Evidence of exposure to SARS-CoV-2 in cats and dogs from households in Italy
- PMID: 33277505
- PMCID: PMC7718263
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-20097-0
Evidence of exposure to SARS-CoV-2 in cats and dogs from households in Italy
Abstract
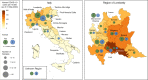
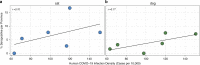
SARS-CoV-2 emerged from animals and is now easily transmitted between people. Sporadic detection of natural cases in animals alongside successful experimental infections of pets, such as cats, ferrets and dogs, raises questions about the susceptibility of animals under natural conditions of pet ownership. Here, we report a large-scale study to assess SARS-CoV-2 infection in 919 companion animals living in northern Italy, sampled at a time of frequent human infection. No animals tested PCR positive. However, 3.3% of dogs and 5.8% of cats had measurable SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody titers, with dogs from COVID-19 positive households being significantly more likely to test positive than those from COVID-19 negative households. Understanding risk factors associated with this and their potential to infect other species requires urgent investigation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Update of
-
Evidence of exposure to SARS-CoV-2 in cats and dogs from households in Italy.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 Jul 23:2020.07.21.214346. doi: 10.1101/2020.07.21.214346. bioRxiv. 2020. Update in: Nat Commun. 2020 Dec 4;11(1):6231. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-20097-0 PMID: 32743588 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
Evidence of exposure to SARS-CoV-2 in cats and dogs from households in Italy.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 Jul 23:2020.07.21.214346. doi: 10.1101/2020.07.21.214346. bioRxiv. 2020. Update in: Nat Commun. 2020 Dec 4;11(1):6231. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-20097-0 PMID: 32743588 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Host traits, ownership behaviour and risk factors of SARS-CoV-2 infection in domestic pets in Mexico.Zoonoses Public Health. 2023 Jun;70(4):327-340. doi: 10.1111/zph.13030. Epub 2023 Feb 9. Zoonoses Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36757053
-
Investigation of SARS-CoV-2 infection in dogs and cats of humans diagnosed with COVID-19 in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil.PLoS One. 2021 Apr 28;16(4):e0250853. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0250853. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33909706 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding the prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) exposure in companion, captive, wild, and farmed animals.Virulence. 2021 Dec;12(1):2777-2786. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2021.1996519. Virulence. 2021. PMID: 34696707 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[SARS-CoV-2 infections in cats, dogs, and other animal species: Findings on infection and data from Switzerland].Schweiz Arch Tierheilkd. 2021 Dec;163(12):821-835. doi: 10.17236/sat00329. Schweiz Arch Tierheilkd. 2021. PMID: 34881715 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Demonstration of SARS-CoV-2 Exposure in Korean Native Cattle and Korean Native Black Goats in Korea.Animals (Basel). 2023 Nov 13;13(22):3498. doi: 10.3390/ani13223498. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38003116 Free PMC article.
-
A pre- and during Pandemic Survey of Sars-Cov-2 Infection in Stray Colony and Shelter Cats from a High Endemic Area of Northern Italy.Viruses. 2021 Apr 3;13(4):618. doi: 10.3390/v13040618. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 33916759 Free PMC article.
-
Possible Human-to-Dog Transmission of SARS-CoV-2, Italy, 2020.Emerg Infect Dis. 2021;27(7):1981-1984. doi: 10.3201/eid2707.204959. Epub 2021 May 12. Emerg Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 33979566 Free PMC article.
-
The role of receptors in the cross-species spread of coronaviruses infecting humans and pigs.Arch Virol. 2024 Jan 24;169(2):35. doi: 10.1007/s00705-023-05956-7. Arch Virol. 2024. PMID: 38265497 Review.
-
Rapid evolution of SARS-CoV-2 in domestic cats.Virus Evol. 2022 Sep 30;8(2):veac092. doi: 10.1093/ve/veac092. eCollection 2022. Virus Evol. 2022. PMID: 36398096 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization, https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situatio.... Accessed on July 10th, 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

