Engineering precision nanoparticles for drug delivery
- PMID: 33277608
- PMCID: PMC7717100
- DOI: 10.1038/s41573-020-0090-8
Engineering precision nanoparticles for drug delivery
Abstract
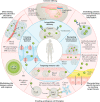
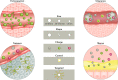
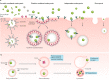
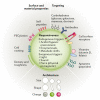
In recent years, the development of nanoparticles has expanded into a broad range of clinical applications. Nanoparticles have been developed to overcome the limitations of free therapeutics and navigate biological barriers - systemic, microenvironmental and cellular - that are heterogeneous across patient populations and diseases. Overcoming this patient heterogeneity has also been accomplished through precision therapeutics, in which personalized interventions have enhanced therapeutic efficacy. However, nanoparticle development continues to focus on optimizing delivery platforms with a one-size-fits-all solution. As lipid-based, polymeric and inorganic nanoparticles are engineered in increasingly specified ways, they can begin to be optimized for drug delivery in a more personalized manner, entering the era of precision medicine. In this Review, we discuss advanced nanoparticle designs utilized in both non-personalized and precision applications that could be applied to improve precision therapies. We focus on advances in nanoparticle design that overcome heterogeneous barriers to delivery, arguing that intelligent nanoparticle design can improve efficacy in general delivery applications while enabling tailored designs for precision applications, thereby ultimately improving patient outcome overall.
Conflict of interest statement
A list of entities with which R.L. is involved, compensated or uncompensated, can be found in the Supplementary information. M.J.M., M.M.B., R.M.H., M.E.W. and N.A.P. declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nanomedicine-based neuroprotective strategies in patient specific-iPSC and personalized medicine.Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Mar 4;15(3):3904-25. doi: 10.3390/ijms15033904. Int J Mol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24599081 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineering nano-drug biointerface to overcome biological barriers toward precision drug delivery.J Nanobiotechnology. 2022 Aug 31;20(1):395. doi: 10.1186/s12951-022-01605-4. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022. PMID: 36045386 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Overview of Drug Delivery Systems.Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2059:1-54. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9798-5_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 31435914 Review.
-
Engineered nanoparticles in non-invasive insulin delivery for precision therapeutics of diabetes.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Aug;275(Pt 1):133437. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.133437. Epub 2024 Jun 27. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 38944087 Review.
-
Recent developments in polymeric nanoparticle engineering and their applications in experimental and clinical oncology.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2006 Nov;6(6):553-561. doi: 10.2174/187152006778699130. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2006. PMID: 17100563 Review.
Cited by
-
Folate-engineered chitosan nanoparticles: next-generation anticancer nanocarriers.Mol Cancer. 2024 Oct 31;23(1):244. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-02163-z. Mol Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39482651 Review.
-
Harnessing extracellular vesicle heterogeneity for diagnostic and therapeutic applications.Nat Nanotechnol. 2024 Oct 28. doi: 10.1038/s41565-024-01774-3. Online ahead of print. Nat Nanotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39468355 Review.
-
Recent Updates on Diverse Nanoparticles and Nanostructures in Therapeutic and Diagnostic Applications with Special Focus on Smart Protein Nanoparticles: A Review.ACS Omega. 2024 Oct 10;9(42):42613-42629. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c05037. eCollection 2024 Oct 22. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 39464472 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Precious Cargo: The Role of Polymeric Nanoparticles in the Delivery of Covalent Drugs.Molecules. 2024 Oct 19;29(20):4949. doi: 10.3390/molecules29204949. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39459317 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhancing Drug Solubility, Bioavailability, and Targeted Therapeutic Applications through Magnetic Nanoparticles.Molecules. 2024 Oct 13;29(20):4854. doi: 10.3390/molecules29204854. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39459222 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- The White House Office of the Press Secretary. National Nanotechnology Initiative: leading to the next industrial revolution. White Househttps://clintonwhitehouse4.archives.gov/WH/New/html/20000121_4.html (2000).
-
- Mitragotri S, et al. Drug delivery research for the future: expanding the nano horizons and beyond. J. Control. Release. 2017;246:183–184. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

