The immunodominant and neutralization linear epitopes for SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 33503420
- PMCID: PMC7837128
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108666
The immunodominant and neutralization linear epitopes for SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
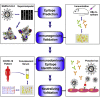
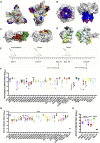
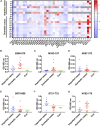
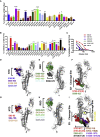
Although vaccines against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) are under development, the antigen epitopes on the virus and their immunogenicity are poorly understood. Here, we simulate the 3D structures and predict the B cell epitopes on the spike (S), envelope (E), membrane (M), and nucleocapsid (N) proteins of SARS-CoV-2 using structure-based approaches and validate epitope immunogenicity by immunizing mice. Almost all 33 predicted epitopes effectively induce antibody production, six of these are immunodominant epitopes in individuals, and 23 are conserved within SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV, and bat coronavirus RaTG13. We find that the immunodominant epitopes of individuals with domestic (China) SARS-CoV-2 are different from those of individuals with imported (Europe) SARS-CoV-2, which may be caused by mutations on the S (G614D) and N proteins. Importantly, we find several epitopes on the S protein that elicit neutralizing antibodies against D614 and G614 SARS-CoV-2, which can contribute to vaccine design against coronaviruses.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; immunodominant epitope; neutralizing epitope; vaccine.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests R.-t.L, S.L., and X.-x.X. have filed a provisional patent on epitopes for designing a coronavirus vaccine.
Figures
Similar articles
-
COVID-19 coronavirus vaccine T cell epitope prediction analysis based on distributions of HLA class I loci (HLA-A, -B, -C) across global populations.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2021 Apr 3;17(4):1097-1108. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2020.1823777. Epub 2020 Nov 11. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2021. PMID: 33175614 Free PMC article.
-
Epitope-based peptide vaccines predicted against novel coronavirus disease caused by SARS-CoV-2.Virus Res. 2020 Oct 15;288:198082. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2020.198082. Epub 2020 Jul 1. Virus Res. 2020. PMID: 32621841 Free PMC article.
-
Revelation of Potent Epitopes Present in Unannotated ORF Antigens of SARS-CoV-2 for Epitope-Based Polyvalent Vaccine Design Using Immunoinformatics Approach.Front Immunol. 2021 Aug 23;12:692937. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.692937. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34497604 Free PMC article.
-
Development of multi-epitope peptide-based vaccines against SARS-CoV-2.Biomed J. 2021 Mar;44(1):18-30. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2020.09.005. Epub 2020 Oct 1. Biomed J. 2021. PMID: 33727051 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vaccines for COVID-19: perspectives from nucleic acid vaccines to BCG as delivery vector system.Microbes Infect. 2020 Nov-Dec;22(10):515-524. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2020.09.004. Epub 2020 Sep 19. Microbes Infect. 2020. PMID: 32961274 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein reveals multiple functional consequences of the C-terminal domain.iScience. 2021 Jun 25;24(6):102681. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.102681. Epub 2021 Jun 1. iScience. 2021. PMID: 34095780 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of tumor antigens and immune subtypes of cholangiocarcinoma for mRNA vaccine development.Mol Cancer. 2021 Mar 8;20(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s12943-021-01342-6. Mol Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33685460 Free PMC article.
-
VOE: automated analysis of variant epitopes of SARS-CoV-2 for the development of diagnostic tests or vaccines for COVID-19.PeerJ. 2024 Jun 19;12:e17504. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17504. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 38912043 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatic elucidation of conserved epitopes to design a potential vaccine candidate against existing and emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 23;10(15):e35129. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35129. eCollection 2024 Aug 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39157328 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of B-Cell Epitopes for Eliciting Neutralizing Antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein through Bioinformatics and Monoclonal Antibody Targeting.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 14;23(8):4341. doi: 10.3390/ijms23084341. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35457159 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alphs H.H., Gambhira R., Karanam B., Roberts J.N., Jagu S., Schiller J.T., Zeng W., Jackson D.C., Roden R.B. Protection against heterologous human papillomavirus challenge by a synthetic lipopeptide vaccine containing a broadly cross-neutralizing epitope of L2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2008;105:5850–5855. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barnes C.O., Gristick H.B., Freund N.T., Escolano A., Lyubimov A.Y., Hartweger H., West A.P., Jr., Cohen A.E., Nussenzweig M.C., Bjorkman P.J. Structural characterization of a highly-potent V3-glycan broadly neutralizing antibody bound to natively-glycosylated HIV-1 envelope. Nat. Commun. 2018;9:1251. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barnes C.O., West A.P., Jr., Huey-Tubman K.E., Hoffmann M.A.G., Sharaf N.G., Hoffman P.R., Koranda N., Gristick H.B., Gaebler C., Muecksch F. Structures of Human Antibodies Bound to SARS-CoV-2 Spike Reveal Common Epitopes and Recurrent Features of Antibodies. Cell. 2020;182:828–842.e16. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

