Effects of ALA-PDT on the Healing of Mouse Skin Wounds Infected With Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Its Related Mechanisms
- PMID: 33344449
- PMCID: PMC7746815
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2020.585132
Effects of ALA-PDT on the Healing of Mouse Skin Wounds Infected With Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Its Related Mechanisms
Abstract
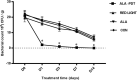
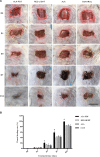
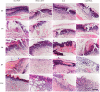
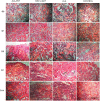
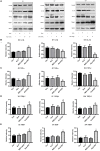
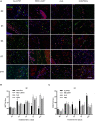
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a promising new method to eliminate microbial infection and promote wound healing. Its effectiveness has been confirmed by some studies; however, the mechanisms of PDT in wound healing remain obscure. We used mouse skin wounds infected with Pseudomonas aeruginosa as a research object to explore the therapeutic effects and mechanisms of 5-aminolevulinic acid photodynamic therapy (ALA-PDT). ALA-PDT treatment significantly reduced the load of P. aeruginosa in the wound and surrounding tissues and promoted the healing of skin wounds in mice. Hematoxylin-eosin (HE) and Sirius red staining showed that ALA-PDT promoted granulation tissue formation, angiogenesis, and collagen regeneration and remodeling. After ALA-PDT treatment, the expression of inflammatory factors (TNF-α and IL-1β) first increased and then decreased, while the secretion of growth factors (TGF-β-1 and VEGF) increased gradually after treatment. Furthermore, ALA-PDT affected the polarization state of macrophages, activating and promoting macrophages from an M1 to an M2 phenotype. In conclusion, ALA-PDT can not only kill bacteria but also promote wound healing by regulating inflammatory factors, collagen remodeling and macrophages. This study further clarifies the mechanism of PDT in the healing of infectious skin wounds and provides further experimental evidence for its clinical treatment of skin wounds infected by P. aeruginosa.
Keywords: Pseudomonas aeruginosa; inflammatory factor; macrophagocyte; photodynamic therapy; wound healing.
Copyright © 2020 Yang, Tan, Zhang, Yang, Luo, Chen, Liu, Yang and Lei.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of ALA-PDT on the macrophages in wound healing and its related mechanisms in vivo and in vitro.Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2022 Jun;38:102816. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2022.102816. Epub 2022 Apr 1. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2022. PMID: 35378277
-
Efficacy of the therapy of 5-aminolevulinic acid photodynamic therapy combined with human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus-infected wound in a diabetic mouse model.Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2021 Dec;36:102480. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2021.102480. Epub 2021 Aug 8. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2021. PMID: 34375775
-
5-aminolevulinic acid photodynamic therapy for chronic wound infection in rats with diabetes.Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Sep;178:117132. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.117132. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 39047418
-
Research Progress of Photodynamic Therapy in Wound Healing: A Literature Review.J Burn Care Res. 2023 Nov 2;44(6):1327-1333. doi: 10.1093/jbcr/irad146. J Burn Care Res. 2023. PMID: 37747820 Review.
-
Cellular Mechanisms in Acute and Chronic Wounds after PDT Therapy: An Update.Biomedicines. 2022 Jul 7;10(7):1624. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10071624. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35884929 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Accelerating skin regeneration and wound healing by controlled ROS from photodynamic treatment.Inflamm Regen. 2022 Oct 4;42(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s41232-022-00226-6. Inflamm Regen. 2022. PMID: 36192814 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Photodynamic Therapy, Probiotics, Acetic Acid, and Essential Oil in the Treatment of Chronic Wounds Infected with Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jun 13;15(6):1721. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15061721. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37376169 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Photodynamic disinfection and its role in controlling infectious diseases.Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2021 Nov;20(11):1497-1545. doi: 10.1007/s43630-021-00102-1. Epub 2021 Oct 27. Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34705261 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TGF-β1 mediates tumor immunosuppression aggravating at the late stage post-high-light-dose photodynamic therapy.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2023 Sep;72(9):3079-3095. doi: 10.1007/s00262-023-03479-3. Epub 2023 Jun 23. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2023. PMID: 37351605 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of inflammation during wound healing: the function of mesenchymal stem cells and strategies for therapeutic enhancement.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Feb 15;15:1345779. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1345779. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38425646 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cappugi P., Comacchi C., Torchia D. (2014). Photodynamic therapy for chronic venous ulcers. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat 22 129–131. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

