TRPM3 Channels Play Roles in Heat Hypersensitivity and Spontaneous Pain after Nerve Injury
- PMID: 33478988
- PMCID: PMC7984590
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1551-20.2020
TRPM3 Channels Play Roles in Heat Hypersensitivity and Spontaneous Pain after Nerve Injury
Abstract
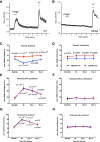
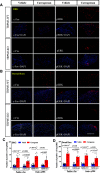
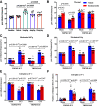
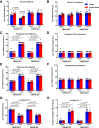
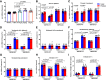
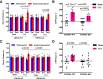
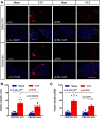
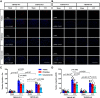
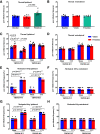
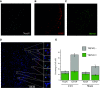
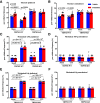
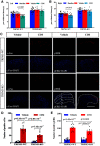
Transient receptor potential melastatin 3 (TRPM3) is a heat-activated ion channel in primary sensory neurons of the dorsal root ganglia (DRGs). Pharmacological and genetic studies implicated TRPM3 in various pain modalities, but TRPM3 inhibitors were not validated in TRPM3-/- mice. Here we tested two inhibitors of TRPM3 in male and female wild-type and TRPM3-/- mice in nerve injury-induced neuropathic pain. We found that intraperitoneal injection of either isosakuranetin or primidone reduced heat hypersensitivity induced by chronic constriction injury (CCI) of the sciatic nerve in wild-type, but not in TRPM3-/- mice. Primidone was also effective when injected locally in the hindpaw or intrathecally. Consistently, intrathecal injection of the TRPM3 agonist CIM0216 reduced paw withdrawal latency to radiant heat in wild-type, but not in TRPM3-/- mice. Intraperitoneal injection of 2 mg/kg, but not 0.5 mg/kg isosakuranetin, inhibited cold and mechanical hypersensitivity in CCI, both in wild-type and TRPM3-/- mice, indicating a dose-dependent off-target effect. Primidone had no effect on cold sensitivity, and only a marginal effect on mechanical hypersensitivity. Genetic deletion or inhibitors of TRPM3 reduced the increase in the levels of the early genes c-Fos and pERK in the spinal cord and DRGs in CCI mice, suggesting spontaneous activity of the channel. Intraperitoneal isosakuranetin also inhibited spontaneous pain related behavior in CCI in the conditioned place preference assay, and this effect was eliminated in TRPM3-/- mice. Overall, our data indicate a role of TRPM3 in heat hypersensitivity and in spontaneous pain after nerve injury.SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT Neuropathic pain is a major unsolved medical problem. The heat-activated TRPM3 ion channel is a potential target for novel pain medications, but the pain modalities in which it plays a role are not clear. Here we used a combination of genetic and pharmacological tools to assess the role of this channel in spontaneous pain, heat, cold, and mechanical hypersensitivity in a nerve injury model of neuropathic pain in mice. Our findings indicate a role for TRPM3 in heat hyperalgesia, and spontaneous pain, but not in cold and mechanical hypersensitivity. We also find that not only TRPM3 located in the peripheral nerve termini, but also TRPM3 in the spinal cord or proximal segments of DRG neurons are important for heat hypersensitivity.
Keywords: TRPM3; heat; pain.
Copyright © 2021 the authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The newest TRP channelopathy: Gain of function TRPM3 mutations cause epilepsy and intellectual disability.Channels (Austin). 2021 Dec;15(1):386-397. doi: 10.1080/19336950.2021.1908781. Channels (Austin). 2021. PMID: 33853504 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Downregulations of TRPM8 expression and membrane trafficking in dorsal root ganglion mediate the attenuation of cold hyperalgesia in CCI rats induced by GFRα3 knockdown.Brain Res Bull. 2017 Oct;135:8-24. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2017.08.002. Epub 2017 Sep 1. Brain Res Bull. 2017. PMID: 28867384
-
Promiscuous G-Protein-Coupled Receptor Inhibition of Transient Receptor Potential Melastatin 3 Ion Channels by Gβγ Subunits.J Neurosci. 2019 Oct 2;39(40):7840-7852. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0882-19.2019. Epub 2019 Aug 26. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31451581 Free PMC article.
-
FUS Contributes to Nerve Injury-Induced Nociceptive Hypersensitivity by Activating NF-κB Pathway in Primary Sensory Neurons.J Neurosci. 2023 Feb 15;43(7):1267-1278. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2082-22.2022. Epub 2023 Jan 10. J Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36627209 Free PMC article.
-
Transient receptor potential TRPM3 channels: Pharmacology, signaling, and biological functions.Pharmacol Res. 2017 Oct;124:92-99. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2017.07.014. Epub 2017 Jul 16. Pharmacol Res. 2017. PMID: 28720517 Review.
Cited by
-
Assessment of orofacial nociceptive behaviors of mice with the sheltering tube method: Oxaliplatin-induced mechanical and cold allodynia in orofacial regions.Mol Pain. 2024 Jan-Dec;20:17448069241261687. doi: 10.1177/17448069241261687. Mol Pain. 2024. PMID: 38818803 Free PMC article.
-
TRPM3, TRPM4, and TRPM5 as thermo-sensitive channels.J Physiol Sci. 2024 Sep 18;74(1):43. doi: 10.1186/s12576-024-00937-0. J Physiol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39294615 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The newest TRP channelopathy: Gain of function TRPM3 mutations cause epilepsy and intellectual disability.Channels (Austin). 2021 Dec;15(1):386-397. doi: 10.1080/19336950.2021.1908781. Channels (Austin). 2021. PMID: 33853504 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Partial Agonistic Actions of Sex Hormone Steroids on TRPM3 Function.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 20;22(24):13652. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413652. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34948452 Free PMC article.
-
TRPM3 Is Expressed in Afferent Bladder Neurons and Is Upregulated during Bladder Inflammation.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 22;23(1):107. doi: 10.3390/ijms23010107. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 35008533 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adriaenssens AE, Biggs EK, Darwish T, Tadross J, Sukthankar T, Girish M, Polex-Wolf J, Lam BY, Zvetkova I, Pan W, Chiarugi D, Yeo GSH, Blouet C, Gribble FM, Reimann F (2019) Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor-expressing cells in the hypothalamus regulate food intake. Cell Metab 30:987–996.e6. 10.1016/j.cmet.2019.07.013 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
