Rheological and Drug Delivery Characteristics of Poloxamer-Based Diclofenac Sodium Formulations for Chronic Wound Site Analgesia
- PMID: 33333773
- PMCID: PMC7765230
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12121214
Rheological and Drug Delivery Characteristics of Poloxamer-Based Diclofenac Sodium Formulations for Chronic Wound Site Analgesia
Abstract
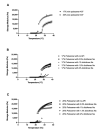
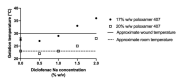
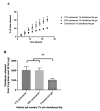
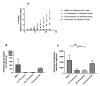
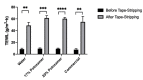
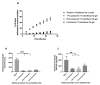
Chronic wounds are a significant and growing health problem, and clinical treatment is often a painful experience. A topical dosage form would be optimal to treat this pain. Poloxamer 407, a thermosensitive polymer that is a liquid at low temperatures but gels at higher temperatures, is well suited to administer topical analgesics to chronic wound sites. The goal of this study was to evaluate the gelation and drug delivery properties of poloxamer 407 gels containing diclofenac sodium for potential use in chronic wound analgesic delivery. The gelation properties of poloxamer formulations were evaluated rheologically. Drug delivery properties of poloxamers loaded with diclofenac sodium were evaluated using snakeskin dialysis membranes, intact porcine ear skin, and porcine ear skin impaired via tape stripping. A commercial gel product and a solution of diclofenac sodium in water were used as control formulations. Poloxamer concentration and gelation temperature varied inversely, and the addition of higher concentrations of diclofenac sodium correlated to significant increases in poloxamer gelation temperature. Poloxamer solutions were effective in limiting the permeation of diclofenac sodium through membranes with impaired barrier properties, and delivery of diclofenac sodium from poloxamer 407 did not vary significantly from delivery observed from the commercial gel product. The amount of drug delivered in 24 h did not change significantly with changes in poloxamer 407 concentration. The results of this study indicate that poloxamer 407 may be a useful formulation component for administration of an analgesic product to a chronic wound site.
Keywords: analgesia; chronic wounds; poloxamer; thermogelation; topical.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
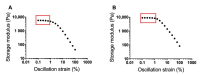
Similar articles
-
Effect of Salt Form on Gelation and Drug Delivery Properties of Diclofenac-Loaded Poloxamer Gels for Delivery to Impaired Skin.Pharm Res. 2022 Oct;39(10):2515-2527. doi: 10.1007/s11095-022-03356-1. Epub 2022 Aug 24. Pharm Res. 2022. PMID: 36002613 Free PMC article.
-
Physicochemical characterization of diclofenac sodium-loaded poloxamer gel as a rectal delivery system with fast absorption.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2003 May;29(5):545-53. doi: 10.1081/ddc-120018643. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2003. PMID: 12779284
-
Effect of sodium chloride on the gelation temperature, gel strength and bioadhesive force of poloxamer gels containing diclofenac sodium.Int J Pharm. 2001 Sep 11;226(1-2):195-205. doi: 10.1016/s0378-5173(01)00809-2. Int J Pharm. 2001. PMID: 11532582
-
Effect of sodium chloride on the release, absorption and safety of diclofenac sodium delivered by poloxamer gel.Int J Pharm. 2003 Sep 16;263(1-2):105-11. doi: 10.1016/s0378-5173(03)00362-4. Int J Pharm. 2003. PMID: 12954185
-
Formulation strategies to modulate drug release from poloxamer based in situ gelling systems.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2020 Apr;17(4):495-509. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2020.1731469. Epub 2020 Feb 23. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2020. PMID: 32067500 Review.
Cited by
-
Thermosensitive biomaterial gels with chemical permeation enhancers for enhanced microneedle delivery of naltrexone for managing opioid and alcohol dependency.Biomater Sci. 2023 Aug 22;11(17):5846-5858. doi: 10.1039/d3bm00972f. Biomater Sci. 2023. PMID: 37455601 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound and x-ray imageable poloxamer-based hydrogel for loco-regional therapy delivery in the liver.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 3;14(1):20455. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-70992-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39227382 Free PMC article.
-
Thermosensitive Gels Used to Improve Microneedle-Assisted Transdermal Delivery of Naltrexone.Polymers (Basel). 2021 Mar 18;13(6):933. doi: 10.3390/polym13060933. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33803552 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound and x-ray imageable poloxamer-based hydrogel for loco-regional therapy delivery in the liver.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 27:rs.3.rs-4555123. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-4555123/v1. Res Sq. 2024. Update in: Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 3;14(1):20455. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-70992-5. PMID: 38978563 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Monoketonic Curcuminoid-Lidocaine Co-Deliver Using Thermosensitive Organogels: From Drug Synthesis to Epidermis Structural Studies.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Jan 27;14(2):293. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14020293. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35214026 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lawton S. Skin 1: The structure and functions of the skin. Nurs. Times. 2019;115:30–33.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

