Cancer associated talin point mutations disorganise cell adhesion and migration
- PMID: 33431906
- PMCID: PMC7801617
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-77911-4
Cancer associated talin point mutations disorganise cell adhesion and migration
Abstract
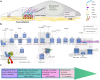
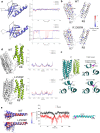
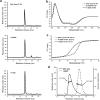
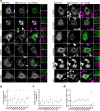
Talin-1 is a key component of the multiprotein adhesion complexes which mediate cell migration, adhesion and integrin signalling and has been linked to cancer in several studies. We analysed talin-1 mutations reported in the Catalogue of Somatic Mutations in Cancer database and developed a bioinformatics pipeline to predict the severity of each mutation. These predictions were then assessed using biochemistry and cell biology experiments. With this approach we were able to identify several talin-1 mutations affecting integrin activity, actin recruitment and Deleted in Liver Cancer 1 localization. We explored potential changes in talin-1 signalling responses by assessing impact on migration, invasion and proliferation. Altogether, this study describes a pipeline approach of experiments for crude characterization of talin-1 mutants in order to evaluate their functional effects and potential pathogenicity. Our findings suggest that cancer related point mutations in talin-1 can affect cell behaviour and so may contribute to cancer progression.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The talin head domain reinforces integrin-mediated adhesion by promoting adhesion complex stability and clustering.PLoS Genet. 2014 Nov 13;10(11):e1004756. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004756. eCollection 2014 Nov. PLoS Genet. 2014. PMID: 25393120 Free PMC article.
-
HDAC1/2 control mesothelium/ovarian cancer adhesive interactions impacting on Talin-1-α5β1-integrin-mediated actin cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix protein remodeling.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024 Jan 23;43(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s13046-023-02930-8. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38254102 Free PMC article.
-
FAK promotes recruitment of talin to nascent adhesions to control cell motility.J Cell Biol. 2012 Jan 23;196(2):223-32. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201108078. J Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22270917 Free PMC article.
-
Talin - the master of integrin adhesions.J Cell Sci. 2017 Aug 1;130(15):2435-2446. doi: 10.1242/jcs.190991. Epub 2017 Jul 12. J Cell Sci. 2017. PMID: 28701514 Review.
-
Talin: an emerging focal point of adhesion dynamics.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2004 Feb;16(1):94-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2003.11.007. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15037311 Review.
Cited by
-
The mechanical cell - the role of force dependencies in synchronising protein interaction networks.J Cell Sci. 2022 Nov 15;135(22):jcs259769. doi: 10.1242/jcs.259769. Epub 2022 Nov 18. J Cell Sci. 2022. PMID: 36398718 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrin-Mediated Tumorigenesis and Its Therapeutic Applications.Front Oncol. 2022 Feb 11;12:812480. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.812480. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35223494 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The C-terminal actin-binding domain of talin forms an asymmetric catch bond with F-actin.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Mar 8;119(10):e2109329119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2109329119. Epub 2022 Mar 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 35245171 Free PMC article.
-
Talin‑1 interaction network in cellular mechanotransduction (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2022 May;49(5):60. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2022.5116. Epub 2022 Mar 10. Int J Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35266014 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomics-Based Identification of Dysregulated Proteins and Biomarker Discovery in Invasive Ductal Carcinoma, the Most Common Breast Cancer Subtype.Proteomes. 2023 Apr 3;11(2):13. doi: 10.3390/proteomes11020013. Proteomes. 2023. PMID: 37092454 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hemmings L, et al. Talin contains three actin-binding sites each of which is adjacent to a vinculin-binding site. J. Cell. Sci. 1996;109(Pt 11):2715–2726. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

