Cost of Diabetic Foot Ulcer Management in China: A 7-Year Single-Center Retrospective Review
- PMID: 33204131
- PMCID: PMC7667006
- DOI: 10.2147/DMSO.S275814
Cost of Diabetic Foot Ulcer Management in China: A 7-Year Single-Center Retrospective Review
Abstract
Background: The cost of care for diabetic foot ulcers has became a global economic burden. The study aimed to analyze diabetic foot ulcer cost changes over time and to identify factors associated with these variables, so as to strengthen and improve the management of diabetic foot ulcers.
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed the data in the electronic medical record system of our wound treatment center. The homepage of the system was queried using the national clinical version 2.0 disease diagnosis code (ICD-10), the data of patient's basic information were exported. Through the statistics and analysis of these data, the socioeconomic changes and possible risk factors of diabetic foot ulcers management in recent years were obtained.
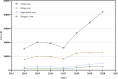
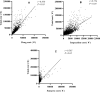
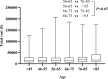
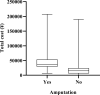
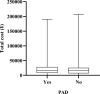
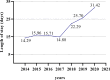
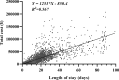
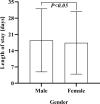
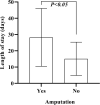
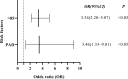
Results: There were 3654 patients included in the study, an average of 522 per year. The total cost per patient increased from ¥15,535.58 in 2014 to ¥42,040.60 in 2020, with an average of ¥21,826.91. The average length of stay between 14.29 days and 31.4 days from 2014 to 2020, with an average of 18.10 days. Besides, the average incidence of peripheral arterial disease in diabetic foot ulcers patients admitted was as high as 81.9%, and the average amputation rate was 9.9%. The study reflected the total cost and length of stay of diabetic foot patients increased significantly from 2014 to 2020, which were related to age (>85 years), gender (male), peripheral arterial disease, amputation (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: A heavy cost from diabetic foot ulcers and its complications was significantly increased yearly, which was related to older age, co-morbidity, amputation and duration of hospitalization. The prevention and treatment of diabetic foot ulcers have a long way to go, early comprehensive prevention and multi-disciplinary cooperation may still be an effective way.
Keywords: cost; diabetic foot ulcers; electronic medical record system; multi-disciplinary; retrospective analysis; socioeconomic.
© 2020 Lu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Poorly designed research does not help clarify the role of hyperbaric oxygen in the treatment of chronic diabetic foot ulcers.Diving Hyperb Med. 2016 Sep;46(3):133-134. Diving Hyperb Med. 2016. PMID: 27723012
-
[Recurrence and influencing factors of diabetic foot ulcer in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus].Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2020 Oct 20;36(10):947-952. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501120-20190726-00315. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 33105947 Chinese.
-
Trends and determinants of costs associated with the inpatient care of diabetic foot ulcers.J Vasc Surg. 2014 Nov;60(5):1247-1254.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2014.05.009. Epub 2014 Jun 14. J Vasc Surg. 2014. PMID: 24939079 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic reviews of wound care management: (3) antimicrobial agents for chronic wounds; (4) diabetic foot ulceration.Health Technol Assess. 2000;4(21):1-237. Health Technol Assess. 2000. PMID: 11074391 Review.
-
The costs of diabetic foot: the economic case for the limb salvage team.J Vasc Surg. 2010 Sep;52(3 Suppl):17S-22S. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2010.06.003. J Vasc Surg. 2010. PMID: 20804928 Review.
Cited by
-
Association of vitamin D status with all-cause mortality and outcomes among Chinese individuals with diabetic foot ulcers.J Diabetes Investig. 2023 Jan;14(1):122-131. doi: 10.1111/jdi.13917. Epub 2022 Oct 6. J Diabetes Investig. 2023. PMID: 36200877 Free PMC article.
-
Risk Factors for Major Amputation in Diabetic Foot Ulcer Patients.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2021 May 4;14:2019-2027. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S307815. eCollection 2021. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2021. PMID: 33976562 Free PMC article.
-
Nanomaterials for diabetic wound healing: Visualization and bibliometric analysis from 2011 to 2021.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jan 25;14:1124027. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1124027. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36761188 Free PMC article.
-
Risk Factors Associated with Amputation for Patients with Diabetic Foot Ulcers: A Retrospective Study.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024 Nov 7;17:4201-4209. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S490614. eCollection 2024. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2024. PMID: 39529615 Free PMC article.
-
Factors Associated With Foot Self-Care in Patients With Diabetes-Related High-Risk Feet: A Cross-Sectional Design.Inquiry. 2023 Jan-Dec;60:469580231220135. doi: 10.1177/00469580231220135. Inquiry. 2023. PMID: 38140753 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

