13(6):1441. doi: 10.3390/cancers13061441. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33809973 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Revisiting the Syndecans: Master Signaling Regulators with Prognostic and Targetable Therapeutic Values in Breast Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Mar 16;15(6):1794. doi: 10.3390/cancers15061794. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36980680 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Torre L.A., Bray F., Siegel R.L., Ferlay J., Lortet-Tieulent J., Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2015;65:87–108. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

