PI3K-driven HER2 expression is a potential therapeutic target in colorectal cancer stem cells
- PMID: 33436496
- PMCID: PMC8666826
- DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-323553
PI3K-driven HER2 expression is a potential therapeutic target in colorectal cancer stem cells
Abstract
Objective: Cancer stem cells are responsible for tumour spreading and relapse. Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) expression is a negative prognostic factor in colorectal cancer (CRC) and a potential target in tumours carrying the gene amplification. Our aim was to define the expression of HER2 in colorectal cancer stem cells (CR-CSCs) and its possible role as therapeutic target in CRC resistant to anti- epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) therapy.
Design: A collection of primary sphere cell cultures obtained from 60 CRC specimens was used to generate CR-CSC mouse avatars to preclinically validate therapeutic options. We also made use of the ChIP-seq analysis for transcriptional evaluation of HER2 activation and global RNA-seq to identify the mechanisms underlying therapy resistance.
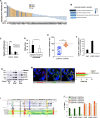
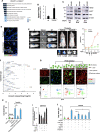
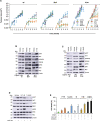
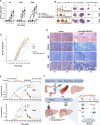
Results: Here we show that in CD44v6-positive CR-CSCs, high HER2 expression levels are associated with an activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT pathway, which promotes the acetylation at the regulatory elements of the Erbb2 gene. HER2 targeting in combination with phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) and mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MEK) inhibitors induces CR-CSC death and regression of tumour xenografts, including those carrying Kras and Pik3ca mutation. Requirement for the triple targeting is due to the presence of cancer-associated fibroblasts, which release cytokines able to confer CR-CSC resistance to PI3K/AKT inhibitors. In contrast, targeting of PI3K/AKT as monotherapy is sufficient to kill liver-disseminating CR-CSCs in a model of adjuvant therapy.
Conclusions: While PI3K targeting kills liver-colonising CR-CSCs, the concomitant inhibition of PI3K, HER2 and MEK is required to induce regression of tumours resistant to anti-EGFR therapies. These data may provide a rationale for designing clinical trials in the adjuvant and metastatic setting.
Keywords: antibody targeted therapy; colorectal cancer; drug resistance; stem cells.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Comment in
-
ERBB2 in anti-EGFR-resistant colorectal cancer: cancer stem cells come into play.Gut. 2022 Jan;71(1):4-5. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-323924. Epub 2021 Feb 22. Gut. 2022. PMID: 33619166 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Prostaglandin E2 Promotes Colorectal Cancer Stem Cell Expansion and Metastasis in Mice.Gastroenterology. 2015 Dec;149(7):1884-1895.e4. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.07.064. Epub 2015 Aug 7. Gastroenterology. 2015. PMID: 26261008 Free PMC article.
-
Receptor tyrosine kinase-dependent PI3K activation is an escape mechanism to vertical suppression of the EGFR/RAS/MAPK pathway in KRAS-mutated human colorectal cancer cell lines.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Jan 28;38(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1035-0. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30691487 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting chemoresistant colorectal cancer via systemic administration of a BMP7 variant.Oncogene. 2020 Jan;39(5):987-1003. doi: 10.1038/s41388-019-1047-4. Epub 2019 Oct 7. Oncogene. 2020. PMID: 31591478 Free PMC article.
-
Dual Inhibition of MEK and PI3K Pathway in KRAS and BRAF Mutated Colorectal Cancers.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Sep 23;16(9):22976-88. doi: 10.3390/ijms160922976. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26404261 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting PIK3CA Alterations in Hormone Receptor-Positive, Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-2-Negative Advanced Breast Cancer: New Therapeutic Approaches and Practical Considerations.Clin Breast Cancer. 2020 Aug;20(4):e439-e449. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2020.02.002. Epub 2020 Feb 20. Clin Breast Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32278641 Review.
Cited by
-
Integrated network pharmacology and experimental verification to investigate the mechanisms of YYFZBJS against colorectal cancer via CDK1/PI3K/Akt signaling.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 15;12:961653. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.961653. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36457504 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro and in vivo antineoplastic activities of solamargine in colorectal cancer through the suppression of PI3K/AKT pathway.Histol Histopathol. 2024 Oct;39(10):1317-1328. doi: 10.14670/HH-18-717. Epub 2024 Jan 31. Histol Histopathol. 2024. PMID: 38357981
-
Impact of KRAS mutation on the tumor microenvironment in colorectal cancer.Int J Biol Sci. 2024 Mar 3;20(5):1947-1964. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.88779. eCollection 2024. Int J Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38481800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The efficacy and potential mechanisms of pyrotinib in targeting EGFR and HER2 in advanced oral squamous cell carcinoma.BMC Oral Health. 2024 Aug 6;24(1):898. doi: 10.1186/s12903-024-04459-4. BMC Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 39107736 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Role of ERBB2 in Targeted Therapy for Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: Signaling Pathways to Therapeutic Strategies.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Oct 21;14(20):5160. doi: 10.3390/cancers14205160. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36291943 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Russo M, Siravegna G, Blaszkowsky LS, et al. . Tumor heterogeneity and lesion-specific response to targeted therapy in colorectal cancer. Cancer Discov 2016;6:147–53. 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-15-1283 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
