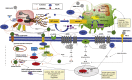
Dexmedetomidine: another arrow in the quiver to fight COVID-19 in intensive care units
- PMID: 33190859
- PMCID: PMC7556802
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bja.2020.10.010
Dexmedetomidine: another arrow in the quiver to fight COVID-19 in intensive care units
Keywords: COVID-19; ICU; NETosis; dexmedetomidine; inflammation; sedation.
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations of interest The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
Dexmedetomidine does not directly inhibit neutrophil extracellular trap production.Br J Anaesth. 2022 Feb;128(2):e51-e54. doi: 10.1016/j.bja.2021.11.015. Epub 2021 Nov 19. Br J Anaesth. 2022. PMID: 34916052 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Comment on
-
A novel role for lidocaine in COVID-19 patients?Br J Anaesth. 2020 Oct;125(4):e391-e394. doi: 10.1016/j.bja.2020.07.015. Epub 2020 Jul 23. Br J Anaesth. 2020. PMID: 32792138 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Dexmedetomidine in COVID-19: probing promises with prudence!Am J Emerg Med. 2021 Aug;46:708-709. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2020.10.034. Epub 2020 Oct 27. Am J Emerg Med. 2021. PMID: 33168381 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
[A comparative study on clinical effects of dexmedetomidine and midazolam on patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019 on non-invasive ventilation].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2020 Jun;32(6):677-680. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20200305-00187. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2020. PMID: 32684211 Chinese.
-
Dexmedetomidine versus standard care sedation with propofol or midazolam in intensive care: an economic evaluation.Crit Care. 2015 Feb 19;19(1):67. doi: 10.1186/s13054-015-0787-y. Crit Care. 2015. PMID: 25887576 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha-2 agonists for sedation of mechanically ventilated adults in intensive care units: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2016 Mar;20(25):v-xx, 1-117. doi: 10.3310/hta20250. Health Technol Assess. 2016. PMID: 27035758 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sedation and analgesia in the intensive care unit: evaluating the role of dexmedetomidine.Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2007 Jan 1;64(1):37-44. doi: 10.2146/ajhp050508. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2007. PMID: 17189578 Review.
Cited by
-
Hemodynamic and respiratory effects of dexmedetomidine sedation in critically ill Covid-19 patients: A retrospective cohort study.Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2021 Nov;65(10):1447-1456. doi: 10.1111/aas.13970. Epub 2021 Aug 22. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2021. PMID: 34368946 Free PMC article.
-
Sedation in mechanically ventilated covid-19 patients: A narrative review for emergency medicine providers.Am J Emerg Med. 2022 Apr;54:309-311. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2021.05.030. Epub 2021 May 14. Am J Emerg Med. 2022. PMID: 34020844 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Anaesthesia-related drugs and SARS-CoV-2 infection.Br J Anaesth. 2021 Jul;127(1):e32-e34. doi: 10.1016/j.bja.2021.03.026. Epub 2021 Apr 5. Br J Anaesth. 2021. PMID: 33934887 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The impact of stress and anesthesia on animal models of infectious disease.Front Vet Sci. 2023 Feb 2;10:1086003. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1086003. eCollection 2023. Front Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 36816193 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Post-operative Non-sustained Ventricular Tachycardia in a COVID-19 Positive Patient After Ketamine and Dexmedetomidine Infusion.Cureus. 2021 Dec 9;13(12):e20300. doi: 10.7759/cureus.20300. eCollection 2021 Dec. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 35024255 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pandharipande P.P., Pun B.T., Herr D.L., et al. Effect of sedation with dexmedetomidine versus lorazepam on acute brain dysfunction in mechanically ventilated patients: the MENDS randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2007;298:2644–2653. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

