N-Phenyl-6-Chloro-4-Hydroxy-2-Quinolone-3-CarboxAmides: Molecular Docking, Synthesis, and Biological Investigation as Anticancer Agents
- PMID: 33375766
- PMCID: PMC7795513
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26010073
N-Phenyl-6-Chloro-4-Hydroxy-2-Quinolone-3-CarboxAmides: Molecular Docking, Synthesis, and Biological Investigation as Anticancer Agents
Abstract
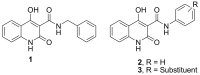
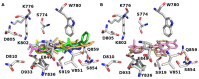
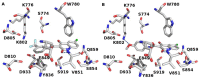
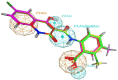
Cancer is a multifactorial disease and the second leading cause of death worldwide. Diverse factors induce carcinogenesis, such as diet, smoking, radiation, and genetic defects. The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3Kα) has emerged as an attractive target for anticancer drug design. Eighteen derivatives of N-phenyl-6-chloro-4-hydroxy-2-quinolone-3-carboxamide were synthesized and characterized using FT-IR, NMR (1H and 13C), and high-resolution mass spectra (HRMS). The series exhibited distinct antiproliferative activity (IC50 µM) against human epithelial colorectal adenocarcinoma (Caco-2) and colon carcinoma (HCT-116) cell lines, respectively: compounds 16 (37.4, 8.9 µM), 18 (50.9, 3.3 µM), 19 (17.0, 5.3 µM), and 21 (18.9, 4.9 µM). The induced-fit docking (IFD) studies against PI3Kαs showed that the derivatives occupy the PI3Kα binding site and engage with key binding residues.
Keywords: AKT; PI3Kα; anticancer; colon cancer; docking; quinolone-3-carboxamide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Molecular Modeling, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of N-Phenyl-4-Hydroxy-6-Methyl-2-Quinolone-3-CarboxAmides as Anticancer Agents.Molecules. 2020 Nov 16;25(22):5348. doi: 10.3390/molecules25225348. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33207767 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-Based Design: Synthesis, X-ray Crystallography, and Biological Evaluation of N-Substituted-4-Hydroxy-2-Quinolone-3-Carboxamides as Potential Cytotoxic Agents.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2018;18(2):263-276. doi: 10.2174/1871520617666170911171152. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 28901259
-
Benzoin Schiff Bases: Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation as Potential Antitumor Agents.Med Chem. 2018;14(7):695-708. doi: 10.2174/1573406414666180412160142. Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 29651943
-
Ligand-Based Drug Design: Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Substituted Benzoin Derivatives as Potential Antitumor Agents.Med Chem. 2019;15(4):417-429. doi: 10.2174/1573406414666180912111846. Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30207238
-
N-Phenyl-4-hydroxy-2-quinolone-3-carboxamides as selective inhibitors of mutant H1047R phosphoinositide-3-kinase (PI3Kα).Bioorg Med Chem. 2012 Dec 15;20(24):7175-83. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2012.09.059. Epub 2012 Oct 12. Bioorg Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 23121722
Cited by
-
Synthesis and α-Glucosidase Inhibition Activity of 2-[3-(Benzoyl/4-bromobenzoyl)-4-hydroxy-1,1-dioxido-2H-benzo[e][1,2]thiazin-2-yl]-N-arylacetamides: An In Silico and Biochemical Approach.Molecules. 2021 May 20;26(10):3043. doi: 10.3390/molecules26103043. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34065194 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Cyclic Sulfonamides with an N-Arylacetamide Group as α-Glucosidase and α-Amylase Inhibitors: Biological Evaluation and Molecular Modeling.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Jan 17;15(1):106. doi: 10.3390/ph15010106. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35056163 Free PMC article.
-
BiCl3-catalyzed green synthesis of 4-hydroxy-2-quinolone analogues under microwave irradiation.RSC Adv. 2023 Sep 21;13(40):28030-28041. doi: 10.1039/d3ra05289c. eCollection 2023 Sep 18. RSC Adv. 2023. PMID: 37746335 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Investigation of the Antitumor Effects of Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors in Breast Cancer Cells.Biomed Res Int. 2023 Oct 5;2023:2592691. doi: 10.1155/2023/2592691. eCollection 2023. Biomed Res Int. 2023. PMID: 37841082 Free PMC article.
-
Design and Synthesis of Thionated Levofloxacin: Insights into a New Generation of Quinolones with Potential Therapeutic and Analytical Applications.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2022 Oct 3;44(10):4626-4638. doi: 10.3390/cimb44100316. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 36286031 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

