Sterols and Triterpenes: Antiviral Potential Supported by In-Silico Analysis
- PMID: 33375282
- PMCID: PMC7823815
- DOI: 10.3390/plants10010041
Sterols and Triterpenes: Antiviral Potential Supported by In-Silico Analysis
Abstract
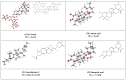
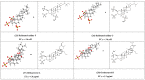
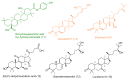
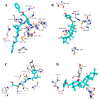
The acute respiratory syndrome caused by the novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) caused severe panic all over the world. The coronavirus (COVID-19) outbreak has already brought massive human suffering and major economic disruption and unfortunately, there is no specific treatment for COVID-19 so far. Herbal medicines and purified natural products can provide a rich resource for novel antiviral drugs. Therefore, in this review, we focused on the sterols and triterpenes as potential candidates derived from natural sources with well-reported in vitro efficacy against numerous types of viruses. Moreover, we compiled from these reviewed compounds a library of 162 sterols and triterpenes that was subjected to a computer-aided virtual screening against the active sites of the recently reported SARS-CoV-2 protein targets. Interestingly, the results suggested some compounds as potential drug candidates for the development of anti-SARS-CoV-2 therapeutics.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; antiviral potential; sterols; triterpenes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures











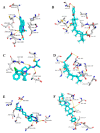
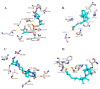
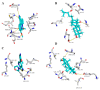
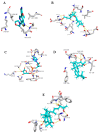
Similar articles
-
Current status of antivirals and druggable targets of SARS CoV-2 and other human pathogenic coronaviruses.Drug Resist Updat. 2020 Dec;53:100721. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2020.100721. Epub 2020 Aug 26. Drug Resist Updat. 2020. PMID: 33132205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In silico approach of secondary metabolites from Brazilian herbal medicines to search for potential drugs against SARS-CoV-2.Phytother Res. 2021 Aug;35(8):4297-4308. doi: 10.1002/ptr.7097. Epub 2021 Apr 1. Phytother Res. 2021. PMID: 33797123 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of novel compounds against three targets of SARS CoV-2 coronavirus by combined virtual screening and supervised machine learning.Comput Biol Med. 2021 Jun;133:104359. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104359. Epub 2021 Mar 30. Comput Biol Med. 2021. PMID: 33845270 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial Metabolites: The Emerging Hotspot of Antiviral Compounds as Potential Candidates to Avert Viral Pandemic Alike COVID-19.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Sep 7;8:732256. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.732256. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34557521 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current Strategies of Antiviral Drug Discovery for COVID-19.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 May 13;8:671263. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.671263. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34055887 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Wound Healing and Antioxidant Capabilities of Zizyphus mauritiana Fruits: In-Vitro, In-Vivo, and Molecular Modeling Study.Plants (Basel). 2022 May 24;11(11):1392. doi: 10.3390/plants11111392. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35684165 Free PMC article.
-
Strong Inhibitory Activity and Action Modes of Synthetic Maslinic Acid Derivative on Highly Pathogenic Coronaviruses: COVID-19 Drug Candidate.Pathogens. 2021 May 19;10(5):623. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10050623. Pathogens. 2021. PMID: 34069460 Free PMC article.
-
New cytotoxic dammarane type saponins from Ziziphus spina-christi.Sci Rep. 2023 Nov 23;13(1):20612. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-46841-2. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37996449 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 spike protein with phytoconstituents of Momordica charantia.J Ovarian Res. 2021 Sep 27;14(1):126. doi: 10.1186/s13048-021-00872-3. J Ovarian Res. 2021. PMID: 34579761 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro Anti-Oxidant, In Vivo Anti-Hyperglycemic, and Untargeted Metabolomics-Aided-In Silico Screening of Macroalgae Lipophilic Extracts for Anti-Diabetes Mellitus and Anti-COVID-19 Potential Metabolites.Metabolites. 2023 Nov 27;13(12):1177. doi: 10.3390/metabo13121177. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 38132859 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vil V.A., Terent’ev A.O., Savidov N., Gloriozova T.A., Poroikov V.V., Pounina T.A., Dembitsky V.M. Hydroperoxy steroids and triterpenoids derived from plant and fungi: Origin, structures, and biological activities. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019;190:76–87. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2019.03.020. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Withering W. An Account of the Foxglove, and Some of Its Medical Uses. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge, UK: 2014.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

