Baricitinib treatment resolves lower-airway macrophage inflammation and neutrophil recruitment in SARS-CoV-2-infected rhesus macaques
- PMID: 33278358
- PMCID: PMC7654323
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.11.007
Baricitinib treatment resolves lower-airway macrophage inflammation and neutrophil recruitment in SARS-CoV-2-infected rhesus macaques
Abstract
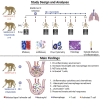
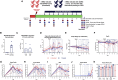
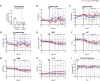
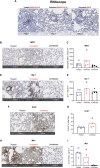
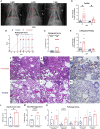
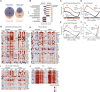
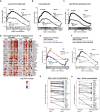
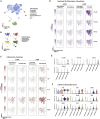
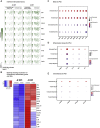
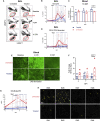
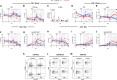
SARS-CoV-2-induced hypercytokinemia and inflammation are critically associated with COVID-19 severity. Baricitinib, a clinically approved JAK1/JAK2 inhibitor, is currently being investigated in COVID-19 clinical trials. Here, we investigated the immunologic and virologic efficacy of baricitinib in a rhesus macaque model of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Viral shedding measured from nasal and throat swabs, bronchoalveolar lavages, and tissues was not reduced with baricitinib. Type I interferon (IFN) antiviral responses and SARS-CoV-2-specific T cell responses remained similar between the two groups. Animals treated with baricitinib showed reduced inflammation, decreased lung infiltration of inflammatory cells, reduced NETosis activity, and more limited lung pathology. Importantly, baricitinib-treated animals had a rapid and remarkably potent suppression of lung macrophage production of cytokines and chemokines responsible for inflammation and neutrophil recruitment. These data support a beneficial role for, and elucidate the immunological mechanisms underlying, the use of baricitinib as a frontline treatment for inflammation induced by SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; baricitinib; immune activation; immunology; inflammation; nonhuman primate; pathogenesis.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests R.F.S. served as an unpaid consultant for Eli Lilly whose drugs are being evaluated in the research described in this paper. In addition, R.F.S. owns shares in Eli Lilly. The terms of this arrangement have been reviewed and approved by Emory University in accordance with its conflict of interest policies. Eli Lilly had no role in the design of this study and did not have any role during its execution, analyses, interpretation of the data, or decision to submit results. All other authors do not have any conflicts to declare.
Figures



Update of
-
Baricitinib treatment resolves lower airway inflammation and neutrophil recruitment in SARS-CoV-2-infected rhesus macaques.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 Sep 16:2020.09.16.300277. doi: 10.1101/2020.09.16.300277. bioRxiv. 2020. Update in: Cell. 2021 Jan 21;184(2):460-475.e21. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.11.007. PMID: 32995780 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Baricitinib treatment resolves lower airway inflammation and neutrophil recruitment in SARS-CoV-2-infected rhesus macaques.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 Sep 16:2020.09.16.300277. doi: 10.1101/2020.09.16.300277. bioRxiv. 2020. Update in: Cell. 2021 Jan 21;184(2):460-475.e21. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.11.007. PMID: 32995780 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Baricitinib restrains the immune dysregulation in patients with severe COVID-19.J Clin Invest. 2020 Dec 1;130(12):6409-6416. doi: 10.1172/JCI141772. J Clin Invest. 2020. PMID: 32809969 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Baricitinib: A Review of Pharmacology, Safety, and Emerging Clinical Experience in COVID-19.Pharmacotherapy. 2020 Aug;40(8):843-856. doi: 10.1002/phar.2438. Epub 2020 Jul 27. Pharmacotherapy. 2020. PMID: 32542785 Free PMC article. Review.
-
JAK inhibition during the early phase of SARS-CoV-2 infection worsens kidney injury by suppressing endogenous antiviral activity in mice.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2024 Jun 1;326(6):F931-F941. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00011.2024. Epub 2024 Apr 18. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38634132 Free PMC article.
-
Janus kinase signaling as risk factor and therapeutic target for severe SARS-CoV-2 infection.Eur J Immunol. 2021 May;51(5):1071-1075. doi: 10.1002/eji.202149173. Epub 2021 Mar 22. Eur J Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33675065 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Care of the Seriously Ill Patient with SARS-CoV-2.Med Clin North Am. 2022 Nov;106(6):949-960. doi: 10.1016/j.mcna.2022.08.002. Epub 2022 Aug 10. Med Clin North Am. 2022. PMID: 36280338 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19 and the potential of Janus family kinase (JAK) pathway inhibition: A novel treatment strategy.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Aug 30;9:961027. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.961027. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36111104 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19 as a mediator of interferon deficiency and hyperinflammation: Rationale for the use of JAK1/2 inhibitors in combination with interferon.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2021 Aug;60:28-45. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2021.03.006. Epub 2021 Apr 14. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2021. PMID: 33992887 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Monitoring and immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 vaccination of laboratory rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta).Sci Rep. 2023 Feb 25;13(1):3274. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-30473-7. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36841887 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of baricitinib plus standard of care for the treatment of critically ill hospitalised adults with COVID-19 on invasive mechanical ventilation or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: an exploratory, randomised, placebo-controlled trial.Lancet Respir Med. 2022 Apr;10(4):327-336. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00006-6. Epub 2022 Feb 3. Lancet Respir Med. 2022. PMID: 35123660 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AI116379/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AI120134/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008169/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI143411/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD025002/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD026799/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL140223/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI149672/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH116695/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P51 OD011092/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI050409/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI141258/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P51 OD011132/OD/NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

