Nitric Oxide Circumvents Virus-Mediated Metabolic Regulation during Human Cytomegalovirus Infection
- PMID: 33323506
- PMCID: PMC7773989
- DOI: 10.1128/mBio.02630-20
Nitric Oxide Circumvents Virus-Mediated Metabolic Regulation during Human Cytomegalovirus Infection
Abstract
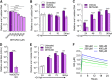
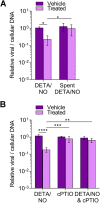
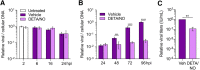
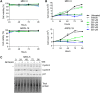
Nitric oxide is a versatile and critical effector molecule that can modulate many cellular functions. Although recognized as a regulator of infections, the inhibitory mechanism of nitric oxide against human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) replication remains elusive. We demonstrate that nitric oxide attenuates viral replication by interfering with HCMV-mediated modulation of several cellular processes. Nitric oxide exposure reduced HCMV genome synthesis and infectious viral progeny with cell-type-dependent differences observed. Mitochondrial respiration was severely reduced in both uninfected and HCMV-infected cells during exposure with little impact on ATP levels indicating changes in cellular metabolism. Metabolomics identified significantly altered small molecules in multiple pathways during nitric oxide exposure including nucleotide biosynthesis, tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, and glutamine metabolism. Glutathione metabolites were increased coinciding with a reduction in the glutathione precursor glutamine. This shift was accompanied by increased antioxidant enzymes. Glutamine deprivation mimicked defects in HCMV replication and mitochondrial respiration observed during nitric oxide exposure. These data suggest that nitric oxide limits glutaminolysis by shuttling glutamine to glutathione synthesis. In addition, lipid intermediates were severely altered, which likely contributes to the observed increase in defective viral particles. Nitric oxide disrupts multiple cellular processes, and we had limited success in rescuing replication defects by supplementing with metabolic intermediates. Our studies indicate that nitric oxide attenuation of HCMV is multifactorial with interference in viral manipulation of cellular metabolism playing a central role.IMPORTANCE Human cytomegalovirus is a prevalent pathogen that can cause serious disease in patients with compromised immune systems, including transplant patients and during congenital infection. HCMV lytic replication likely occurs in localized sites of infection with immune cells infiltrating and releasing nitric oxide with other effector molecules. This nonspecific immune response results in both uninfected and infected cells exposed to high levels of nitric oxide. The absence of nitric oxide synthase has been associated with lethal HCMV infection. We demonstrate that nitric oxide inhibition of HCMV replication is multifactorial and cell type dependent. Our results indicate that nitric oxide controls replication by interfering with viral modulation of cellular metabolism while also affecting proliferation and mitochondrial respiration of neighboring uninfected cells. These studies identify the mechanism and contribution of nitric oxide during immune control of HCMV infection and provide insight into its role in other viral infections.
Keywords: TCA cycle; cytomegalovirus; glutaminolysis; metabolism; mitochondrial respiration; nitric oxide.
Copyright © 2020 Mokry et al.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nitric Oxide Attenuates Human Cytomegalovirus Infection yet Disrupts Neural Cell Differentiation and Tissue Organization.J Virol. 2022 Jul 27;96(14):e0012622. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00126-22. Epub 2022 Jul 7. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 35862705 Free PMC article.
-
Human Cytomegalovirus pUL37x1 Is Important for Remodeling of Host Lipid Metabolism.J Virol. 2019 Oct 15;93(21):e00843-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00843-19. Print 2019 Nov 1. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 31391267 Free PMC article.
-
Human Cytomegalovirus Infection Upregulates the Mitochondrial Transcription and Translation Machineries.mBio. 2016 Mar 29;7(2):e00029. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00029-16. mBio. 2016. PMID: 27025248 Free PMC article.
-
Viral effects on metabolism: changes in glucose and glutamine utilization during human cytomegalovirus infection.Trends Microbiol. 2011 Jul;19(7):360-7. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2011.04.002. Epub 2011 May 12. Trends Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21570293 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human cytomegalovirus riding the cell cycle.Med Microbiol Immunol. 2015 Jun;204(3):409-19. doi: 10.1007/s00430-015-0396-z. Epub 2015 Mar 17. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25776080 Review.
Cited by
-
Computational modeling of protracted HCMV replication using genome substrates and protein temporal profiles.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Aug 30;119(35):e2201787119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2201787119. Epub 2022 Aug 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 35994667 Free PMC article.
-
Nitric Oxide Attenuates Human Cytomegalovirus Infection yet Disrupts Neural Cell Differentiation and Tissue Organization.J Virol. 2022 Jul 27;96(14):e0012622. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00126-22. Epub 2022 Jul 7. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 35862705 Free PMC article.
-
Utility of NO and H2S donating platforms in managing COVID-19: Rationale and promise.Nitric Oxide. 2022 Nov 1;128:72-102. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2022.08.003. Epub 2022 Aug 24. Nitric Oxide. 2022. PMID: 36029975 Free PMC article. Review.
-
β-Cell-selective regulation of gene expression by nitric oxide.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2024 Jun 1;326(6):R552-R566. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00240.2023. Epub 2024 Apr 8. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38586887 Free PMC article.
-
The Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System, Nitric Oxide, and Hydrogen Sulfide at the Crossroads of Hypertension and COVID-19: Racial Disparities and Outcomes.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 11;23(22):13895. doi: 10.3390/ijms232213895. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430371 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mocarski E, Shenk T, Pass R. 2007. Cytomegaloviruses, p 2701–2772. In Knipe DM, Howley PM, Griffin DE, Lamb RA, Martin MA, Roizman B, Straus SE (ed), Fields virology, 5th ed. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, PA.
-
- Sinzger C, Digel M, Jahn G. 2008. Cytomegalovirus cell tropism, p 63–83. In Shenk TE, Stinski MF (ed), Human cytomegalovirus. Springer, Berlin, Germany. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
